
Getty Images/iStockphoto
How to enable User Enrollment for iOS in Microsoft Intune
User Enrollment in iOS can separate work and personal data on BYOD devices. IT teams should learn how to enable it in Microsoft Intune and how it can affect user experience.
The increasing prevalence of BYOD has brought personal iOS devices into the workplace, and Apple's User Enrollment makes it possible to manage those devices more easily.
User Enrollment provides a method to separate work and personal data on personal iOS devices, similar to work profiles on Android devices. However, Android's method relies on creating separate profiles on the device for work and personal use, which lets the user easily turn off everything work-related and provides separate instances of apps depending on the required use case.
Apple User Enrollment, on the other hand, relies on separating the data within apps, providing a different user experience and requiring users to be extra careful to save data to the right location.
Create Managed Apple IDs to begin User Enrollment
User Enrollment comes with some specific requirements. Apple Business Manager (ABM) is generally the starting point for corporate devices and personal devices that rely on User Enrollment. ABM enables organizations to easily integrate with third-party mobile device management (MDM) software, buy Apple devices and ensure those devices are managed. Most of that functionality isn't required for User Enrollment because it deals with personal devices; however, ABM is becoming an important part of managing personal devices because of user identity.
User Enrollment requires the use of Managed Apple IDs because it establishes a work identity for the user on a device. It can be used next to the personal Apple ID of a user, so the different identities don't interact with each other. That differentiation separates the data of the various identities within managed and native apps. Users will have an iCloud Drive for their personal Apple ID, and a separate iCloud Drive for their Managed Apple ID.
IT administrators can create Managed Apple IDs manually or automatically. The automated method involves using System for Cross-Identity Management with Azure Active Directory (AD), or using a sync with Google Workspace.
Use federated authentication to improve the user experience
From a user's perspective, Managed Apple IDs are a strong tool for Apple devices, especially in combination with Azure AD or Google Workspace. While it looks like the same identity can be used cross-platform, it's just the same account in a different system with a different password. This can be confusing for users, so IT can implement federated authentication to improve the user experience. Instead of simply synchronizing user accounts, federated authentication ensures a user can use the same identity and credentials to sign in. In that case, IT uses either Azure AD or Google Workspace to authenticate the user.
Configure User Enrollment with third-party MDM software
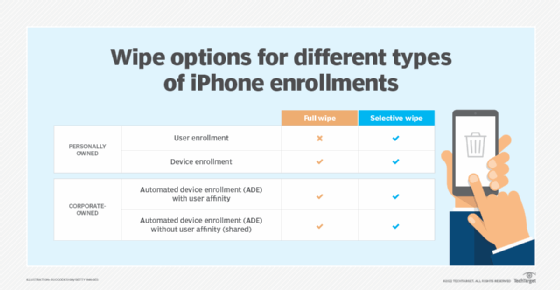
Before User Enrollment, organizations used Device Enrollment to manage personal devices. This enrollment type enables an organization to fully manage the entire device -- including the ability to remotely wipe the device -- which isn't what a user typically wants for their personal devices.
Apple introduced User Enrollment in 2019 to fix this problem. This enrollment type ensures work and personal data are separated and that IT doesn't control the entire device. Only specific management actions are allowed, and a remote wipe isn't possible.
To configure User Enrollment, IT must use a third-party MDM provider that supports the use of User Enrollment and the required Managed Apple IDs. The following steps walk through the process of enabling User Enrollment in Microsoft Intune.
- Open the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center portal and navigate to Devices > iOS/iPadOS > iOS/iPadOS enrollment > Enrollment types.
- On the Enrollment type profiles page, click Create profile > iOS/iPadOS.
- On the Basics page, provide a valid name for the enrollment type profile and click Next.
- On the Settings page, select the appropriate enrollment type noted below and then click Next.
- User Enrollment. Select this option only when the corporate data on the devices in the profile should be managed.
- Device Enrollment. Select this option when the devices in the profile should be fully managed.
- Determine based on user choice. Select this option when the users in the profile should decide which enrollment type should be used.
- On the Assignments page, configure the assignment of the profile and click Next.
- On the Review + create page, review the configuration and click Create.
It's possible to create multiple enrollment profiles with these different types. To prevent conflicts among user profiles, admins can configure different priorities for the various profiles.
Keep user experience in mind for personal iPhones
The main challenge with User Enrollment is the user experience within apps, as the user must be familiar with the different storage locations and how to work with them. Once User Enrollment is complete, a separate volume is created that contains managed apps, notes, calendar attachments, email attachments and keychain items. Within the different apps, that volume is visualized as a separate storage location.
From a user perspective, the User Enrollment process starts with the enrollment of a personal iPhone. That experience depends on the third-party MDM provider and the enrollment options IT has configured. No matter which MDM platform the organization uses, the enrollment is a guided process that starts with downloading the companion app of the MDM platform, such as the Company Portal app for Microsoft Intune. After downloading and opening the app, a user must sign in with their identity. This triggers the User Enrollment and asks the user to confirm the management profile is downloaded and installed.







