What is an automation architect?
An automation architect is a senior IT professional responsible for the strategic design, development and governance of automation initiatives across an organization. Automation architects use automation technologies and workflow engines to streamline processes, lowering costs and enhancing efficiency and accuracy across an organization.
Automation architects typically collaborate with department heads, stakeholders and IT teams to identify gaps in an automation process before deployment. They enforce industry and organizational best practices. For example, they continuously refine and optimize automated workflows to ensure they adhere to compliance standards, regulatory requirements and internal governance policies.
Why automation and automation architects matter
Automation is essential for modern organizations as it simplifies repetitive tasks. It also enhances operational efficiency and accuracy, reduces costs and enables employees to concentrate on more strategic and creative work. This shift ultimately boosts productivity and fosters innovation.
For an automation architect, automation offers various use cases that drive organizational improvement. As businesses strive to reduce manual tasks, minimize errors and speed up processes, the automation architect is tasked with designing and executing an IT automation strategy that aligns with these objectives. This involves selecting appropriate tools, creating scalable frameworks and ensuring that automated workflows integrate smoothly with existing systems.
Key benefits of automation include the following:
- Enhanced efficiency and speed. Automated processes execute tasks much faster than manual methods, accelerating workflows and reducing turnaround times.
- Improved accuracy and reduced errors. Automation minimizes the potential for human error inherent in manual processes, leading to more consistent and reliable outcomes.
- Scalability and consistency. Automated systems offer easy scalability as they can handle increasing workloads without compromising quality or consistency.
- Cost reduction. By optimizing resource allocation and minimizing errors, automation contributes to substantial cost savings in the long run.
- Empowered workforce. Relieved of mundane tasks, employees can focus on more strategic initiatives, creative problem-solving and innovation-driven activities, boosting overall productivity and job satisfaction.
- Enhanced security. Automation consistently applies security protocols and policies, improving an organization's security posture. It reduces the risk of human error in critical tasks such as patch management, access control and threat detection. Also, automated systems can quickly identify vulnerabilities, respond to incidents in real time and ensure compliance with security standards, offering better protection against potential threats.
What does an automation architect do?
The role of automation architect is new and evolving to meet the growing demand for efficiency and innovation. The following are some key roles these IT professionals take on:
- Assessing business processes. Automation architects evaluate existing business processes to find automation opportunities. Analyzing workflows to identify which processes can be automated to boost efficiency and lower costs.
- Designing automation frameworks. Automation architects design the architecture required to establish automation capabilities. This involves test automation, creating a roadmap, defining the scope of automation, setting objectives, establishing timelines and determining resource requirements.
- Creating business cases. A crucial aspect of an automation architect's role is advocating for or against the automation of specific processes. This requires a thorough understanding of automation's technical and business implications.
- Cross-functional collaboration. Automation architects work closely with various stakeholders, including DevOps, operations teams, quality assurance (QA) and business analysts, to ensure automation options align with organizational goals.
- Technology and tool selection. Automation architects identify the most suitable network automation tools, platforms and technologies that align with an organization's budget, business requirements and technical environment. They also make sure that the recommended tools and technologies seamlessly integrate with existing systems, such as enterprise resource planning, customer relationship management and legacy platforms.
- Performance monitoring and optimization. Once the automation options are deployed, automation architects are responsible for monitoring their performance and optimizing their efficiency and effectiveness.
- Leading and mentorship. Automation architects are responsible for leading teams in adopting automation technologies and methodologies. This involves mentoring team members and nurturing a culture of continuous improvement in automation practices.
- Staying up to date on industry trends. Given technology's rapidly evolving nature, automation architects must stay updated on technology trends and advancements in automation tools and practices.
How to become an automation architect
An individual must possess a combination of education, technical skills and practical experience to become an automation architect. The typical steps involved in becoming an automation architect include the following:
- Education. A bachelor's degree in a relevant field is typically the starting point for entering this industry. Ideal areas of study include computer science, IT, software engineering and data analytics. For those seeking advanced roles and career progression, obtaining a master's degree in a related field is beneficial, as it provides more in-depth technical knowledge and helps enhance leadership skills.
- Experience. For individuals aspiring to get into automation architect roles, starting out in software development or QA testing is an excellent way to build the technical expertise and practical experience needed for the role. This foundation provides an understanding of the software development lifecycle (SDLC) and various testing methodologies. From there, they can advance into automation-focused roles, gaining hands-on experience with automation tools and frameworks.
- Technical skills. Individuals interested in this field should become familiar with various automation tools and technologies, such as robotic process automation, continuous delivery/continuous deployment (CI/CD) tools and pipelines, software testing and scripting languages. Additionally, understanding cloud platforms and infrastructure automation can benefit their career aspirations.
- Soft skills. Automation architects should develop their soft skills, including problem-solving, project management and communication skills. For instance, they must be able to design and troubleshoot automation systems while effectively conveying complex ideas to technical and nontechnical stakeholders. They should also be able to manage automation projects, deliver them on time and ensure they align with business objectives.
- Certifications. Certifications enhance an automation architect's marketability. Aspiring individuals should consider pursuing certifications in specific automation tools and vendors, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), UiPath, Microsoft and Automation Anywhere.
- Portfolio building and networking. Individuals seeking to enter the field should demonstrate their automation projects and contributions through a well-crafted portfolio. They should also attend industry events, join online communities and network with other professionals in the automation field.
- Continuous learning. The automation field evolves rapidly. Aspiring individuals should stay updated with the latest trends, tools and technologies, such as AI and machine learning, by enrolling in continuous learning and online courses and regularly reviewing industry publications.
What skills does an automation architect need?
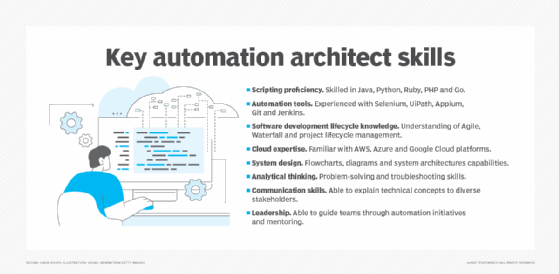
To excel as an automation engineer or architect, a combination of technical expertise, strategic planning and interpersonal skills is essential. Key competencies include the following:
- Ability to code in various scripting languages -- such as Java, Python, Ruby, PHP and Go -- to develop and integrate automation options.
- Experience working with automation tools such as Selenium, UiPath and Appium, and familiarity with CI/CD tools, such as Git and Jenkins, to create efficient workflows.
- A thorough understanding of SDLC processes and methodologies, including Waterfall and Agile, is necessary to oversee automation projects effectively.
- Knowledge of cloud services, such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud, for deploying and managing automation options in cloud environments.
- Demonstrated expertise in creating detailed flowcharts, context diagrams and various system architectures that enhance understanding and streamline processes.
- Strong analytical skills to design efficient automation options and troubleshoot issues as they arise.
- Able to articulate complex technical concepts to technical and nontechnical stakeholders is crucial for collaboration and alignment of business goals.
- The ability to guide teams through automation initiatives and best practices.
In many cases, automation architects are hired to manage automation in specific departments or systems. For example, an automation architect might specialize in AWS, Python or Selenium. Roles such as QA automation architect and test automation architect are also increasingly common.
What's the salary for an automation architect?
Automation architect jobs are becoming more common in both medium-sized and large enterprises. The salary for an automation architect in the U.S. varies based on experience and job responsibilities. According to Glassdoor, the estimated median total pay for an automation architect is $164,000 per year, with an average base salary of $124,000 per year.
In addition, experience and job responsibilities, salaries vary due to geographic location, industry, company size and individual qualifications. Major metropolitan areas or technology hubs offer higher salaries to account for the cost of living and the demand for skilled professionals.
Network automation helps managers streamline repetitive tasks, such as device provisioning and configuration management, enabling them to focus more on strategic initiatives. Explore the key phases to build a successful network automation architecture.








