
James Thew - Fotolia
How to set up MFA for Office 365 on end-user devices
When it comes to authentication factors, more is always better from a security perspective. Find out how to deploy MFA on end-user devices for Microsoft 365 users.
Passwords are still the most common -- and weakest -- method for authenticating users, but there are many methods for preventing compromised passwords and credentials for accounts such as Office and Microsoft 365. For example, IT could train employees to pick strong passwords or set enterprise-wide password requirements.
However, the easiest and most effective way to mitigate compromised accounts is to create an additional barrier for hackers by enabling multifactor authentication (MFA). MFA ensures that even a weak password won't leave an organization completely vulnerable, as MFA requires an additional factor, such as access to a device or a biometric factor.
Setting up MFA for Office 365 on end-user devices offers organizations significant security benefits, and IT administrators should learn how to deploy this policy to their fleet of managed devices.
What are the options to set up MFA for Office 365?
When looking at Office 365, which Microsoft has folded into the Microsoft 365 service, the company provides three solid options for requiring MFA, though creative IT admins may find more.
These options range from a static option that is available for every customer with a Microsoft 365 and Office 365 subscription to a dynamic option that's available for customers with the previously mentioned subscriptions and an additional subscription of Azure AD Premium P1.
With any of the following Office 365 MFA setup options, it's important for IT administrators to stop allowing basic authentication protocols such as POP or IMAP, because they don't support the use of MFA.
1. Use security defaults for basic MFA protection
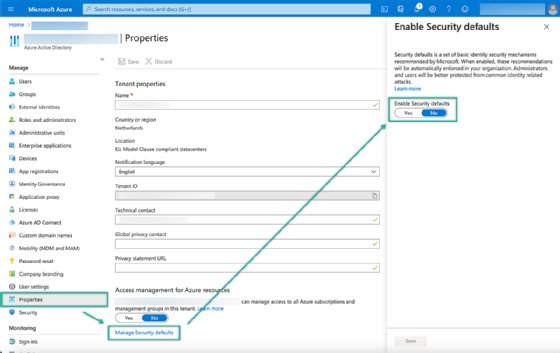
Security defaults provides organizations using Azure Active Directory (AD) with basic MFA capabilities. This capability is not customizable, and it is either on or off with no additional settings available. The security defaults method doesn't differentiate between platforms, so this authentication technology can work with iOS, Android and Windows 10 devices.
When IT enables this feature, Azure AD security defaults will do the following:
- Require users to register for MFA
- Require users to authenticate with MFA
- Force administrators to use MFA
- Require the use of MFA for privileged activities
- Block legacy authentication methods
Administrators can only use security defaults with the Microsoft Authenticator app as the additional factor. There are no other options available for the second authentication factor.
IT can enable security defaults by opening the Azure portal and navigating to Azure Active Directory > Properties > Managing Security defaults. That provides IT with a slider to enable security defaults.
2. Use conditional access for advanced MFA protection (preferred method)
Conditional access, which is the preferred method for configuring MFA, provides organizations that have at least an Azure AD Premium P1 license with advanced MFA capabilities. These capabilities are fully customizable policies and are, essentially, a set of rules that specify the conditions under which user authentication is allowed.
Conditional access via Azure AD can contain a single policy that simply requires all users to use MFA, but it can also contain several more granular policies that only require MFA from a specific location or platform. Besides the added flexibility, conditional access also supports any configurable authentication factor. It's worth noting that conditional access cannot function alongside Azure AD security defaults.
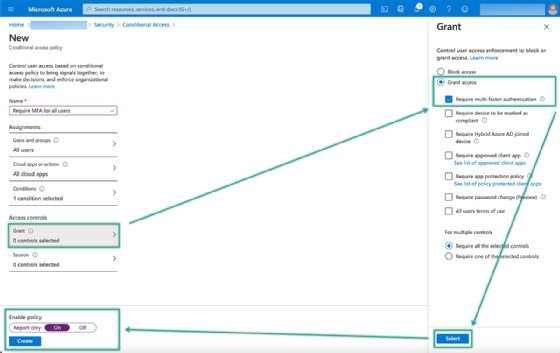
IT can configure conditional access policies by opening the Azure portal and navigating to Azure Active Directory > Properties > Security > Conditional Access. This provides IT with a blade that contains an overview of the existing configured conditional access policies and with the option to create new policies.
IT professionals should follow these six steps to create a basic conditional access policy that requires MFA for all users to access all cloud apps, including Office 365, for any platform.
- Click New policy and provide a valid name for the new policy.
- In the Assignments section, under Users and groups, select All users with Include.
- Note: It's strongly advised to exclude at least one "break the glass" administrator account for emergency access.
- In the Assignments section, under Cloud apps or actions, select All cloud apps with Include.
- In the Assignments section, under Conditions > Client apps, switch the slide to Yes and click Done.
- Note: To make this policy applicable to only certain platforms such as iOS or Windows 10, use Conditions > Device platforms in the Assignments
- In the Access control section, under Grant, select Grant access > Require multi-factor authentication and click Select.
- Select Yes with Enable policy and click Create.
3. Use legacy per-user MFA for basic MFA protection (not recommended)
Microsoft no longer recommends per-user MFA, but it provides organizations that use Azure AD with basic MFA capabilities. This capability is not customizable, and it still allows individual app passwords.
If IT uses security defaults or conditional access alongside per-user MFA, per-user MFA overrides the other configurations. Besides that, per-user MFA can function with any configurable additional factor.
If organizations are in some scenario where per-user MFA is the best option, they can configure it by opening the Azure portal and navigating to Azure Active Directory > Properties > Users > Multi-Factor Authentication. That provides the IT administrators with the option to enable, enforce or disable MFA per-user.






