
Sergey Nivens - Fotolia
Managed IT services glossary: Terms of the trade
Managed service providers represent an important subset of the channel partner ecosystem. Browse the terms below to sharpen your understanding of MSPs and their service offerings.
Managed IT services have evolved over almost three decades into a distinct category of IT services.
The term refers to IT management and monitoring services delivered to a customer organization by a third-party firm. Customers, particularly small and medium-sized businesses, have found value in managed services because it lets them both outsource IT functions and acquire technical expertise, thereby averting the burdensome costs of an in-house IT department. Channel firms, meanwhile, have gravitated toward developing managed services practices because it gives them a potentially more predictable and stable business model than compared with value-added reselling.
This glossary highlights terms commonly used in managed IT services and by the channel firms that deliver them.
Managed service provider (MSP). The MSP is the company that markets, sells and delivers managed IT services. Each provider offers its own unique blend of service offerings, which tend to include remote IT management and monitoring, IT support, data backup and recovery, cybersecurity, and cloud computing services management. MSPs typically tailor their managed services offerings to one or more customer segments. Many MSPs target SMB customers and/or specialize in one or more vertical markets, such as healthcare, financial services and manufacturing.
Remote monitoring and management (RMM). RMM technology is at the heart of most MSP operations. MSPs use RMM software to remotely maintain customers' servers and endpoint systems. Since RMM makes it possible to service customer infrastructure from a remote location, MSPs don't have to devote time and resources to going on site to customer locations. This allows MSPs to service more customers in broader geographical areas than would be otherwise possible. RMM tools can also automate manual systems administration procedures, enabling MSPs to develop increasing levels of operational efficiency.
Professional services automation (PSA). PSA is another type of software typically used by MSPs. PSA software suites provide applications for automating and managing day-to-day business process. Common PSA features include modules for customer relationship management, help desk/service desk, contract management, billing, project management and reporting. MSPs will typically integrate their RMM and PSA application to create more efficient workflows.
Subscription-based model. Managed IT services are sold and purchased as a subscription, requiring customers to pay a flat fee on a scheduled basis. Managed services subscriptions are usually billed monthly, but some MSPs charge customers on other schedules, such as quarterly.
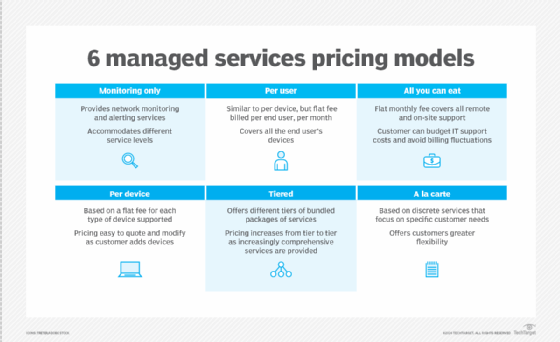
Monthly recurring revenue. MSPs aim to grow revenue from recurring business -- i.e., subscriptions. As noted above, MSPs typically sell managed services as on a monthly subscription basis. Monthly recurring revenue is an important feature of the managed services business model, setting apart MSPs from other types of IT service companies. MSPs use various approaches to pricing IT service packages, with per-device or per-user being popular models. MSPs may also use an all-inclusive ("all you can eat") pricing model, where a customer pays a flat fee for all the services and support they consume.
Service-level agreement (SLA). The SLA is a common component of contracts between MSPs and their customers. SLAs stipulate the services that the MSP will deliver in addition to performance and quality benchmarks the MSP is accountable for. SLAs frequently note the limits of an MSP's liability in the customer relationship. Other components of an MSP contract include a master services agreement, which explains the general terms and conditions of the relationship.
Managed security service provider (MSSP). The MSSP specializes in cybersecurity services. MSSP cybersecurity services are usually more advanced and comprehensive than the average MSP's. Managed security offerings may include security monitoring, vulnerability risk assessment, threat intelligence, and intrusion detection and response. Many MSSPs focus solely on maintaining customers' cybersecurity protection rather than IT infrastructure as MSPs do.
Managed print services (MPS). Managed print services are a type of IT managed service that maintains customers' printing devices. MPS are often in demand in print-heavy industries such as legal services and healthcare.
Break/fix. Break/fix is a form of IT support that stands in stark contrast to managed services. Whereas MSPs aim to offer proactive management and continuous monitoring of customer IT infrastructure, break/fix service providers tend to be reactive and repair-focused. Additionally, unlike managed services, break/fix services are typically charged on a time-and-materials basis. As managed services rose in popularity in early 2000s on, many break/fix providers transitioned into MSPs.







