CPRI (Common Public Radio Interface)
What is CPRI (Common Public Radio Interface)?
CPRI (Common Public Radio Interface) is a specification for wireless communication networks that defines the key criteria for interfacing transport, connectivity and control communications between baseband units (BBUs) and remote radio units (RRUs), which are also called remote radio heads (RRHs).
CPRI defines the key internal interfaces (digitized serial) between radio equipment (RE) and local/remote radio equipment controllers (RECs) in radio base stations. It provides a standardized framework to facilitate the development of equipment for mobile telecommunications networks. As an open specification, the CPRI benefits any entity in the wireless industry.
Radio equipment is the collective term for RRUs or RRHs, while RECs are also known as baseband units. As a specification for a serial interface between BBUs and RRUs, CPRI provides for a high-speed connection between these parts of a radio base station.
CPRI covers Layers 1 and 2 of the OSI model, with Layer 1 supporting both electrical and optical interfaces of base stations and Layer 2 supporting increased flexibility and scalability. In addition to defining the interface of radio base stations, the first version of the specification (CPRI v1.0) also defined the items for transport, connectivity and control, including user plane data, control plane transport mechanisms and synchronization methods.
The CPRI specification was originally developed in 2004 by a consortium of five original equipment manufacturers: Nokia, Huawei Technologies, Ericsson, NEC, and Nortel. Nortel left the consortium in 2009.

CPRI system architecture
The basic system architecture of CPRI consists of a radio base station that is divided into a radio part and a control part with the CPRI link defining the interface between them. Both the REC and RE consist of a control and management module, a sync module, and a user plane -- all on Layer 2 of the OSI stack.
The sync module and its L1 inband protocol are defined in the CPRI specification. In particular, the UMTS protocol is defined in CPRI v1 and v2, WiMax in CPRI v3, LTE in CPRI v4, and so on.
In Layer 1 of the OSI stack, the CPRI specification addresses how time division multiplexing (TDM) will take place. This is important because the specification is based on TDM of the digitized I/Q bits of multiple antennas and carriers in the form of in-phase and quadrature samples. That said, CPRI is not bandwidth efficient although the efficiency can be improved by CPRI compression, with minimal degradation of overall CPRI performance. Since CPRI supports both electrical and optical interfaces, both kinds of transmission can occur (also in Layer 1).
Important features of CPRI
CPRI specifications support L1 inband protocol, High-Level Data Link Control and Ethernet for configuration and management data. Other data types supported by CPRI include synchronization for frame and time alignments. The CPRI specification is not a standard, but it complements 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) and 3GPP2 (3G and Long-Term Evolution or LTE) frameworks.
An important feature of CPRI is its support for separation between the base frequency band and the radio frequency band. Additionally, it supports electrical and optical interfaces, as well as multiple topologies, including point-to-point, star, ring and daisy chain. CPRI focuses on the communication link, the fronthaul network that interfaces between radio transceivers and base stations.
Benefits of CPRI
CPRI has proven its usefulness for fronthaul communications between RRHs and BBUs through multiple generations of wireless networks. The benefits of CPRI include:
- It is a flexible and scalable specification for wireless radio base stations.
- Base station manufacturers can use one common protocol.
- It provides a wide radio base station portfolio that can be easily adapted to multiple deployment scenarios.
- The specifications are free and available to the public.
- The public can contribute ideas and proposals to improve the specifications.
- It provides efficient and flexible data interfaces for multiple wireless standards, including Global System for Mobile Communications, Wideband Code Division Multiple Access, and LTE.
What is eCPRI?
In 2017, the CPRI specification eCPRI 1.0 became available for download. In 2019 eCPRI v2.0 was released. This specification provides intelligent CPRI mapping to minimize bandwidth requirements and allows both new and legacy equipment to coexist in the same Ethernet-based fronthaul network. In addition, the updated specification further extends the flexibility of eCPRI for fronthaul transport between eCPRI nodes and CPRI nodes.
What led to development of eCPRI was that high rates cannot be cost-effectively realized with the CPRI's serial interface, even with CPRI compression of at least 3-to-1. For example, a typical 5G use case would use MIMO (multiple input, multiple output) technology to transfer more data simultaneously and require very high CPRI data rates to the tune of hundreds of Gbps.
This drawback of CPRI led to the development of a new functional split option called eCPRI. eCPRI provides a way to split up and move some of the BBU's functions to the RRUs to reduce the burden on the fiber between the BBU and the RRUs.
The updated specification is expected to provide higher network throughput, improved efficiency, and better connectivity with less fiber. It also provides a good balance between the low latency and high-reliability requirements of 5G. Also, since eCPRI is an open interface, carriers can work together to create more connected and faster 5G networks.
The consortium that developed CPRI and eCPRI continues to work towards refining both specifications. As it improves, eCPRI is expected to become a suitable option for all networks with dedicated fiber connections in fronthaul, including 5G applications.
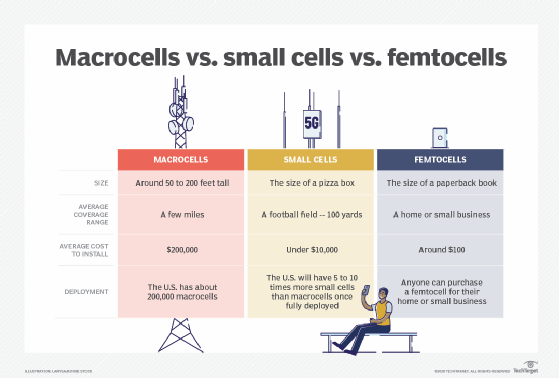
Check out the essential 5G glossary of key terms and phrases and the three different types of 5G technology for enterprises. Explore the differences between the TCP/IP model vs. OSI model and everything you need to know about wireless communications. Read about the differences between macrocell vs. small cell base stations vs. femtocell wireless access points.





