What is mobile threat defense (MTD)?
Mobile threat defense (MTD) software protects organizations and individuals from security threats on mobile platforms. MTD protects against attacks that target mobile devices and operating systems, such as Apple iOS and Google Android.
Hackers also use malware, phishing and network attacks to compromise a user's device, which could then be used to steal data or hurt a business. MTD's goal is to protect users from such incidents.
MTD software is designed to protect mobile devices continuously, both online and offline. It can block threats, alert users, quarantine devices, and detect and remediate issues like zero-day vulnerabilities.
Why is mobile threat defense important?
The popularity of mobile devices has made them a target of cybercriminals. Many organizations use mobile device management (MDM), mobile application management and unified endpoint management to secure mobile devices, but such tools are limited in their security capabilities.
For example, MDM can apply various security policies to mobile devices and mobile operating system patches as they become available. However, it generally lacks attack detection capabilities and the ability to respond to cyberattacks.
In contrast, MTD software provides visibility into cyberthreats directed at mobile devices. It's essential in mitigating mobile security risks while adhering to an organization's compliance mandates, such as HIPAA.
How mobile threat defense works
MTD typically addresses threats at the device, application and network levels.
Device level
At the device level, an MTD tool checks for issues, such as whether devices require lock screens and encryption. An MTD platform can also check for device-level anomalies, such as battery drain caused by malicious apps.
Application level
An MTD platform is designed to detect data leakage and other privacy issues at the application level. Data leaks often occur when apps have access to data in other apps. This can be problematic when data crosses between personal and business-approved applications on a device. Some MTD tools also prevent installing certain apps based on what IT has approved.
Network level
MTD can monitor network packets at the network level to look for known threats and anomalies. This includes detecting man-in-the-middle attacks or Secure Sockets Layer stripping. SSL stripping occurs when an HTTPS connection is downgraded to an insecure connection, enabling attackers to collect sensitive data. MTD software can also automatically encrypt traffic when connected to an open Wi-Fi network.
Modern MTD platforms use machine learning to detect anomalies in device, user and application behavior to identify threats.
Key features of MTD
MTD apps and tools offer a range of features, including the following essential ones:
- Real-time threat detection. An MTD tool continuously monitors devices for signs of threats.
- Behavioral analysis. This approach uses methods such as machine learning to detect unusual behaviors on Android and iOS devices.
- Strong network security. This protects against unsafe Wi-Fi connections and prevents man-in-the-middle attacks.
- App and device risk assessment. This analyzes installed applications and device configurations to detect vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with security policies.
- Endpoint security integration. This works alongside existing cybersecurity tools to provide an additional layer of defense for mobile endpoint security.
- Automated remediation. This takes immediate action against detected threats, such as blocking suspicious apps and restricting network access.
- Policy enforcement. This helps IT teams configure security policies to ensure employees follow MTD best practices.
What does MTD defend against?
MTD solutions protect organizations from a variety of security threats. The following are some of the most important:
- Malware and ransomware.
- Phishing attacks.
- Unsecured networks.
- Device vulnerabilities.
- Unauthorized access.
- Data leaks.
- Compromised credentials.
What are the benefits of MTD?
The main benefit of adopting MTD is improving an organization's overall security posture. An MTD tool analyzes the organization's mobile devices and provides IT with actionable insights to address potential vulnerabilities.
In addition, the tool monitors devices continuously to detect threats and take corrective action if necessary. Organizations reduce their chances of suffering a ransomware attack or security breach when they monitor devices and address known vulnerabilities.
What are the challenges of using MTD?
One of the biggest challenges associated with MTD software is the number of device types a user could be working from. To be effective, an MTD tool must support all mobile devices used throughout the organization.
Another challenge is that a poorly developed MTD tool can get in the user's way or consume too much battery power, leading the user to disable the software. Ideally, MTD software works silently in the background without placing an excessive load on the device.
In addition, MTD is only effective if it is accurate. Most administrators have seen network monitoring tools that generate a large volume of alerts or that create false positives. As such, an organization might hesitate to deploy MTD until it's convinced the tool can provide accurate and useful information without causing alert fatigue.
MTD and enterprise mobility management
MTD is often used in conjunction with enterprise mobility management software. EMM software lets an organization apply security policies to mobile devices, manage applications and apply updates. EMM focuses on device administration and policy enforcement, while MTD protects against cyberattacks.
A mobile security strategy should consider a range of potential risks. However, EMM doesn't cover all possible risks. So, an organization that uses EMM can also implement MTD to make its mobile devices more secure. In this case, IT teams might consider MTD an extension of EMM.
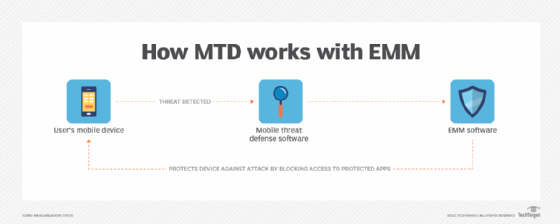
Tools for mobile threat defense
There are various MTD tools. An organization typically assesses its needs and goals before identifying one. Some tools perform different actions and integrate with different EMM platforms.
An organization should ensure its selected tool matches the issues or gaps in its mobile security. The MTD software should also provide more than just general antimalware; it should have device-, application- and network-level protection. The MTD platform should be able to analyze user behavior for anomalies and vulnerabilities, as well as remediate threats. An organization that already uses EMM or MDM should also ensure that its MTD software can integrate with its existing technology.
Most MTD software is deployed through a cloud portal and orchestrated with MDM. Gartner recommends that organizations implement MTD software gradually -- deploying it first to devices that would most benefit from increased security.
According to Gartner, the following MTD tools are worth considering:
- Check Point Harmony Mobile.
- Lookout Mobile Endpoint Security.
- Palo Alto Networks GlobalProtect.
- Sentinel One Singularity Mobile.
- Symantec Endpoint Protection Mobile.
Mobile threat defense is important in protecting the enterprise from security risks. Learn more about how to protect enterprise devices from malware.







