CSU/DSU (Channel Service Unit/Data Service Unit)
What is a CSU/DSU?
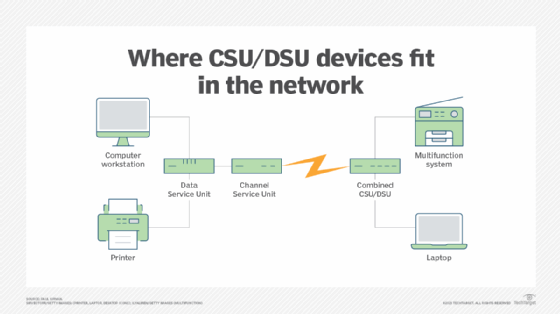
A CSU/DSU (Channel Service Unit/Data Service Unit) is a hardware device about the size of a modem. It converts a digital data frame from local area network (LAN) communication technology into a frame appropriate for a wide area network (WAN) and vice versa.
For example, CSU/DSUs are used as part of a leased digital line -- perhaps a T1 or a fractional T1 line -- that connects to a phone company or to an internet service provider's gateway. In those setups, there is a CSU/DSU at the customer end and another one at the host end.
Why CSU/DSUs are important?
CSU/DSU devices provide a network interface between data terminal equipment (DTE) and a synchronous network link, such as a T1 channel, fractional T1 channel, or 56 kilobits per second (Kbps) or 64 Kbps channels. They handle the clocking and digital signals that synchronous computer networks need, and connect to analog networks.
CSU/DSUs have been in use for decades, and they're reasonably priced and easily adapted to a variety of networking requirements. They can interface with Ethernet and other network connectors. And routers can function as CSU/DSUs.
Anyone who connects terminal equipment to a network uses a CSU/DSU. Advances in broadband internet service, such as wireless internet access for home offices, have eliminated the need for standalone CSU/DSU equipment. However, CSU/DSUs are still present in network architectures; connectivity equipment such as routers and WAN interface cards often have integrated CSU/DSUs.
How does a CSU/DSU work?
CSU and the DSU have separate functions. CSU receives and transmits signals from and to the WAN line. It provides a barrier for electrical interference from either side of the unit. It can also echo loopback signals from the phone company for testing purposes.
DSU manages line control, and converts input and output between RS-232C, RS-449 and V.xx frames from the LAN and the time-division multiplexed DSX frames on the T1 line. The DSU manages timing errors and signal regeneration. It also provides a modemlike interface between the computer as the DTE and the CSU.
CSU/DSUs are made as separate products or are part of a T1 WAN card. A CSU/DSU's DTE interface is usually compatible with the V.xx and RS-232C or similar serial interface.
The CSU originated at AT&T as an interface to its nonswitched digital data system. The DSU provides an interface to the DTE using a standard interface. It also provides testing capabilities.
Pros and cons of CSU/DSUs
In the right telecommunication network configuration, CSU/DSUs provide important connectivity between data terminals and high-speed digital network services. As noted earlier, routers have CSU/DSU capabilities and support the higher Ethernet data speeds in use today. The devices are cost-effective and readily available. While some might consider CSU/DSUs as outdated technology, they are still used in many network applications.
Learn about eight devices commonly used in enterprise network infrastructures.







