Traditional WAN vs. SD-WAN: How do they compare?
While comparing traditional WAN vs. SD-WAN, network professionals can see the many benefits of SD-WAN, including centralized control and dynamic traffic management.
The new software-defined WAN strategy improves the deployment and management of a WAN. When considering the difference between traditional WAN vs. SD-WAN, several key components are at play.
While both of these network deployments rely on some type of circuit -- such as MPLS, broadband, Ethernet or cellular -- and have some type of routing endpoint hardware at the source and destination of the connection, significant differences are also evident.
For example, SD-WANs have a software overlay for connection provisioning and management. This software contains all the connection information, security information and network information. Traditional WANs typically have this information programmed directly into the device via command lines, as opposed to being managed via software.
Additionally, the SD-WAN will usually have a centralized controller that enables the management of multiple WAN connections at the same time by centralizing WAN policies. This capability eliminates the need to program each endpoint individually when making changes.
This article is part of
What is SD-WAN (software-defined WAN)? Ultimate guide
Traditional WAN vs. SD-WAN spotlights network management agility
A traditional WAN does allow for load balancing and disaster recovery through carrier diversity. But the SD-WAN is far more agile and able to make changes more easily in real time versus the individual programming of the traditional devices as environmental situations change.
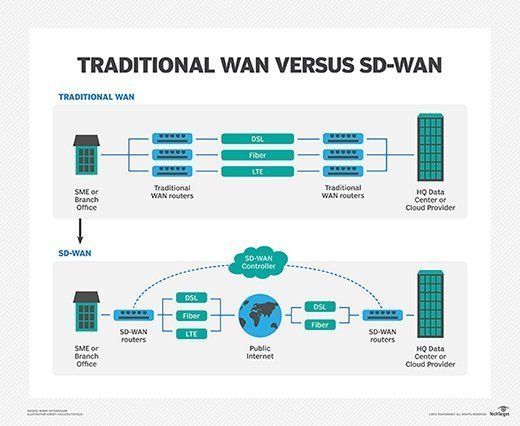
Both the traditional WAN and SD-WAN have a physical connection, but the SD-WAN will have a virtualized connection that is abstracted from the physical connection and sits above. This SD-WAN virtual connection can be moved easily from one device to another or altered quickly based on the needs of the business.
For more on software-defined WAN, read the following articles:
5 common SD-WAN challenges and how to prepare for them
SD-WAN comparison chart: 10 vendors to assess
Follow these 9 steps for SD-WAN testing before deployment
Finally, while both a traditional WAN and SD-WAN can manage traffic, the SD-WAN can do a much better job of dynamically managing traffic. As applications demand more bandwidth, the SD-WAN can reallocate to adjust to the new loads dynamically through a set of rules. For a traditional WAN, this would typically require more hands-on programming every time a change is needed.







