Getty Images/iStockphoto
How to perform a remote wipe of Office 365 on a smartphone
Employees like having email and other Office 365 applications on their smartphones. There are security risks that come with mobile devices accessing corporate data, however.
The Office suite of applications is an essential set of tools for many businesses. With the growth of mobile devices in the workplace, it's also essential to secure these applications everywhere.
What users expect from devices and applications changes constantly. In turn, IT organizations must adapt to user requests for access to work applications and workflows. Admins must ensure teams are productive on both mobile and desktop, wherever they are -- all while trying to secure all that data.
To secure company information on mobile devices, IT teams often use management platforms such as mobile device management (MDM) or unified endpoint management (UEM). However, end users often hesitate to give up control of their devices. Many have concerns about how much control a company has over their devices. To ensure that employees have the freedom they want on their devices while also securing office applications and data, organizations can consider mobile application management (MAM) tools.
What is MAM?
MAM is a capability of an MDM or UEM product. However, there are standalone products that provide MAM functions, but these are often not enough for full mobility management, so organizations tend toward more effective MDM and UEM tools.
IT uses MAM to secure the applications and data on a device without having to enroll it into a device management platform. Microsoft Endpoint Manager provides MAM capability, as do other UEMs such as VMware Workspace One. However, to specifically apply protection policies to Office apps, Microsoft's Intune tool is required. Organizations using Office 365 can subscribe to Intune -- which is a part of Microsoft Endpoint Manager -- at an additional cost.
MAM uses app protection policies to configure applications for both unenrolled and fully managed user devices. Organizations often utilize MAM for personal or BYOD devices, where users want access to corporate data without having to enroll into their company's device management platform. Users can download applications directly from the Apple App Store or Google Play Store and authenticate into the application with their company credentials. The applications will embed specific in-app security configurations. MAM protection policies can include the following:
- block or allow data backup to iCloud (iOS only);
- block or allow import of company data into other managed or unmanaged applications;
- restrict cut, copy and paste between other applications;
- block or allow third-party keyboards;
- enforce application encryption;
- configure pin and credential requirements that users must meet to access managed apps;
- set device and app block; and
- set actions for conditions such as jailbroken devices, maximum pin attempts and offline grace periods.

Platforms such as Intune support the following MAM scenarios, and other MDMs that also support MAM will be similar:
- Fully enrolled, or corporate-owned, personally enabled (COPE). IT manages both at the device level and the application level.
- Not managed by MDM, or BYOD. IT only manages the applications on a device.
- Managed by third-party MDM. IT can utilize Microsoft app protection policies while also using a different MDM for full management and additional security configurations at the device level.
App protection policies require users to have an Azure Active Directory account and proper Microsoft 365 licensing, which must include a Microsoft Enterprise Mobility and Security license. Additionally, app protection policies only work with Microsoft Office mobile applications or applications that have been integrated with the Intune SDK or wrapped by the Intune App Wrapping Tool. Microsoft maintains a list of applications that fit these requirements and are available for public use.
How to set up app protection policies for Office apps
To set up app protection policies in Microsoft Intune, IT administrators can navigate to their Endpoint Management Web Console and select Apps > App protection policies > Create policy.

How to wipe data from Office applications with Microsoft Intune
In addition to being able to restrict data access with MAM-based applications, admins can also remotely remove or selectively wipe application data. A remote wipe is useful if a device is ever lost or stolen, or the end user decides to leave the company. Because mobile devices are smaller and easier to lose than other endpoints, the remote wipe option is especially important. If a device ends up in the hands of a malicious actor, admins must wipe any corporate data from it, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information.
There are three different methods for wiping devices: a full wipe, a retire or a selective wipe. A full wipe removes all data and applications from the device and restores it back to the factory reset state. This is an ideal method when admins no longer have use for a device, need to reset and repurpose a device for another function, or want to ensure data is not lost on a missing device. A retire, on the other hand, is a better option for a BYOD environment. This type of wipe leaves the user's personal data while targeting business data exclusively from select applications, removing the device from the MDM's management.
Both users and admins can issue remote commands from the MDM's portals, such as Intune's Company Portal, to managed devices. This is ideal for self-service for users that want to take back control of their devices and experience.
To initiate a full wipe or retire within Intune, follow these steps:
- Sign in to the Microsoft Endpoint Manager portal.
- Select Devices.
- Select the device you want to wipe.
- At the top of the screen, select Wipe or Retire.

Admins can also apply wipe and retire commands to multiple devices at one time. This is often called bulk or group actions. To apply a bulk device action, select Devices > All Devices > Bulk Device Actions.
A selective wipe is another ideal method for BYOD. With this type of wipe, admins can remove corporate MDM policies and applications from the device, leaving personal applications and data intact. To initiate a selective device or user wipe within Intune, follow these steps:
- Sign in to the Microsoft Endpoint Manager portal.
- Select Apps in the left column.
- Scroll down to "Other" section and select App selective wipe.
- Select preferred wipe request (device-based or user-based).
- For a device-based selective wipe, select Wipe requests and follow prompts for selecting the user and data you want to wipe. Then, select Create wipe request.
- For a user-based selective wipe, select User-Level Wipe, which prompts you to select the user. Then, select Create wipe request.

Self-service requests for users
End users can also wipe, remove and check the status and compliance of their own devices via the MDM portal's applications. For an end user to self-service remove or factory reset a device via Microsoft Intune, admins can direct the user to follow this process:
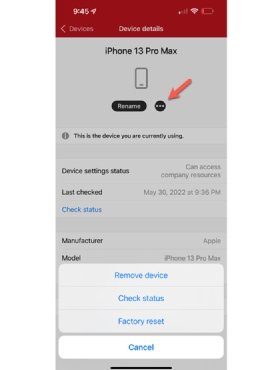
- Open the iOS or Android Intune Company Portal
- Select Devices at the bottom of the screen.
- Select the device you need to reset or remove.
- Select the ellipsis icon, which looks like this: ….
- Depending on which action you wish to perform, select one of the following options:
- Remove device
- Check status
- Factory reset