
Process mining vs. data mining: What's the difference?
Both process mining and data mining tools can help business leaders make better decisions. Here's a look at how each works and what their differences are.
Both process mining and data mining can help business leaders gain a competitive edge, but they work in different ways.
Here's a look at what process mining and data mining do and how they are different and similar.
What is data mining?
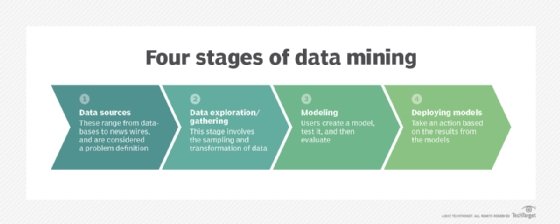
Data mining is the process of analyzing large amounts of data -- in other words, big data -- to discover relationships and patterns and predict future trends.
Data mining software creates association rules by searching for frequent if-then patterns in the data. An if-then pattern illustrates a variable and a consequence. A simple example would be: "If a product goes on sale, then more people will buy it."
Companies can use data mining software in myriad ways to make better business decisions. For example, they can use data mining to uncover commonalities of loyal customers, spot unhappy ones, decide where to place products on supermarket shelves or predict the risk of giving a loan to a certain customer. Manufacturers use data mining software to improve their product safety, identify issues in quality, manage their supply chain and streamline operations. Retailers can use a type of data mining called web mining, which uses traditional data mining methods over the web to understand customer behavior and gain insights into a website's effectiveness. Retailers can use information gained by web mining to tailor their websites to better satisfy their customers' desires. Healthcare companies can analyze data to spot fraud, and doctors can use it to better understand how to treat patients.
What is process mining?
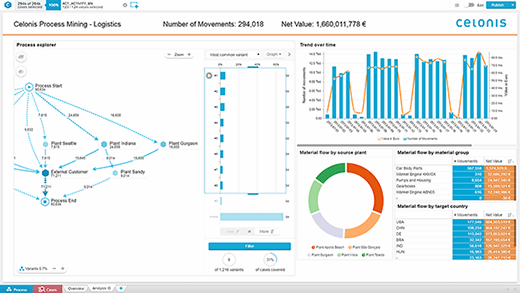
Process mining analyzes data paths within a company's software systems, especially its ERP system, to understand what it takes to complete a particular business process, how well the process is working and what deviations exist. Business process management is a closely related practice, but whereas that uses interviewing and other subjective measures, process mining uses the concrete data in corporate systems.
Process mining software analyzes complex processes, such as supply chain management and order to cash. For example, process mining might uncover bottlenecks in the supply chain. And, for order-to-cash processes, it might log and analyze keystrokes to uncover that credit holds for certain customers are causing unnecessary delays.
Comparing data mining and process mining
Data mining and process mining share a number of commonalities, but they are different.
Both data mining and process mining fall under the umbrella of business intelligence. Both use algorithms to understand big data and may also use machine learning. Both can help businesses improve performance.
However, the two areas are distinct. Process mining is more concerned with how information is generated and how that fits into a process as a whole, whereas data mining relies on data that's available. Data mining is more concerned with the what -- that is, the patterns themselves -- while process mining seeks to answer the why. As part of that, process mining is concerned with exceptions and the story those exceptions help to tell about the holistic answer, while data mining discards exceptions, as outliers can prevent finding the dominant patterns.







