
Getty Images
How do I maintain an Azure VM static IP during a reboot?
Microsoft Azure users can assign static IP addresses to VMs, but doing so has notable downsides as well as benefits. Learn how and why to assign static IPs to Azure VMs.
While static IPs are often a source of angst in Microsoft Azure, they don't need to be.
By default, VMs created in Azure are assigned dynamic IP addresses that can change. Explore how and when to create static IPs in Azure in case of a system restart or failure, rather than trying to change IPs in the VM OS itself.
Creating a static IP address for Azure VMs
Microsoft has changed how IPs are allocated, and IT admins can now reserve a static IP when creating a VM. This IP address can be reassigned to other VMs as long as an organization owns it. Reserved IP addresses incur a monthly fee as well as fees for every hour reserved -- not just the duration of their use.
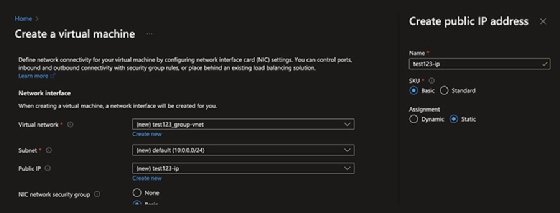
To build a VM on a static rather than dynamic IP address and obtain an IP that will survive reboots, select the Create new option in the Public IP portion of the IP setup. Give the IP a useful name and set the assignment option to Static.
It's strongly recommended that IT teams choose the standard stockkeeping unit (SKU), which has certain features that the basic SKU doesn't -- for example, support for use in load-balancing scenarios. Keep in mind that it isn't possible to change the SKU type after creation.
Another option is to create an IP address upfront, which makes it easier to create and assign IPs as needed. This is essentially the same process used to create a VM, but with more options.
To create IPs ahead of time, go to All services > Networking, select Public IP addresses and fill in the form. This achieves the same outcome, but enables IT admins to create several IP allocations at one time.
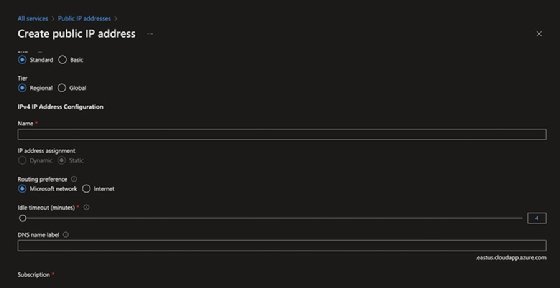
When creating an IP address upfront, IT admins can choose its availability, such as zone redundancy. IT admins can configure this setting to ensure the IP is redundant beyond the region's most local data center.
These IPs are associated with newly created objects and objects capable of IP assignment. Use the Associate button to assign the IP to the correct device.
Static IP best practices
Using static IPs directly can be difficult, especially when combined with automation. One of the easiest -- and most Azure-friendly -- ways to address this is to configure Azure to manage the DNS and to front services with a load balancer.
Assigning IPs directly to IaaS VMs will result in an outage. It also prevents IT admins from using key technologies such as scaling, wherein the IP is assigned directly to a VM rather than being fronted by a load balancer, which handles traffic in a failure scenario.
The Azure hypervisor patches automatically, causing VMs on the host to restart without notice. As with any directly exposed VM, ensure appropriate resilience measures are in place. In addition, assigning static IP addresses isn't restricted to VMs -- it's an option for many Azure components.





