What is order to cash (OTC or O2C)?
Order to cash, or OTC or O2C, is a business process that involves receiving and fulfilling customer requests for goods or services. It is a top-level, or context-level, term that management uses to describe the finance-related component of customer sales.
Other context-level business processes include marketing to lead, procure to pay, hire to retire, concept to launch and sustain and retain.
Businesses must optimize the O2C cycle to maintain smooth operations. Activities within O2C can affect supply chain management, inventory management and required labor. Therefore, operations can be negatively affected or disrupted if a bottleneck occurs in one of the steps of O2C.
Additionally, a company's cash inflow and working capital are determined by O2C functions. A delay in invoicing or payment collection can halt business processes that require spending profit, such as payroll.
Major vendors of enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems offer O2C services, such as Oracle, SAP and Workday. These systems can supplement the O2C cycle with related technologies like order management, credit management, reporting and data management.
O2C cycle steps
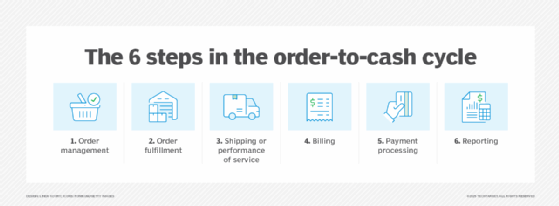
The O2C cycle starts when a customer purchases and runs through the company's entire order processing system. The cycle consists of multiple subprocesses around the following steps:
- The customer's order is documented. The order is recorded and stored in the order management system, with all customer information, order details, payment and shipping information, status, date-time stamps and any relevant notes.
- The order is fulfilled or the service is scheduled. The order is prepared for shipping, which includes inventory management updates, or the service is prepared for the customer via granting of access.
- The order is shipped to the customer or the service is performed. The product is shipped, often tracked in transit; delivery updates are communicated to the customer.
- Accounts receivable creates an invoice and sends it to the customer. An invoice is generated, including details of items, pricing, discounts and applicable taxes; it is stored in-house, and a copy is forwarded to the customer.
- The customer sends payment that the company collects. The customer renders payment; accounts receivable records the payment.
- The payment is recorded in the general ledger. The payment is posted to the general ledger, ensuring the transactional data is available to the accounting reporting system.
Once the cycle is complete, organizations should collect data around the O2C activity to pinpoint weaknesses or inefficiencies and identify opportunities for improvement.
Difference between order to cash and quote to cash
Quote to cash (Q2C) refers to all business processes involved in selling a product. Therefore, O2C is just one component of the Q2C cycle. Q2C also includes customer purchase intent, configuration price quoting and contract lifecycle management.
Customers' needs are more integrated into the Q2C lifecycle as prices are determined, products and services are bundled, and negotiations are made. O2C simply handles the customer transactions.
Top business models for O2C
There are several business models within which the O2C framework is implemented, including the following:
- Direct-to-customer (D2C). In this model, the business sells products or services directly to the end customer without intermediaries. It is the go-to model for e-commerce and is usually implemented in the simplest possible form.
- Business-to-business. Businesses sell goods and services to other businesses in this model. It differs from D2C in that bulk orders are more common, credit is central to those relationships and the relationships are often contractual.
- Subscription-based. Customers or businesses buy regularly, with the business fulfilling orders based on recorded subscription terms. Payment is usually automated. This model benefits from its automated nature in making order scaling, proration based on usage and other variations amenable to automation.
O2C best practices
There are several best practices to keep in mind when managing an order-to-cash framework.
Use automation and integration
Modern enterprise tools can help automate O2C processes, and integrating those processes into others can create efficiency gains. For example, a company's accounting system, order management system, customer relationship management system and ERP system are generally all automated and should be integrated, yielding smooth data flow and fewer errors.
Adopt artificial intelligence
AI and generative AI can help improve O2C financial processes. AI algorithms can analyze customer data, predict payment behaviors and flag potential issues.
Provide payment flexibility
A solid O2C framework makes deploying and managing various payment options and complex payment terms easier. This builds goodwill with the customer base.
Extend proactive credit management
Strong integration and a flexible O2C framework make credit policy management using analytics possible, enabling stronger credit risk assessment. AI enables businesses to reduce the risk of defaults and helps them extend credit to the right customers.
Track key performance indicators
Monitoring O2C metrics like order cycle time, sales order processing time, invoice and order fulfillment accuracy, and payment turnaround time helps measure the company's sales process efficiency and identify areas for improvement.
Learn the difference between customer success and sales, which group brings in new customers and which group increases retention.







