value stream mapping
What is value stream mapping?
Value stream mapping is a lean manufacturing tool that visualizes every repeatable step required to deliver a product or service to the customer. It is also known as material- and information-flow mapping.
Using the principles of lean manufacturing, value stream mapping creates value for customers while optimizing resources and reducing waste and inefficiencies. Value can be thought of as anything the customer is willing to pay for; any process that doesn't provide value is called waste.
This sort of mapping incorporates material processing steps and information such as the people needed, digital and raw materials, and supply chain and inventory data into a comprehensive flow chart. The steps are labeled as value adding if they add value or nonvalue adding if they are wasteful or inefficient.
This visualization process helps organizations visualize the process of bringing a product to market. Using it, they can identify bottlenecks, delays and other issues that cause downtime, and eliminate unnecessary steps and resources. By improving this overall process, value stream mapping improves the overall production process, reducing lead time, which is the time between the start of a process and its conclusion.
The value stream mapping process originated in manufacturing but is frequently used in healthcare, IT operations and software development. When used in DevOps, for example, value stream mapping reveals steps in development, test, release and operations support that waste time or are needlessly complicated. It's also helpful in automating certain steps and reducing costs.
History of value stream mapping
Diagrams of material and information flows similar to value stream maps were first recorded in the 1918 book Installing Efficiency Methods by Charles E. Knoeppel. Toyota adopted this practice when it developed its lean production system in the mid-20th century. Value stream mapping in the Toyota production system emphasized the Kaizen methodology, also known as continuous improvement.
By the 21st century, value stream mapping and the philosophy of lean management had spread to many industries outside manufacturing, such as healthcare, product and software development, IT operations and logistics.
How to use value stream mapping
To make effective use of value stream mapping, follow these steps:
- Identify the value stream to map. Before doing any sort of process mapping, an organization must identify what product or service it wants to map and improve. It also must fully understand its customer and which performance metrics to consider.
- Identify the right people. One person or team in an organization shouldn't create a value stream map on their own. Insight from all the relevant employees, team members and stakeholders in the process is needed. Because a value stream often crosses department boundaries, it can be challenging to identify everyone who should be involved in the creation of a map.
- Map the current state of the value stream. Gather all the stakeholders, ideally in person, to go through each step in the process and document repeatable actions. The material, information, process and product flows should be visualized physically or using value stream mapping software, also known as value stream management platforms. The current state map is typically created as a one-page flow chart depicting the various steps involved in moving a product, project or service from start to finish. Although software can be used to create value stream maps, some experts feel that mapping programs impose artificial constraints during the collaboration process, and it's more efficient to use low-tech whiteboards while people are gathered together.
- Identify waste. Stakeholders use the shared visualization to identify limitations and deficiencies and brainstorm changes that eliminate waste. The value stream should be analyzed for bottlenecks in the material and information flows, steps that don't add value, overproduction and general inefficiencies.
- Design a new future state map. Typically, a process mapping session concludes with the creation of a value stream map that documents agreed upon changes. The mapping process should be continued in an iterative manner, with regular meetings called to analyze the map.
- Put the new map into action. Once an organization has its new map, it should create an implementation plan and put the new workflow into action.
- Continuously improve. Successful value stream mapping shouldn't stop at one session. Instead, it should be used to identify new areas for improvement and continually look for ways to reduce waste and inefficiencies.
Benefits of value stream mapping
Value stream mapping tools are used to eliminate waste and increase efficiency. Some of the benefits that make them popular include the following:
Visualization. Learning to see all the steps in a product delivery process is the main benefit of value stream maps. This sort of visualization helps organizations understand every element of their workflow.
Waste elimination. Once visualized, the steps in a value stream map are analyzed for whether they add value or not. Once identified, inefficient steps and resources can be removed or adjusted, eliminating waste.
Continuous improvement. Value stream maps are often used as tools to achieve continuous improvement, an approach that makes ongoing and proactive changes to products and services by reducing waste and streamlining processes. The mapping process forces an organization to analyze and revise its workflow.
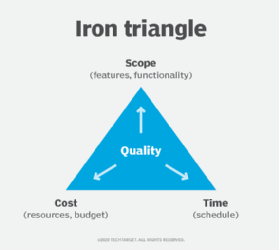
Process improvement. The elimination of bottlenecks, quality issues and defects in products and services helps organizations improve the overall quality of their process, product or service and its delivery. This can help organizations deal with built-in scope limitations, such as the triple constraint or iron triangle, a model that identifies scope, schedule and cost as the three biggest constraints on any project.
Decreased lead and cycle time. Value stream mapping helps identify areas where wait times can be reduced between steps. This approach helps organizations deliver final products and services to customers faster. It also speeds up cycle time, the total time it takes for a supplier to deliver its product to a customer.
Cost savings. The elimination of wasteful steps cuts costs and lets resources be redeployed to more beneficial uses.
Increased customer satisfaction. Value stream mapping can result in higher quality products and services that are delivered faster to better meet customer demand and improve the customer experience.
Challenges of value stream mapping
Value stream mapping is largely a beneficial tool, though it comes with some challenges:
Resource use. Creating a value stream map can require a lot of time and resources, including outreach to multiple teams and stakeholders. This can be difficult when companies have a siloed structure or don't have an efficient way to collect the relevant process data.
Change management. Implementing the changes proposed by value stream maps can be expensive and require difficult resource reallocation.
Dealing with unknowns. Value stream mapping and the steps it eliminates aren't guaranteed to improve a workflow. It also can't predict changes in customer needs or indicate the workflow that another product might best operate.
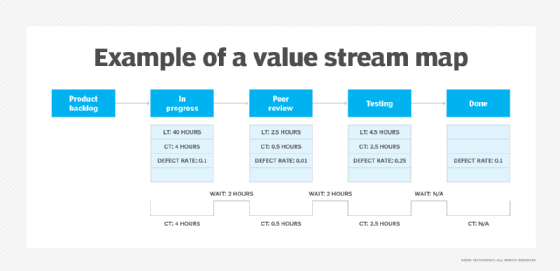
Example of value stream mapping
Value stream maps look different depending on what industry they're used in. The following industries all have different steps:
- Manufacturing. These maps include steps such as raw material procurement, assembly, inspection and shipping. They also show how the flow of materials happens through the entire process, where bottlenecks and waste arise, and how the process being mapped fits into the overall supply chain.
- Software development. When creating software, mapping steps include design, coding, testing and deployment. Maps also indicate how products move through the process flow, which stakeholders are responsible for each step and where the process can be optimized to reduce lead times.
- Healthcare. Value stream maps in healthcare include patient intake, examination, diagnosis, prescribed treatment and potential follow-ups. Maps indicate how fast patients move through the process, where delays are and how patient care can be improved.
Value stream mapping is a beneficial tool for improving business processes. Learn other ways to optimize business processes.







