
WAN (wide area network)
What is a WAN (wide area network)?
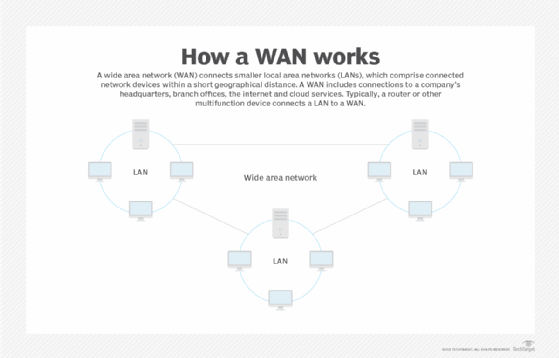
A wide area network (WAN) is a geographically distributed private telecommunications network that interconnects multiple local area networks (LANs). A LAN is a group of computers and network devices that are connected to each other, typically within a short relative geographical distance.
In a business, a WAN includes connections to a company's headquarters, branch offices, colocation facilities, cloud services and other facilities. Typically, a router or other multifunction device is used to connect a LAN to a WAN.
Enterprise WANs enable users to access applications, services and other centrally located resources. This connectivity eliminates the need to install the same application server, firewall or other resources in multiple locations.
WANs are not restricted to the same geographical location as a LAN. A LAN can be set up in different geographical areas and be connected to a WAN, meaning a WAN is not constrained to one specific location.
This article is part of
What is SD-WAN (software-defined WAN)? Ultimate guide
A virtual private network (VPN) facilitates connectivity and security between WAN sites. Different VPNs can be used for different use cases.
An IPsec VPN is more commonly used in continuously open site-to-site connections, such as those between branch offices and headquarters locations. A Secure Sockets Layer VPN is often the preferred choice for enabling remote access for individual users because the data transmitted from users across the WAN is encrypted. Direct fiber optic links are also used to connect sites on a WAN, and they almost always offer greater performance, reliability and security than VPNs. But they are cost-prohibitive for most enterprises to procure and operate.
Types of WAN connections
WAN connections can include wired and wireless technologies. Wired WAN services can consist of the following:
Wireless WAN (WWAN) technologies can include cellular data networks, like 5G, as well as public Wi-Fi or satellite networks.
WANs over wired network connections remain in place for many enterprises, but WWAN technologies are gaining traction.
How WAN connections work
WAN infrastructure may be privately owned or leased as a service from a third-party service provider, such as a telecommunications carrier, internet service provider, private IP network operator or cable company. The service itself may operate over a dedicated, private connection -- often backed by a service-level agreement -- or over a shared, public medium, like the internet. Hybrid WANs employ a combination of private and public network services.
Software-defined WAN (SD-WAN) is designed to make hybrid WAN architectures easier for enterprises to deploy, operate and manage. Using a combination of virtualization, application-level policies and network overlays, on-site SD-WAN devices, software platforms or customer premises equipment (CPE) perform two functions:
- They aggregate multiple public and private WAN links.
- They automatically select the most optimal path for traffic, based on real-time conditions.
The latter function has historically required network managers to manually reconfigure their networks any time they wanted to shape the direction of traffic over multiple routes.
WAN optimization
Latency and bandwidth constraints often cause enterprise WANs to suffer from performance issues. WAN optimization appliances use a variety of techniques to counteract them, including deduplication, compression, protocol optimization, traffic shaping and local caching. SD-WAN CPE or platforms provide another level of application performance control through the use of lower-cost bandwidth connections, usually in the form of commercial internet services, along with traffic shaping and quality of service tools, to increase reliability.
WAN security
WAN security should be expanded to wherever end users employ their devices, including at home. End users who use WAN should also use firewalls and antivirus software to prevent unauthorized access or compromises of their devices.
The use of a VPN helps create connectivity in a WAN and has the added benefit of encrypting data. Users should be required to connect to a WAN via a VPN, including network devices that are connected to a WAN from a remote site. Additionally, SD-WAN has a key-exchange function, which is used to authenticate devices on different endpoints.
Even though a WAN can be as secure, a WAN service provider should not be assumed to give a certain amount of security. Even the use of a VPN does not ensure the total security of a WAN system.
Advantages and disadvantages of WAN
Advantages of WAN include the following:
- Large geographical area coverage.
- Centralized infrastructure.
- Network security.
- Increased bandwidth with the use of leased lines, as opposed to broadband connections.
The disadvantages of WAN include the following:
- High setup cost.
- Possible security gaps.
- Antivirus software and firewall requirements.
For more on software-defined WAN, read the following articles:
How to build an SD-WAN RFP to evaluate vendors
Top 9 SD-WAN benefits for businesses
5 common SD-WAN challenges and how to prepare for them
WAN vs. LAN vs. MAN
A WAN is a global service, while LAN connections pertain to a small area, such as a home, office suite and building. A metropolitan area network (MAN) operates within city limits. LAN environments use Ethernet and Ethernet switches, while MANs are composed of Metro Ethernet, MPLS and point-to-point or point-to-multipoint wireless technologies.







