Gorodenkoff - stock.adobe.com
Where does SDN fit in edge computing architecture?
SDN and edge computing can work together to apply data processing decisions that make better use of network links and bandwidth, especially when it comes to edge versus cloud.
Edge computing is the concept of pushing data processing to the edge of the network -- closest to where the data is generated. The idea of an edge computing architecture is to use an edge device's computational power, so data doesn't always have to be uploaded to a private data center or a cloud service provider's network to be processed.
The benefits of edge computing architecture are twofold. First, by pushing computational processes to the edge, edge computing reduces the amount of CPU needed in the cloud, which means cost savings.
The second benefit is less data traverses the network, because processing is performed locally at the edge. This results in network and performance efficiencies that can significantly boost application speeds.
Where SDN meets edge computing architecture
Software-defined networking (SDN) is a technology that can help bridge the gap when combining edge computing and traditional clouds. For example, SDN can be used to act as a decision-maker on whether tasks should be uploaded and processed in the cloud or at the edge.
SDN controllers include built-in AI that can determine when periods of high network utilization occur on specific links. The controller can then request more processing to be completed at the edge to eliminate network bottlenecks.
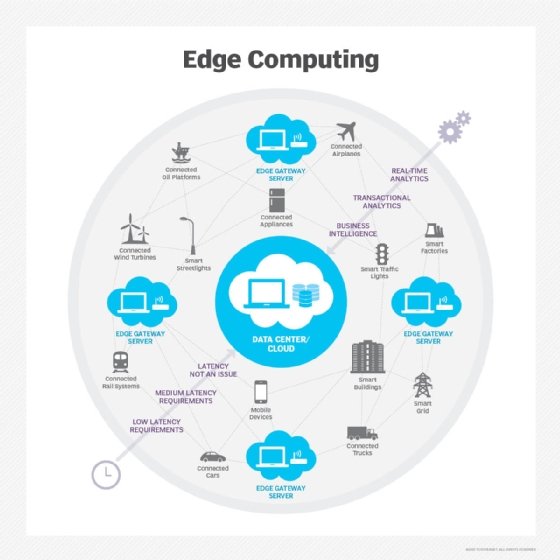
Both SDN and edge computing are still in the infancy stage. Likely, SDN will be implemented first, with edge computing following shortly after. As both technologies continue to increase in adoption rate, look for the pair to become increasingly intertwined.