NBASE-T Ethernet
What is NBASE-T Ethernet?
NBASE-T Ethernet is an IEEE standard and Ethernet-signaling technology that enables existing twisted-pair copper cabling to exceed the cable's specified limit of 1 gigabit per second (Gbps) for distances of up to 100 meters. The standard, 802.3bz, established two new speeds at 2.5 Gbps and 5 Gbps. NBASE-T Ethernet was approved as a standard in September 2016.
It is also known as 2.5GBASE-T and 5GBASE-T.
NBASE-T was developed to enable organizations to support the faster data transfer rates of 802.11ac Wave 2, which exceed 1 Gbps, without having to replace existing Cat5e and Cat6 twisted-pair cabling. The next higher Ethernet standard, 10 Gigabit Ethernet, required cabling capable of supporting high frequency ranges for long runs, which Cat5e and Cat6 cabling cannot. Without the NBASE-T standard, organizations would have had to spend millions of dollars to upgrade their infrastructure to Cat6a cables.
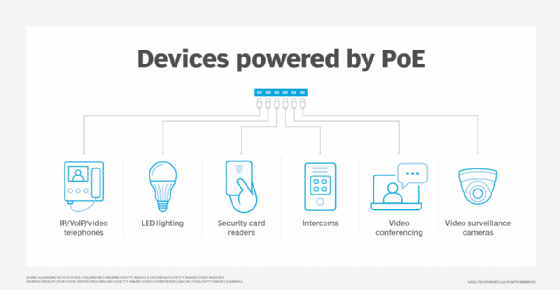
In addition to enabling organizations to use existing twisted-pair cabling to support faster data transfer rates, NBASE-T supports Power over Ethernet, which enables devices to be powered by a single cable. PoE is becoming more important as more devices, like IP cameras and high-speed access points (APs), are added to the network.
Origins of NBASE-T
NBASE-T Ethernet is an iteration of the earliest Ethernet standard, 10BASE5, ratified in 1983. That standard, also known as thick Ethernet, had a maximum data transfer speed of 10 megabits per second. It was engineered to maximize the transmission speed of local area networks anchored by copper-based cabling. During the late 1990s, the fate of copper cabling was in doubt, as network designers evaluated whether or not asynchronous transfer mode, which ran almost exclusively on fiber optic cable, would replace Ethernet for higher-bandwidth networking. The speculated replacement of copper cabling never took place, ultimately prompting the evolution of faster data transfer rates over twisted-pair cabling.
Gigabit Ethernet, or 1000BASE-T, standard was introduced in 1999 and the much faster 10 Gigabit Ethernet (10GBASE-T) standard in 2006. Most organizations have standardized on the cheaper Cat5 cables, which only supported gigabit links over long runs.
With the release of faster wireless standards, it was soon possible for the wireless signal to have more bandwidth than the data cable feeding it. This resulted in some APs requiring two Ethernet cables and a power cable, which often necessitate expensive cable runs in buildings.
The 2.5 Gbps and 5 Gbps speeds were introduced with PoE standards as stopgap measures to reduce the need for expensive new cable runs. Some early examples of 2.5 Gbps links were available as early as 2013, with it receiving full IEEE standardization in 2016.
NBASE-T use cases
The "in between" speeds of 2.5 Gbps and 5 Gbps were introduced to provide better speeds than the existing 1 Gbps, while still being cheaper than 10 Gbps. It is uncommon to see them in data centers and server rooms, where 10 Gbps has been standard for some time, and 40 or 100 Gbps links are now common. Fiber optic and passive optical networks have also become common in the enterprise for long backbone cable runs, largely eliminating the need for these speeds.
NBASE-T speeds are increasingly becoming more common in home and small business environments. As internet speed increases and fiber to the home becomes more common, the standard Gigabit Ethernet port is no longer enough for many homes. Many home routers now have 2.5 Gbps ports to support these faster internet connections.
How NBASE-T Ethernet works
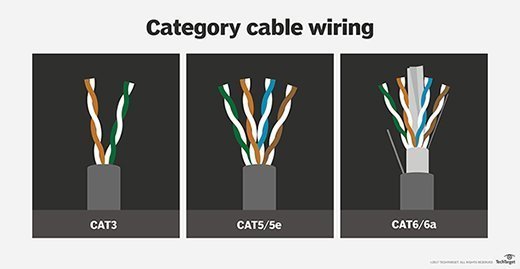
The amount of data transmitted in digital communications is measured in symbols. A symbol can be used to encode multiple bits. In 10 Gigabit Ethernet, each wire pair in twisted-pair cabling must transmit 800 million symbols per second; a new symbol must be transmitted in a little more than a billionth of a second. Cabling performance must be high to support this rate of transmission -- up to 500 megahertz (MHz). Cat6 cabling, by contrast, has a frequency range of up to 250 MHz.
NBASE-T uses a technique to downshift the signaling rate used in 10 Gigabit Ethernet to either one-quarter (2.5 Gbps) or one-half (5 Gbps) the rate. This modification enables existing copper cabling to handle the higher speeds.
NBASE-T Alliance
The NBASE-T Alliance is a consortium founded in 2014 by Aquantia, Cisco, Broadcom and more than 40 other organizations to promote 2.5 Gbps and 5 Gbps. The consortium appears at conferences and hosts interoperability demonstrations and exhibits. The alliance compiles a searchable list of interoperable products, ranging from network interface card (NIC) offerings to NBASE-T Ethernet switch products and other NBASE-T Ethernet systems. The NBASE-T Alliance consolidated under the Ethernet Alliance in 2019.
SmartNICs can offload packet processing tasks from server central processing units. Check out our guide to smartNICs and their role in networking. Also, explore the types of networks and their use cases.







