What is biomedical informatics?
Biomedical informatics is the branch of health informatics that uses data to help clinicians, researchers and scientists improve human health and provide healthcare. This interdisciplinary field combines computer science, data science and statistics, biology and healthcare.
The goal of biomedical informatics is to use technology to improve the relationship between medical knowledge and clinical practice. Although medical practitioners collect and review significant amounts of healthcare data, turning that knowledge into practice is often problematic. Biomedical informatics aims to use technology to collect, integrate, analyze and interpret extensive data to provide more accurate and personalized care to patients.
Biomedical informatics is an evolving discipline that has grown along with advances in biomedicine, which applies the principles of the natural sciences, especially biology and biochemistry, to medicine and healthcare. While not solely tied to computers and IT, biomedical informatics has become more reliant on software, AI and cloud computing with the rise of the biotechnology industry and the widespread digitization of personal health data.
Why biomedical informatics is important
Biomedical informatics uses big data and new ways of presenting it, together with traditional scientific research, to reach across medical disciplines to provide clinical insights, uncover disease, treatment and response patterns and point to new lines of scientific and medical inquiry.
Cloud-based supercomputing power has enabled dramatic advances in genomics and DNA sequencing. At the same time, advanced wearable devices are collecting large volumes of physiological data, and sophisticated medical imaging and visualization software and hardware -- such as ultra-high definition displays and three-dimensional printing (3D printing) -- are providing many more high-quality and relatively inexpensive data sources and ways to view data for clinicians and researchers.
The problem with so much data is that even the most skilled human clinicians cannot readily identify relationships and patterns in it, meaning that precise diagnoses and optimal treatments are easily overlooked. Biomedical informatics analytics can help find these patterns and relationships, supporting better medical research, healthcare decision-making and patient outcomes.
Examples of biomedical informatics
Biomedical informatics can aid in a wide range of areas, including the following:
- Electronic health records. EHRs provide complete and consolidated access to a patient's medical history, which hospitals and clinics can share and analyze. This single unified electronic record can streamline communication between providers and reduce errors.
- Clinical decision support systems. These analytical platforms use patient data and collective knowledge to offer clinicians real-time suggestions for patient care, such as the preferred medications, or to recommend procedures based on patient symptoms.
- Improved treatments. Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh Department of Biomedical Informatics have studied how computational and biomathematical modeling tools can help provide better biological knowledge that can be applied to individual cancer treatment.
- Drug safety. Biomedical informaticians in the pharmaceutical drug industry create and manage pharmacovigilance programs to improve the safety of clinical trials and drug testing. Pharmacovigilance software systems use data science and predictive analytics to detect drug trial errors or unknown side effects.
- Personalized medicine. Patient treatments are tailored to their specific needs based on their genetic makeup, lifestyle and other factors. Data analytics can sift through enormous volumes of data to identify patients at risk for specific conditions or diseases or predict patient outcomes.
- Enhanced patient outcomes. Automating tasks such as appointment scheduling, EHR management, patient intake and prescription management can help streamline healthcare processes, ultimately delivering better outcomes and reducing inefficiencies and costs.
- Genetic testing. By analyzing genetic data, researchers can predict disease risk, identify those at a higher risk for specific conditions and tailor treatments to individual genetic profiles. This genomic information is stored in databases, helping facilitate future research and applications.
Emerging technologies in health informatics
An array of new and emerging technologies is changing the potential capabilities of biomedical informatics. Some of the emerging technologies impacting informatics today include the following:
- Machine learning and AI. ML algorithms and models can analyze vast amounts of information to find patterns and relationships in otherwise disassociated data. AI can use the results of ML analytics to suggest possible diagnoses, predict patient outcomes and make treatment recommendations.
- Internet of things. A wide assortment of medical wearable, implantable and remote monitoring devices can collect patient data in real time, allowing clinicians and ML and AI platforms to monitor patients remotely, offer early warnings of patient emergencies, and track patient progress against predicted outcomes.
- Blockchain technology. Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that securely records and verifies transactions, ensuring the immutability and transparency of recorded data. Adding blockchain to healthcare records platforms can provide a secure and auditable means of storing and sharing patient data, enhancing data security and integrity.
- Unified healthcare systems. Interoperable healthcare IT systems will adopt communication, storage and security standards to share patient data seamlessly. This will reduce errors in patient data and service delivery between different providers and healthcare organizations.
- Telehealth. Video and audio communication technologies can deliver a range of remote health services such as consultations, education and patient monitoring. This can improve the efficiency of healthcare delivery and offer health services to remote or mobility-impaired patients.
- AR and VR. Augmented reality (AR) can combine data analytics with visual displays, adding context and identifying details for clinicians to see in real time. Virtual reality (VR) can simulate biological structures, enabling clinicians to train and learn about surgical procedures and therapies before performing on human patients.
- 3D printing. As 3D printing technologies develop to include biological materials, 3D bioprinting can potentially use patient data and analytics to create personalized implants, organs, tissues and other medical devices tailored to specific patients.
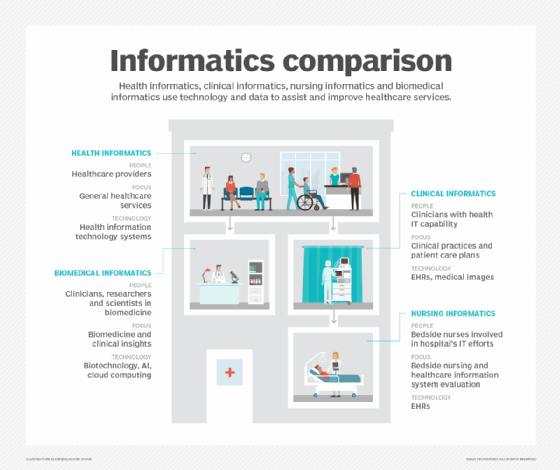
Differences between biomedical informatics, health informatics and clinical informatics
These distinct but related fields use technology and data in the following ways:
Biomedical informatics. Biomedical informatics focuses on using computational and traditional methods in biology and medicine and on research in genomics, proteomics -- the large-scale study of protein -- pharmacology and other disciplines that cut across medical disciplines.
Health informatics. Health informatics is broader and more directly related to healthcare treatment approaches. It uses data from specialized healthcare technologies such as EHRs, clinical health terminology sets and other sources. It also directly uses health data exchange standards like Health Level Seven International and Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources.
Clinical informatics. Clinical informatics is used in daily patient care by providing physicians, nurses, physical therapists, aides and other clinicians with information to form a care plan. Clinical informaticians also help caregivers view and use health data from IT systems.
Comparing bioinformatics vs. biomedical informatics
The combination of biology, computer science and IT has established the foundation of various types of informatics, including bioinformatics and biomedical informatics. Both technologies can support medical research and healthcare, but there are subtle differences to consider.
Bioinformatics uses computers and processing to collect, store, process and analyze large amounts of biological data. Consequently, bioinformatics is often applied to research-focused medical endeavors, such as genetic data analysis to advance genetic research and potentially identify medical cures. For example, bioinformatics researchers could use computational biology platforms to build 3D models to test the effectiveness of new drug therapies.
By comparison, biomedical informatics is a more patient-centric application of informatics technology that uses the specific data extracted from patients and collective knowledge of symptoms and conditions to make accurate diagnoses, reduce medical errors, manage healthcare costs and offer the most effective treatments for a given patient.
It is common for practitioners in biomedical informatics to use the data and discoveries created by bioinformatics experts. For example, a clinician using a biomedical informatics platform might also reference genetic or other research data available through bioinformatics systems.
Growing demand for professionals qualified in biomedical informatics
There is an increasing demand for a range of health informatics professions. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) projects the number of medical and health services manager positions -- including bioinformatics and biomedical informatics practitioners -- will grow from 562,700 jobs to 725,883 jobs by 2033 -- a 29% increase. In 2024, the BLS listed the annual median salary for these professionals as $117,960.
Although the BLS lists a minimum entry-level education as a bachelor's degree and less than five years of experience, it's important to note that biomedical informatics professionals often possess an interdisciplinary background involving computer science and medicine. Many possess a master's degree or Ph.D. and are often licensed clinicians.
Requirements vary. Professionals seeking employment in any type of informatics field should carefully review prospective employers' job requirements and gauge those specific requirements against their own background before pursuing job opportunities.
Due to the increasing need for data analysis, there is a growing demand for professionals skilled in AI and biomedical informatics. Explore the top degree programs available for those interested in these fields.







