Rawpixel - Fotolia
What types of VHD files does Hyper-V support?
Fixed VHD files, dynamic VHD files, and differential or differencing VHD files are all supported by Hyper-V. Learn more about these file types and the best use cases for each.
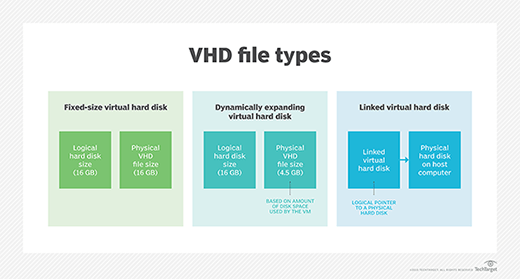
Hyper-V generally supports three types of virtual hard disk files: fixed, dynamic and differential. No type is best -- each type is designed to fill a specific role or purpose for the associated VM.
Fixed VHD files
Fixed VHD files are basically static entities that are completely provisioned when the VM is first provisioned. Because all of the disk space is committed to the VM upfront, the storage space is almost always contiguous on the physical disk itself. This helps to prevent fragmentation in the VHD file and keeps storage read/write performance high.
The static nature of a fixed VHD file also mitigates system CPU demands because the system doesn't need to check the underlying mapping of storage blocks.
When administrators employ the traditional VHD file format, fixed file types are almost always recommended. Fixed file types are also preferred when storage capacity isn't monitored regularly. This prevents the possibility of capacity expansions accidentally exhausting the available storage capacity and causing the VHD file to run out of space -- impairing or crashing the associated VM.
Dynamic VHD files
Dynamic VHD files are essentially thin provisioned storage instances where additional storage space is provided to the VHD on demand -- only a small portion of the VHD is actually backed by real storage capacity -- and the blocks involved in the dynamic VHD are typically not initialized. When a block is first written, the hypervisor must prepare the VHD for the block and update the associated VHD metadata.
Hyper-V storage simplified
With helpful features like storage quality of service and Storage Spaces Direct and advancements in technology, including 512e disks, admins can more effectively manage their Hyper-V environment.
This block mapping and metadata work demands additional CPU usage, lowering the overall performance of the dynamic VHD file. However, VM files using the current VHDX format often benefit from the built-in resiliency features of dynamic VHD files. And environments that actively monitor storage capacity can mitigate storage use with dynamic -- thin provisioned -- files.
Differential VHD files
Finally, differential or differencing VHD files offer a specialized kind of dynamic VHD file. As with a dynamic VHD, a differential VHD isn't provisioned upfront. Instead, blocks are added and initialized as data is written over time. This increases CPU usage and I/O demands.
However, a differential VHD points to another -- parent -- VHD, and reads are only read from the differential VHD if they have been written; otherwise, those blocks are read from the parent VHD. In this way, the differential VHD is ideal for capturing and managing changes to another VHD file, and differential VHDs are typical for VM snapshots.







