Cloud security vs. network security: What's the difference?
While network security focuses on solely protecting networks, cloud security provides protection for networks, servers, containers, apps and more.
Cloud computing has been around for a while, but confusion still surrounds the correct meaning of certain terms. An example of this is differentiating between cloud security vs. network security.
First, let's look at the term network security to understand what it encompasses. We'll then compare the term with cloud security to see how the two are related yet different in several key areas.
What is network security?
Network security focuses on tools used to protect data, applications and resources at the network level. The primary focus is to protect against unauthorized access into or between parts of the overall network infrastructure.
When most people think about unauthorized access, they tend to imagine a person or device that attempts to connect to the wired or wireless LAN without authorization. The network security tools to prevent against this type of unauthorized access include network access control and enterprise mobility management platforms for both wired and wireless networks.
Another way to protect against unauthorized access is to place a firewall and an intrusion prevention system (IPS) at the corporate network's internet edge. These tools protect against bad actors that aim to use network, server and application vulnerabilities within maliciously crafted packets to gain access to internal resources.
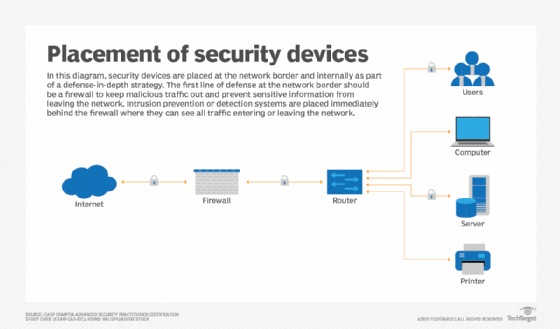
Other external attack methods include email attacks, malicious websites, brute-force attacks and distributed denial-of-service attacks. A firewall, IPS, network-centric email and secure web gateway can handle these issues as well.
Network security also provides a way for remote users on the internet to securely access internal data and applications while preventing access for all others. Both site-to-site and remote access VPNs fulfill this purpose.
Finally, the network layer is a great place to monitor for malicious activity within corporate infrastructure. Modern network detection and response systems use packet capture, NetFlow and other streaming network telemetry methods to baseline normal network behavior and alert security administrators when changes to network behavior might indicate a network breach.
What is cloud security?
Cloud security and network security differ because the term cloud security encompasses more of the overall corporate infrastructure than network security.
Generally, when people refer to cloud security, it's in the context of IaaS cloud environments that third-party service providers offer. In this case, cloud security not only includes network security tools, but also server-, container-, application- and service-level security.
Security tools for cloud networks might or might not be the same as the private corporate network. In most cases, IaaS providers will offer their own proprietary network security services such as firewalls, IPSes and VPN connectivity.
Alternatively, businesses can opt to deploy VMs on an IaaS cloud environment that can run the exact same security platforms they operate on the corporate LAN. IT teams can find these third-party security tools on the service provider's third-party cloud marketplace.
Beyond the network, cloud security can also include the following protections:
- Data encryption.
- Multifactor authentication.
- Server and application malware prevention software.
- Server, application, database monitoring, scanning and analytics tools.
What's the main difference between cloud security and network security?
IT professionals should consider network security as both an on-premises term and a cloud computing term. However, network security is a subset of an overall cloud security posture.
Andrew Froehlich is founder of InfraMomentum, an enterprise IT research and analyst firm, and president of West Gate Networks, an IT consulting company. He has been involved in enterprise IT for more than 20 years.








