What is HR technology (human resources tech)?
HR technology (human resources tech) refers to the hardware and software that support an organization's human resources management (HRM) functions. As organizations continue to improve internal operations through digital transformation initiatives, HR software has become an increasingly important tool for managing distributed workforces, enabling hybrid work models and supporting compliance in complex regulatory environments.
The right HR technology can help an organization improve efficiency, reduce administrative overhead and make better data-driven decisions about workforce planning.
In the enterprise, for example, core HR technology applications and software modules that are integrated into broader human capital management (HCM) or human resources information systems (HRIS) make it easier for stakeholders to align people-related data with business strategy. This more holistic approach encourages HR teams to be treated as strategic business partners and the return on investment for HR technology to be assessed in terms of organizational goals.
Why is HR technology important?
HR technology is important because it reduces the need to manage core HR operations manually, and it allows HR professionals to focus more of their attention on strategic priorities such as talent development. By digitizing many of the time-consuming administrative burdens associated with payroll, onboarding and performance management -- and by automating workflows to increase efficiency and reduce errors -- HR technology can help department managers anticipate skills gaps, reduce turnover and ensure workforce planning initiatives are consistently aligned with business goals.
HR technology is also important from the employee perspective. Employee self-service tools can reduce the time workers spend waiting for HR to answer questions, respond to requests or update personnel records. The right self-service tools, when rolled out successfully, can not only boost job satisfaction, they can also help improve employee retention rates and make workforce planning easier and more efficient.
Examples of how HR technology is used
HR tech can reduce administrative burdens, support data-driven decisions for HR-related issues and give both HR professionals and employees better control over HR service delivery. Essentially, HR technology allows human resources representatives (HR reps) to enhance the employee journey at their organization by using HR analytics to discover insights that can improve business outcomes.
Traditionally, the most common use of technology in human resources management has been in core HR. Core HR refers to the basic administrative functions of a human resources department. It typically includes payroll, benefits administration, employee records management and compliance reporting.
In recent years, the evolution of HR technology has been driven by advances in AI, machine learning and cloud computing. Cloud computing has allowed HR systems to be deployed, accessed and updated more flexibly; machine learning has enabled predictive models to identify useful patterns in workforce data faster and more accurately; and AI is helping organizations automate repetitive HR tasks and personalize learning experience recommendations.

HR technology, especially AI-enhanced HR technology, is also allowing HR professionals to optimize their own HR tech skills and spend more time on higher-value functions like reducing employee detachment and improving employee engagement metrics.
To reduce administrative overhead while also encouraging employee engagement, many of today's platforms that support core HR functions allow employees to enroll in healthcare, retirement or wellness programs through a self-service portal. Self-service portals can not only relieve HR staff from the administrative burden of setting up and maintaining detailed records for each employee, they can also encourage employees to become more active participants in their own benefits management and overall workplace wellbeing.
Core functions supported by HR tech
Today, core HR technology is often used as a foundation to support more comprehensive (and expensive) human capital management and human resource information systems. Here are some of the core HR functions that HCM and HRIS systems provide:
Payroll
Payroll management software can be purchased as a stand-alone application or be acquired as a software module within a larger, more comprehensive HR platform. Small businesses often choose stand-alone payroll applications because they are easier to set up and manage, while enterprises tend to use integrated payroll modules that can support compliance and tax withholding across multiple jurisdictions. Cloud-based payroll management tools delivered through scalable software-as-a-service (SaaS) subscription models often have tiered plans that charge more for advanced features such as automated payroll tax filing.
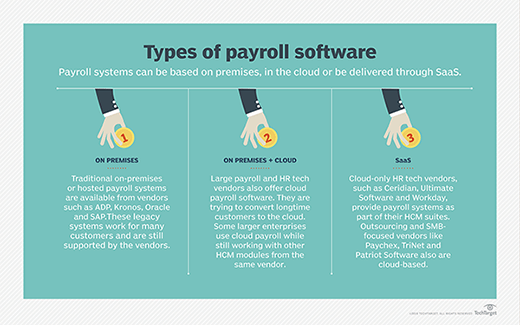
Compensation management
Compensation management is related to payroll, but this type of HR software is also used by recruiters and HR specialists to help determine the best pay rates for attracting and retaining employees and rewarding performance. Compensation management software is included in many enterprise-level talent management suites and can be used to automate salary calculations, determine salary benchmarks and integrate performance data with market insights to help align pay with both internal and external considerations.

Travel and expense (T&E) management
HR departments often use travel management stand-alone software or software components to record employee expenses, reimburse employees and analyze travel budgets. Expense report modules can provide stakeholders with a clear picture of spending at both individual and organizational levels. Mobile expense tools allow employees to track mileage, request reimbursements and submit receipts directly from a smartphone or tablet.
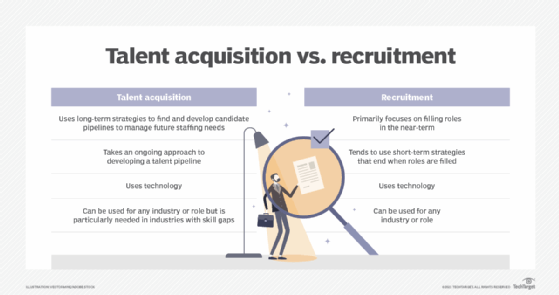
Talent acquisition and management
Talent management is the strategic process of attracting, developing, retaining and optimizing an organization's workforce to help ensure employee performance aligns with current business goals. It includes all the data and workflows used to build a talent pipeline and drive business success. Examples of different types of talent management software systems include the following:
- Applicant tracking systems can be used to post job openings on a corporate website or job board, screen resumes and generate interview requests to potential candidates by email or text message. Additional features an ATS might offer include resume ranking, prescreening questions, response tracking and multilingual capabilities.
- Candidate relationship management software allows recruiters to identify and maintain a pool of qualified candidates they can consider for open roles.
- Employee referral software allows HR staff to collect recommendations from current employees about potential and current candidates.
- Employee assessment software can help hiring managers decide whether a job candidate is well suited for an open position. Some HR assessment technology can screen resumes to evaluate a candidate's soft skills and cultural fit while others can only assess hard skills through multiple-choice questions.
- Succession planning software can help organizations identify, develop and prepare employees to fill critical leadership or specialized roles in the future. This type of HR software module is typically included in high-end enterprise HR suites to reduce the risks associated with sudden departures or retirements.
Performance management
HR software enables HR specialists, managers and team leaders to evaluate employee performance more often, align individual work with changing organizational goals and close performance gaps faster. Today's performance management enterprise platforms often include features such as real-time feedback, reward and recognition modules, customizable surveys and integration with learning and development tools.
Today, many employers are moving toward continuous performance management in place of (or alongside of) annual reviews. Features like automated reminders, mobile apps, analytics dashboards and integrations with learning systems make it easier to sustain continuous performance management at scale, and tie employee development initiatives directly to business outcomes.
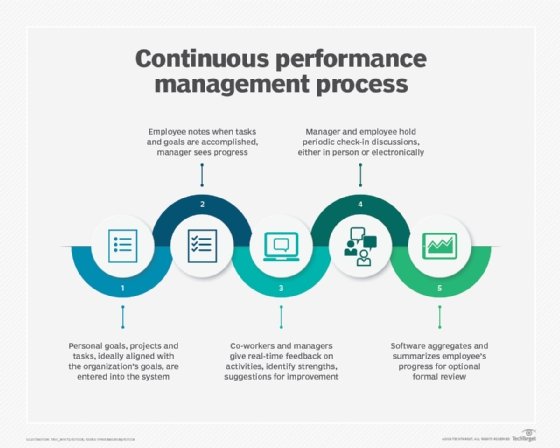
Workforce analytics
Workforce analytics is the practice of collecting, analyzing and interpreting HR data to generate insights that improve long-range workforce planning, optimize talent management and align HCM with business objectives. Workforce analytics software, which is also referred to as people analytics software, can help HR staff members evaluate the effectiveness of their HR initiatives and understand employee/candidate challenges better. This type of HR software can be purchased as a stand-alone application. Basic analytics functionality is included in many HCM and HRIS platforms.

Employee engagement
Employee engagement software is another popular type of core HR technology. This type of HR tech often includes features like gamification, pulse surveys and fast feedback loops to help organizations understand workforce engagement and identify areas where employee satisfaction may be slipping. A major challenge of using employee engagement software to track and analyze sentiment, however, is that the data might simply reflect adoption rates for the HR software itself rather than providing genuine insight into job satisfaction.
Benefits management
Benefits administration software is HR technology that streamlines the management of employee benefits programs (such as health insurance and retirement plans) by automating employee enrollment, ensuring compliance with relevant regulations and providing employees with self-service access to their benefits. This type of HR software is often included in enterprise HR software stacks, but it can also be purchased as a cloud service.
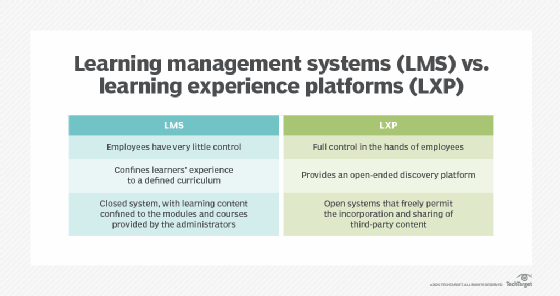
Learning management software/Learning management system
In enterprise HR software suites, a learning management system (LMS) is a type of talent management module that can be used to deliver, track and manage employee training and development programs. An LMS can help HR and learning and development (L&D) teams create training content, assign courses, track completion and measure learning outcomes. Many HR suites that have LMS modules also support compliance training, certifications and personalized learning paths, which directly tie into HR's role in workforce development and retention.
Challenges of HR Technology
Despite its many benefits, HR technology has some significant challenges that organizations need to address before they can realize the technology's full potential. Enterprises often struggle with integrating multiple systems, managing global compliance requirements and proving return on investment for HR software, while small to midsize businesses (SMBs) often have to deal with issues around the cost of HR software and software support.
User adoption is a hurdle that must be overcome across all company sizes because even the best-designed HR software cannot deliver results without employee buy-in and consistent use.
Compliance risks and security are other concerns. HR platforms handle sensitive employee information and personnel records that contain personally identifiable information (PII). A breach that involves employee data can not only damage employee trust, it can also expose the organization to reputational harm and financial penalties.
What is human capital management?
Human capital management refers to the best practices and tools used by organizations to recruit, manage and develop their workforce. HCM software allows employees to be viewed as valuable business assets whose skills and performance need to be managed strategically, not just administratively.<
HCM platforms often include modules for recruitment, onboarding, performance management, learning and development, compensation, succession planning and compliance. In some tech-oriented enterprise environments, the data from an HCM data platform is integrated with other types of enterprise resource planning (ERP) data to facilitate strategic alignment with business objectives.
HCM vs. HRIS and HRMS
In the past, HR platforms were often marketed under the label "human resources information system" or "human resources management system." In recent years, however, the label human capital management has begun to displace both HRIS and HRMS. The shift in terminology is meant to reflect the evolution of HR tech's capabilities.
That said, the three labels are still used in some settings to differentiate scope. An HRIS primarily handles administrative tasks, and an HRMS builds on that by adding additional functions for recruiting, performance management and reporting. Full HCM suites include all those functionalities and provide additional software tools for succession planning, compensation planning, workforce analytics and talent development.
Current trends in HR software
The future of HR technology is being shaped by rapid advances in AI, automation and data analytics. While these technologies are already being used to automate some repetitive tasks --such as resume screening -- AI is expected to enable increasingly accurate predictive insights in the future and expand self-service HR's ability to personalize wellness incentives and skill development tools.
In some organizations, the ultimate objective for employee engagement tools will be to create employee journey maps that can support every stage of an employee's lifecycle, from recruitment through offboarding. Currently, the technologies and best practices that are being considered to make this possible include the following:
- AI. AI is being used to automate certain types of HR tasks, like resume scoring.
- Cloud-based HR systems. Cloud-based HR software has made it easier to provide employees with self-service portals.
- Self-service technology. HR chatbots embedded in HR portals, mobile apps or collaboration platforms can provide instant answers to FAQs.
- Data integration tools. Some enterprise HR tech suites can already aggregate data from different sources to provide stakeholders with a more holistic view of the employee experience from onboarding to offboarding.
- Learning management software. Many enterprise-level HR technology suites have learning management components designed to help employees upskill their soft skills and reskill their hard skills. This trend has accelerated with advancements in AI-driven learning recommendations and a growing demand for continuous learning, especially in hybrid workplaces.
- Pulse tools and surveys. Pulse and survey tools can make feedback loops a regular part of the workplace, not just a quarterly or annual event.

HR tech vendors
HR tech has developed rapidly in recent years, and employers around the world are using both enterprise HR technology from big tech companies such as Oracle, SAP and Workday and specialized HR tech from vendors like Deel and Salary.com.
Here are some of the most popular HR technology vendors, arranged by their primary focus:
Payroll
- QuickBooks Payroll. Integrated payroll for small businesses.
- Gusto. SMB-friendly, full-service payroll with taxes, benefits and optional HR add-ons.
- Deel. Global payroll with 150+ country coverage and compliance.
- Paylocity. Integrated payroll suite with native expense/spend controls
- ADP. Payroll and HCM offerings for organizations of all sizes.
Compensation management
- Aeqium. Fully customizable; can accommodate complex rules.
- Pave. Compensation intelligence platform powered by AI; known for benchmarking and merit planning features.
- Salary.com. Can use local market data in compensation models.
- Beqom. Enterprise tools for pay equity and transparency, compensation and performance management.
- CaptivateIQ. Can automate commission/variable compensation.
T&E management
- SAP Concur Expense. Popular enterprise travel and expense software.
- Expensify. Known for integration with a wide variety of apps.
- Zoho Expense. Can automate T&E reimbursements through policy controls.
- Fyle. Known for deep accounting integrations.
- Spendesk. Spend/expense management with cards, approvals, and real-time visibility.
Performance management and talent management
- Lattice. Widely used by mid-market-sized organizations.
- PerformYard. Can accommodate flexible review cycles.
- BambooHR. Provides lightweight performance module for SMBs.
- Workleap Performance. Can accommodate 360 feedback; known for analytics.
- Workable. This popular ATS system now has HR features for talent management.
Employee engagement and recognition
- Bonusly. Recognition and rewards with culture analytics.
- Nectar. Peer recognition and rewards for SMBs.
- Qualtrics. Features that help turn employee analytics into action plans.
- Kudos. Recognition platform with surveys and integrations.
- Culture Amp. Engagement surveys, analytics, and EX suite.
Human capital management
- Workday. Enterprise HCM suite enhanced by AI.
- Oracle Cloud HCM. Unified cloud HCM.
- SAP SuccessFactors. Comprehensive cloud HCM.
- UKG (Pro). HCM + workforce management at scale for organizations of all sizes.
- Dayforce. Global HCM platform (pay, HR, time, talent).
Human resources information system
- Namely. HRIS for mid-sized U.S. companies; core HR.
- BerniePortal. Provides benefits administration and compliance for small HR teams.
This buyer's guide for HR software will help you identify your organization's needs and pinpoint which software features your HR department will need and which you can do without.






