end-user computing (EUC)
What is end-user computing (EUC)?
End-user computing (EUC) is a term that refers to the technologies that IT professionals use to deploy, manage and secure the devices, applications and data that workers require to perform their jobs.
The major components of EUC are physical desktop computing, virtual desktop computing and mobile computing, each of which involves several different technologies.
Types of EUC
End-user computing encompasses a wide variety of user-facing resources, including the following:
- Desktop and notebook computers.
- Desktop operating systems and applications.
- Smartphones, tablets, wearables and other mobile devices.
- Mobile, web and cloud applications.
- Virtual desktops and applications.
EUC also covers the following technologies, which IT professionals use to provide access to user-facing resources:
- Windows management and security tools.
- Enterprise mobility management software, which includes mobile device management (MDM) and mobile application management.
- Desktop virtualization and application virtualization platforms and management tools.
- Enterprise file sync-and-share services.
End-user computing services
Traditionally, IT managed the different components of end-user computing separately. As the consumerization of IT and the bring your own device trend gained steam, however, more organizations realized the need to provide access to corporate applications and data across multiple device types.
In an attempt to simplify this process, vendors began offering products and services designed to work across multiple areas of EUC. Examples of these products and services include the following:
- Tools that provide monitoring and management of both physical and virtual desktops and applications.
- App refactoring, which uses virtualization to create mobile-friendly versions of Windows and web apps.
- Unified endpoint management (UEM), which allows IT to apply and enforce MDM policy on PCs.
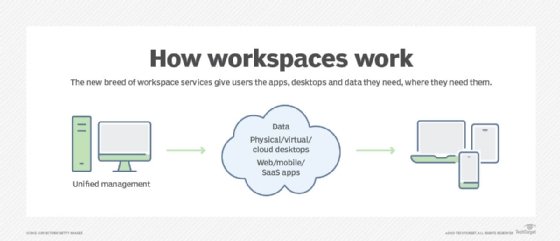
- Workspace suites, which aim to provide centralized consoles where end users can access all of their required applications and data, and IT can securely manage that access.
Advantages and disadvantages of EUC
End-user computing benefits organizations by securely enabling a mobile, distributed workforce. Its major disadvantage, despite all the work that has gone into unified management, is its complexity.
If organizations can't take advantage of UEM due to running outdated operating systems, for example, they have to use separate products to manage PCs and mobile devices. Workspace suites do not yet provide complete integration between all of the disparate products they bundle together. Additionally, trying to run an application on an operating system or device that it wasn't built for can result in problems with compatibility and user experience.







