What role do ERP systems play in supply chain management?
ERP is involved in every major step in manufacturing products and delivering the right ones to consumers. Here's an overview of its key SCM modules and features.
Investing in an ERP system is a major decision for a business. ERP provides benefits to every part of an organization, from finance and HR to planning and operations.
One area where a well-implemented ERP system can make a big difference is in supply chain management (SCM). As supply chains become increasingly complex, an ERP can cut through the noise, integrate with other logistics systems, support product flow and ensure availability.
What's the role of ERP in supply chain management?
ERP software provides several important capabilities for managing supply chains and logistics:
- Visibility into supply, demand, capacity and product flow so businesses understand the products they need and when they need them.
- Reporting and real-time tracking of various aspects of the supply chain to ensure everything is running smoothly and to identify issues when they occur.
- Control of different supply chain processes so supply chain managers can make changes to optimize product manufacturing, transportation, storage and distribution.
- Forecasting changes in supply and demand and planning for shifts in consumer behavior.
High-level benefits of using ERP in supply chains
There are many benefits to building supply chain management into ERP. At a high level, ERP software provides business-wide benefits, including the following:
- Giving visibility into how supply chain operations fit into the business as a whole.
- Allowing operational teams to understand how the ordering, transportation, storage and distribution of products contributes to business goals.
- Applying strong financial management practices to the supply chain to enhance cash flow and capital expenditures.
- Optimizing logistics and operational processes to maximize supply chain operational efficiency, reduce waste and improve profit margins.
- Improving workforce management and other resource allocation to ensure there are enough employees to meet the needs of customers.
- Forecasting product supply and consumer demand to maximize product availability and boost revenue.
ERP integration with other supply chain and logistics platforms
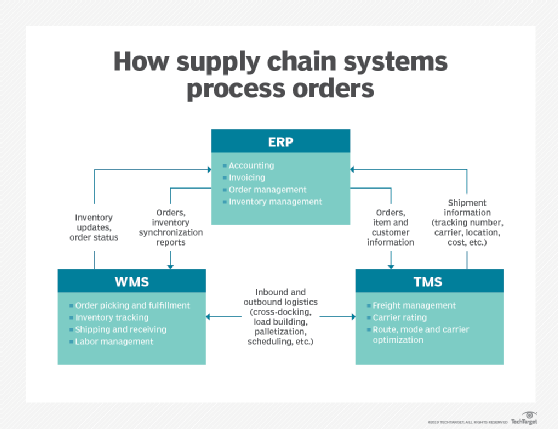
There are two main ways to take advantage of supply chain features in ERP. The first is through optional features you can add to an ERP system to expand its capabilities. The second is by integrating with a supply chain platform from another vendor, such as a warehouse management system (WMS) or transportation management system (TMS).
This article is part of
Guide to supply chain management
Supply chain features and functions vary between ERP platforms. It's important to review a platform's capabilities in detail to ensure it can meet current and future business needs.
Supply chain features of an ERP system
Key ERP functions for supply chain management include the following:
- Demand planning for forecasting and understanding future consumer needs.
- Procurement to source materials and parts and control costs.
- Manufacturing to optimize production of goods.
- Order management to minimize lead times and maintain availability.
- Warehouse and inventory management to hold stock and fulfill consumer demand.
- Transportation and distribution to get products into the hands of consumers.
Here's more detail on each one.
Demand planning to forecast and plan for consumer and business needs
Demand planning measures and predicts current and future demand for the products that a business sells. It looks at trends in consumer behavior, seasonal patterns, upcoming promotions and numerous other factors to forecast correct inventory levels and maximize product availability.
Accurate demand planning matters because a business needs to do the following:
- Hold just enough of each product line so it can meet the demand while not tying up too much capital in slow-moving stock.
- Plan ahead by using accurate forecasts to align supply, demand and storage levels across the supply chain.
- Ensure that suppliers and manufacturers have enough capacity to produce items on time.
Good demand planning maximizes availability and supports a healthy and continuous product flow throughout the supply chain.
Procurement to source raw materials and products cost-effectively
Procurement is the process of sourcing and buying the raw materials, parts and services needed to produce finished products. Procurement touches every part of the supply chain, from suppliers and manufacturers through transportation, storage and distribution.
Procurement matters because a business needs to do the following:
- Source competitive prices and services from third parties to maximize profit margins.
- Track where it is spending money so it can control and reduce expenses, while maintaining inventory levels in a cost-effective way.
- Ensure that raw materials, parts and logistics services are available when needed to minimize delays and disruption.
- Issue purchase orders, make payments and optimize supply chain-related cash flows.
Healthy procurement focuses strongly on cost reduction and control. It helps businesses to reduce operational expenses and contributes to the bottom line.
Manufacturing to optimize the production of goods
Manufacturing is the process of turning raw materials and parts into finished products. In-house production departments and third-party manufacturers can use the ERP manufacturing module to understand, track and optimize their production schedules.
Manufacturing matters because a business needs to do the following:
- Ensure that it has the workforce, equipment, materials and services it needs to produce high-quality goods in line with business requirements.
- Track real-time data including the inputs and outputs of production processes to minimize costs and identify bottlenecks, delays and disruptions.
- Know when products will be ready to pick up and transport through the supply chain network.
Carefully controlled manufacturing means that items are produced on time and in line with specifications and business requirements. Quality assurance and control are essential to keeping buyers happy and ensuring repeat purchases.
Order management to minimize lead times and ensure adequate inventory
Order management aligns demand and supply by processing orders for products efficiently according to the needs of customers and the business. Strong order management is central to reducing lead time, the delay between requesting the manufacture of a product and being able to sell it to a consumer.
Order management matters because a business needs to do the following:
- Order new products before running low on in-stock items.
- Balance inventory levels against likely consumer demand to maximize availability.
- Understand the time needed for sourcing materials, manufacturing and distribution.
Effective order management maximizes the availability of products before they're needed. It takes into account multiple factors to plan around manufacturing and transportation times so inventory levels remain healthy.
Warehouse and inventory management to ensure stock meets consumer needs
Warehousing and inventory management allow businesses to receive, store and track products and use those goods to fulfill customer orders. The WMS is a central platform that manages warehouse and inventory operations. It might be automatically included or offered as an option in the ERP system or provided through integration with a third-party WMS.
Warehouse and inventory management matter because a business needs to do the following:
- Securely receive and store a wide range of products that can be sent to consumers.
- Track inventory levels for reordering and to minimize waste and loss.
- Fulfill customer orders by picking and packing products before distributing them to retailers and end consumers.
Warehouse and inventory management ensure that products are available across different markets and geographic regions. They help ensure that consumers get what they want, when and how they want it.
Transportation and distribution for getting products into the hands of consumers
Transportation is the process of moving goods through the supply chain, whereas distribution focuses on getting products from the warehouse to the consumer. The central platform that manages transportation and distribution is the TMS, which like the WMS might be part of the ERP or integrated as an external application often sold by a different software vendor.
Transportation and distribution management matter because a business needs to do the following:
- Closely track the movement of products through transportation networks using real-time data.
- Identify potential delays in moving stock between manufacturers, ports, warehouses and distribution centers.
- Optimize delivery dates and processes to ensure products arrive safely and on time.
Transportation and distribution management are central to customer satisfaction. High-quality, on-time delivery means consumers get products when they need them.
How ERP supply chain features work together
All these supply chain processes and features are deeply integrated with each other in an ERP system. Demand planning feeds into order management to ensure that a business can efficiently manage inventory at all times of the year. Procurement works alongside manufacturing to provide competitively priced materials when manufacturers need them. Warehouse management supports distribution by fulfilling consumer orders and getting them delivered on time.
Taking full advantage of these features in an ERP system provides supply chain managers with strong oversight, control and visibility. They can react quickly to changing circumstances to remove delays, maximize availability and ensure customer satisfaction.
ERP integration with other logistics software
Not every business will want to run all its supply chain functions with the SCM modules and features that come with the ERP. There are often good reasons to use third-party logistics systems, especially for warehouse or transportation management. Fortunately, many of these technology platforms will fully integrate with an ERP, so businesses get a full suite of specialized features, together with the centralized control and overview offered by ERP.
Bringing together ERP with strong supply chain management helps businesses to optimize their products and logistics, which helps to ensure they can meet demand, boost revenue and improve profit margins.
Paul Maplesden is a freelance writer who strives to simplify complex business, finance and technology topics, with expertise in supply chain and SaaS platforms.







