
Getty Images
7 Windows 10 issues and how to troubleshoot them
Microsoft offers different troubleshooters to fix common Windows 10 problems, and once you find the right one for your issue, these troubleshooters are easy to use.
Fixing a Windows 10 issue such as disabled background apps can feel like a daunting challenge, but the troubleshooting process does not have to be difficult because Windows offers unique troubleshooters.
These troubleshooters can automate the process of resolving many common issues in Windows 10. They are easy to use, and as a Windows 10 administrator you can simply select the troubleshooter that best matches the problem you are having. From there, Windows 10 will do the rest.
Where is the Windows 10 Troubleshooter?
You can access the Troubleshooter in Windows 10 by opening Settings and clicking on Update and Security, followed by the Troubleshoot tab. This will bring you to the Troubleshoot screen (Figure 1).
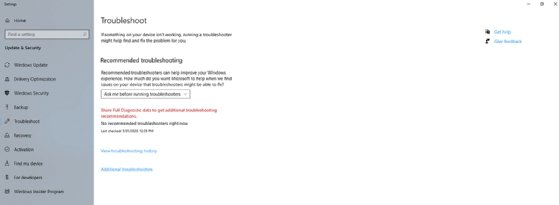
The first option on this screen asks if you want to be notified before Windows runs a troubleshooter. By default, if a problem occurs and a troubleshooter could help, Windows will ask if you want to run a troubleshooter. However, you can also configure this option to run a troubleshooter automatically -- with or without notifying you -- or to disable troubleshooting altogether.
The window also contains a link to the history of Troubleshooter use within the OS. This type of historical data allows you to see what issues Windows has experienced in the past. For example, the System Protection Troubleshooter ran several times in May 2020, when the machine was running low on disk space (Figure 2).

Common Windows 10 issues to troubleshoot
If you need to troubleshoot a specific problem, click on the Additional Troubleshooters link (Figure 1). This will take you to the Additional Troubleshooters screen (Figure 3).
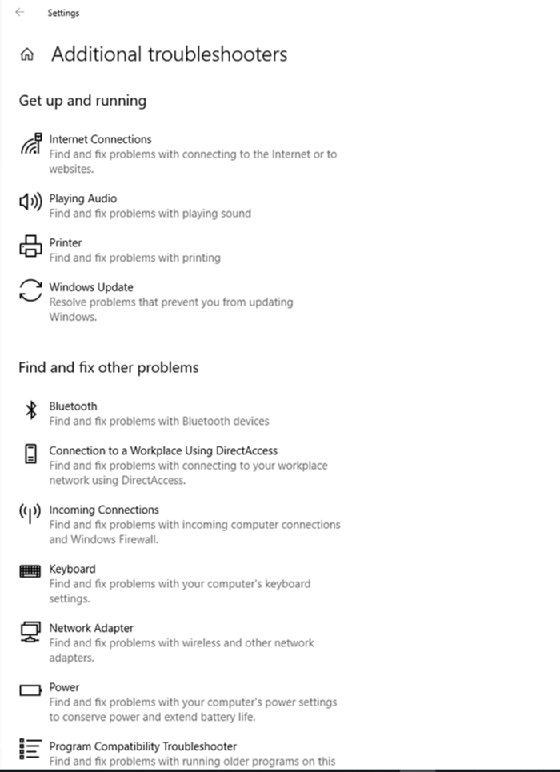
This screen provides access to the individual troubleshooters. However, not all Windows 10 issues can be resolved with these native troubleshooters. Still, there are other simple fixes you can try for many of these problems.
Updating issues or a problem after the update
If you experience problems with a Windows Update or if Windows exhibits problems following an update, you can use the Windows Update Troubleshooter to resolve the issue. On the Additional Troubleshooters screen, click on the Windows Update icon (Figure 3), followed by the Run the Troubleshooter button.
The Windows Update Troubleshooter checks for several issues, such as missing service registrations or settings that have been changed.
Issues with background apps
If you are having trouble with background apps, running the Windows Store Apps Troubleshooter can be an easy fix. This troubleshooter will check for missing and corrupt files, as well as other issues associated with Windows Store apps.
If the troubleshooter cannot resolve the issue and you continue to have problems with disabling or disabled background apps, go to Settings and click Privacy. Next, click the Background Apps tab. This tab includes an option to allow apps to run in the background. There is also a separate "run in the background" option for each individual app.
Missing DLL files
If your computer is experiencing issues with missing dynamic link library (DLL) files, you can begin your troubleshooting efforts by running the Windows Update Troubleshooter and the Windows Store Apps Troubleshooter. These will both look for missing or corrupt files.
If the troubleshooter cannot correct the problem, open an elevated Command Prompt window and enter the following command:
SFC / ScanNow
This will run the System File Checker, which scans for missing DLL files.
Wi-Fi connectivity issues
If you are having trouble connecting to a Wi-Fi network, you should start with the Network Adapter Troubleshooter.
When the troubleshooter begins, it will display a list of the network adapters that are present in your PC. Select the wireless network adapter and click Next. Windows will perform a series of diagnostic tests to determine why network connectivity is not working properly.
Problems with Bluetooth
If you are having problems with Bluetooth connectivity, you can run the Bluetooth Troubleshooter. From there, Windows will begin looking for Bluetooth-related problems.
The troubleshooter may report that the device does not have Bluetooth in some cases. This is especially true if Bluetooth is disabled within the computer's BIOS, or if you are using an external Bluetooth adapter. In these situations, make sure that Bluetooth is enabled -- if it is integrated into the computer's system board -- and that any required device drivers are installed.
Can't start in safe mode
If you are unable to boot your computer into safe mode, you might start the troubleshooting process by running the Windows Update Troubleshooter. If this troubleshooter fails to find any problems, enter the MSConfig command at the computer's Run prompt. This will launch the System Configuration tool. Select the tool's Boot tab and make sure that the safe mode checkbox is selected and click OK.
Another option is to boot the machine from the Windows installation media and click the Troubleshoot option, rather than installing Windows. Select Troubleshoot, followed by Advanced Options. Go to Windows Startup Settings and click the Restart button when prompted. You will be taken to a screen that allows you to enable safe mode.
Problems with PnP devices
If the plug and play (PnP) device that you are having trouble with happens to be an audio device or a network adapter, you can run the Playing Audio Troubleshooter or the Network Adapter Troubleshooter.
For other PnP devices, open the Windows Device Manager, right-click on the device that you are having trouble with and select the Update Driver command from the shortcut menu. Windows will help you to find a more suitable driver for the malfunctioning device.







