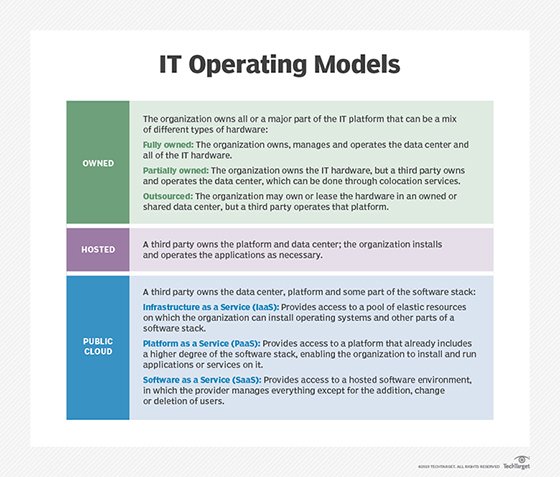
hosted services
Hosted services are applications, IT infrastructure components or functions that organizations access from external service providers, typically through an internet connection. Hosted services cover a wide spectrum of offerings, including web hosting, off-site backup and virtual desktops. Cloud services also fall within the hosted services category, although not every hosted service resides in the cloud. A customer, for example, may access an application from a hosting provider's dedicated server.
While the term hosted typically describes services provided by an external service provider, the term internally hosted may be used to describe applications, infrastructure components or functions that remain within an organization's in-house data center -- in contrast with externally hosted services. A private cloud is one example of internally hosted IT.
Categorizing hosted services
Hosted services accessed from an external provider take a range of forms and may be categorized in different ways.
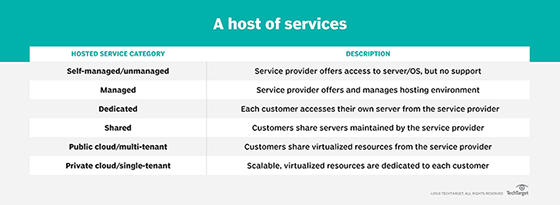
For example, a hosted service may be self-managed -- sometimes referred to as unmanaged -- or managed. In the case of a self-managed hosted service, the external provider provides the server and the operating system (OS), but it's up to the customer to install the application and provide ongoing management. A provider of a managed hosting service, however, provides that ongoing management and may also offer additional features, such as data backup and managed security.
In addition, hosted services may be provided on a dedicated or shared-services model. In a dedicated hosting environment, the service provider reserves servers and infrastructure elements for each client. In shared hosting, services are provided to multiple clients from a single server. These services may hybridize with other hosting categories -- managed dedicated hosting, for instance, in which a service provider wraps managed services around single-tenant hosting.
Hosted services vs. cloud services
Hosted services are also offered through the public cloud computing model. In the public cloud, multiple customers, or tenants, share virtualized resources -- virtual machines (VMs), also known as cloud servers -- as opposed to physical servers. Customers can access infrastructure as a service (IaaS), applications and storage through public cloud hosting environments.
Hosted services may also run in a private cloud, in which virtualized, scalable resources are dedicated to a single customer, as opposed to the Multi-tenancy of public clouds.
Hosted services and cloud services are terms that are sometimes used interchangeably. But some hosted services -- dedicated hosting, for example -- are based on physical servers rather than virtualized resources, as is the case for hosted services following the cloud computing model.
Types of hosted services
Within those broad categories of hosted services, there are numerous types of specific services an organization can adopt. Web hosting provides a widely used example. With web hosting, a service provider offers customers the infrastructure necessary to maintain a website.
In the cloud, IaaS, software as a service (SaaS) and platform as a service (PaaS) may be considered hosted services. Disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS) is another cloud-based hosted service, in which processing can fail over to the cloud if a customer's on-premises systems experience an outage.
While some hosted services aim to protect the data center, they also extend to the desktop. Desktop as a service (DaaS) offerings host desktop OSes, applications and data in the cloud.






