Windows 2000
What is Windows 2000?
Windows 2000 is an operating system (OS) developed by Microsoft. Released in February 2000, it was designed to run application programs, store files, support networking and run multimedia features. Extended support for Windows 2000 was discontinued in 2010.
Windows 2000 was a direct successor to Windows NT 4.0 and was followed by Windows XP. This version of Windows OS offered better and more stable support for computer hardware than prior Microsoft OSes.
Previously called Windows NT 5.0, Microsoft emphasized that Windows 2000 was evolutionary and built on NT technology, which was a combination of Windows NT Workstation and Windows NT Server. Windows 2000 was designed to appeal to small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) and professional users, as well as to the more technical and larger business market for which NT was designed.
The Windows 2000 product line consisted of the following four products:
- Windows 2000 Professional was aimed at individuals and businesses of all sizes. It included security and mobile use enhancements. It was the most economical choice.
- Windows 2000 Server was created for SMBs. It functioned as a web server and a workgroup, or branch office, server. This product could also be part of a two-way symmetric multiprocessing system (SMP).
- Windows 2000 Advanced Server was designed to be a network OS server and an Application Server, including those in large databases. This server facilitated clustering and load balancing. NT 4.0 servers with up to eight-way SMP could upgrade to this product.
- Windows 2000 Datacenter Server was created for large data warehouses, online transaction processing, econometric analysis and other applications that required high-speed computation and large databases. This product supported up to 16-way SMP.
What are the features of Windows 2000?
Windows 2000 was reported to be more stable than Windows 98 and NT systems, as it was designed to be less apt to crash. A significant new feature was Microsoft's Active Directory services; among other capabilities, it enabled an organization to set up virtual private networks, encrypt data locally or on the network, and give users access to shared files in a consistent way from any network computer.
Additional new features in this update included Active Desktop, Universal Serial Bus, NT File System 3.0 and File Allocation Table 32. Microsoft Installer provided a uniform experience for installing and uninstalling programs. The Microsoft Management Console aided in managing vital system functions, and a Recovery Console helped resolve software failures. Also included in the OS was an Encrypting File System, which offered accessibility and networking features. For example, as a networking feature, the server message block protocol could now directly interface with TCP/IP.
What are the Windows 2000 system requirements?
System requirements differed by Windows version. Minimum system requirements for Windows 2000 Professional included the following:
- 133 megahertz (MHz) or faster processor
- 32 megabytes (MB) of RAM
- 650 MB of hard drive space
Windows 2000 Server required the following:
- Intel Pentium 133 MHz or equivalent
- 128 MB of RAM
- 1 gigabyte (GB) of hard drive space
Windows 2000 Advanced Server required the following:
- 133 MHz or higher Pentium-compatible processor
- 256 MB of RAM
- 2 GB hard disk with 650 MB of free space
Windows 2000 Datacenter Server required the following:
- Pentium III Xeon processor or higher
- 256 MB of RAM
- 2 GB hard disk with 1 GB of free space
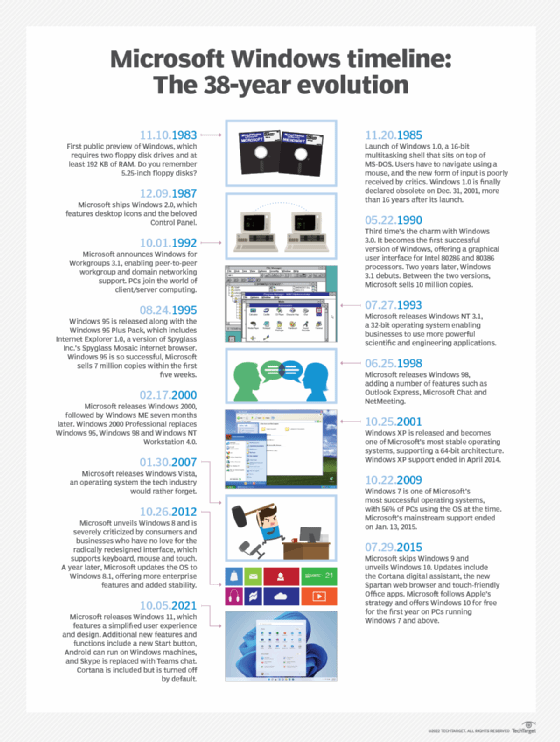
Windows 2000 history and end of life
Windows 2000 was created from the previous Windows NT desktop OS and was originally called Windows NT 5.0. The name was changed to Windows 2000 in 1998. The OS went through multiple testing versions, the first of which was released in September 1997; this led to the release of Windows 2000 on Feb. 17, 2000.
Upon release, the press began calling Windows 2000 one of the most stable OSes Microsoft had released. As time progressed, Microsoft also released several Windows updates called service packs. Service Pack 1 was released in August 2000, Service Pack 2 was released in May 2001, and Service Packs 3 and 4 were released in August 2002 and June 2003, respectively. After Service Pack 4, Microsoft began releasing updates as smaller update rollups to Service Pack 4.
Windows XP was released shortly after Windows 2000 on Oct. 25, 2001. Windows 2000 was still supported all the way up to July 13, 2010. As of this date, both Windows 2000 Server and Professional are no longer supported with security hotfixes or patches.
The current Windows OS is Windows 11, which was released in October 2021.
Is it time to upgrade to Windows 11? Learn how this desktop operating system differs from Windows 10 by comparing design features and performance improvements.






