Using Zabbix with embedded devices via SNMP monitoring
Some devices you want to monitor with Zabbix cannot have software installed. For these appliances, SNMP monitoring may be the right choice.
In the previous two articles in this three-part series on monitoring network devices with Zabbix, we learned how to monitor network devices using the Zabbix agent. But there are some devices you cannot install the Zabbix agent on to monitor. Think of embedded devices or appliances that cannot have software installed. For those devices, SNMP monitoring might be an option.
This article is part two in a three part series. For part one, click here. For part two, click here.
Many devices offer support for SNMP. In most cases, just a simple configuration is required: You need to turn on the SNMP service, make it accessible over the network and configure it with minimal security settings. Default security in SNMP is handled by defining communities. The command get community is used to request the information from the device, and set community is used to change parameters on the device and traps are used to send alerts to a network monitor such as Zabbix.
After enabling SNMP, add the device as a host to Zabbix:
1. Log in to the Zabbix Web interface (http://yourhost/zabbix) and select Configuration>Hosts. From here, click Create Hosts to add the device you want to monitor.
2. Enter the properties of the device:
- Name: Insert the name that you want to be displayed in Zabbix.
- New host group: It might be convenient to create a dedicated host group for all SNMP devices
- DNS name/IP address: Insert the DNS name or IP address of the device.
- Connect to: Depending on which you are using, select either the IP address or DNS name to connect to the device.
3. Click Save to add the device. It will now be added to the list of monitored hosts in Zabbix.
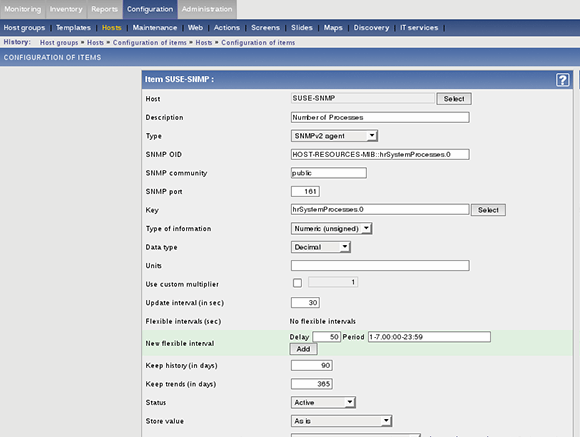
A host that doesn't have any items configured cannot be monitored with Zabbix. To create one or more items, select the host and click the Item link. Next, click Create Item. You'll now see a form in which you can identify the item and its monitoring properties. The most important piece of information to enter here is the SNMP object identifier (OID). This is entered in the MIB-NAME::ItemName format. If you don't know what to use here, use the command snmpwalk -v 2c -c public <ip-address> to request a list of all available items. In this example we'll configure an item that requests the number of processes running on the host. This item comes from the HOST-RESOURCES-MIB and it uses the following form:
HOST-RESOURCES-MIB::hrSystemProcesses.0
Based on this, you can enter the following information while specifying the item:
- Description: As we want the display the amount of processes that is currently running, use Number of Processes.
- Type: SNMPv2 agent. If this doesn't work, try SNMPv1 agent. All devices that are manageable with SNMP are compatible with SNMP version 1.
- SNMP OID: HOST-RESOURCES-MIB::hrSystemProcesses.0
- SNMP community: This is the password for the monitoring community. It is set on the SNMP agent, and normally the value to select is public.
- SNMP port: Use the default SNMP port 161
- Key: This is the value you want to monitor as described in the Management Information Base (MIB). In this case, use hrSystemProcesses.0
- Type of information: This corresponds to the type of output you expect. In this case, that would be numeric.
For the moment, leave all other parameters and click Save to write the new item to Zabbix.
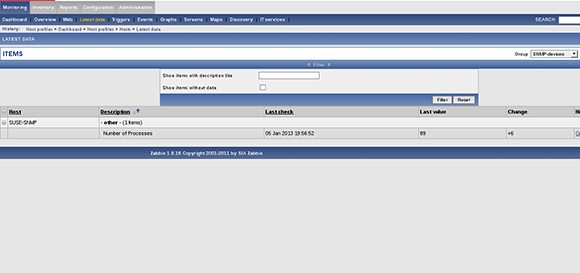
From the Zabbix interface, you can select Monitoring>Latest data. Select the group SNMP-devices to see the test host with one item configured. Opening the item shows the current amount of processes, including the last time Zabbix checked it. In this instance, the item value is automatically updated every 30 seconds
Now that you have configured the first item on your SNMP host you can add additional items.
The initial setup takes some time; you'll need to analyze the MIBs to see which items are available and then decide which should be monitored. One big benefit to this approach is, once you have it set up, Zabbix will monitor exactly what you need to get the pulse of the SNMP-managed devices in your network.
ABOUT THE AUTHOR: Sander van Vugt is an independent trainer and consultant based in the Netherlands. He is an expert in Linux high availability, virtualization and performance, and has completed several projects that implement all three. He is also the author of various Linux-related books, such as Beginning the Linux Command Line, Beginning Ubuntu LTS Server Administration and Pro Ubuntu Server Administration.