Microsoft 365 Copilot features and architecture explained
Microsoft's new assistant adds generative AI to the workplace, using various features and architectural components for automated suggestions, content creation and data insights.
In today's digital workspaces, businesses constantly seek ways to enhance productivity. To address these needs, Microsoft introduced Copilot, an AI-driven assistant integrated into the Microsoft 365 suite of products.
Copilot for Microsoft 365 marked a major step in the integration of generative AI into productivity tools. Built on OpenAI's Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) language model, Copilot offers real-time personal AI assistance within Microsoft Office applications and Microsoft Teams. Its integration with Microsoft 365 enables direct content creation and interaction, and is designed to enhance productivity and efficiency.
Copilot consists of various architectural components that integrate with Microsoft applications like Word, Excel and Outlook. Recent updates, including new features for incorporating third-party data sources, further demonstrate how Copilot can improve efficiency and productivity in the workplace.
What is Copilot for Microsoft 365?
Copilot for Microsoft 365 is an AI-powered service that uses Azure OpenAI to provide generative AI functionalities within the Microsoft 365 ecosystem. Simply put, Copilot is a ChatGPT-like AI tool integrated into Microsoft Office. It also utilizes users' personal data stored in Microsoft 365 for personalization when creating new content or generating insights.
As an embedded service in Office applications such as Word and PowerPoint, Copilot can directly interact with and create content in those applications. In addition to these integrations, it also serves as a chatbot in Microsoft Teams.
Copilot aids in content creation and summarization by assisting with tasks such as drafting, outlining and generating ideas. For instance, in Microsoft Teams, Copilot can summarize a meeting and answer questions like "What was talked about?" and "What were the action points?" In Microsoft Word, it can help draft documents based on a prompt or using existing data.

Microsoft 365 Copilot architecture
Microsoft 365 Copilot consists of several core components, including its language model. Through an exclusive partnership with OpenAI, Microsoft offers the GPT language model directly from its platform via a service called Azure OpenAI. This service also powers Copilot 365's large language model capabilities. Although Azure OpenAI features the latest versions of the GPT model, such as GPT-4o, Copilot still uses earlier versions of GPT-4.
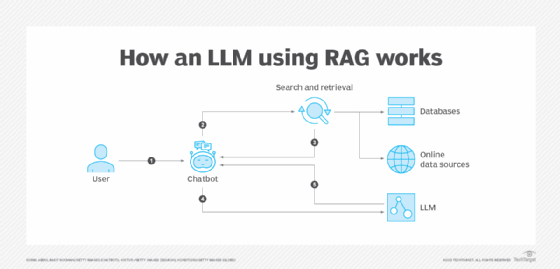
When Copilot 365 is activated for an organization, Microsoft also enables a feature known as semantic indexing. This feature adds extra metadata to all content, enhancing search functions within Microsoft 365. Another included functionality is vector search, which represents data as mathematical vectors alongside the original content. These search features use retrieval-augmented generation, a method that fetches data via a search engine and then sends that content to an LLM.
Copilot works by searching based on user context and access. For Copilot 365 to function effectively, high-quality data must be available for the search mechanism to explore. Old or irrelevant data can compromise search results, making it harder to find relevant information.
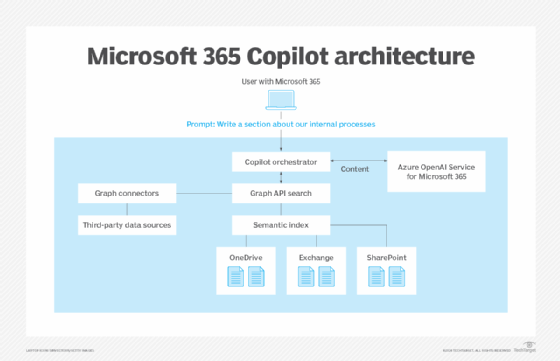
When a user sends a prompt through Copilot 365 to generate content, several events occur. First, the prompt triggers a request to the Copilot orchestrator, which fetches content from Microsoft 365 via the Graph API. The orchestrator includes safety mechanisms to filter out specific malicious content, apply sensitive labels if needed and define the system prompt for the LLM.
The search within the Graph API looks for relevant content that the requesting user has access to, using keywords and vector search -- known as a hybrid search -- within supported data sources such as SharePoint, OneDrive and Exchange. Examples of potential data sources include Teams chats, PowerPoint presentations and email conversations. The search engine also explores third-party data sources connected via Graph connectors, such as SQL Server or Confluence.
Next, relevant information found through the search is sent to the dedicated Azure OpenAI Service for Microsoft 365. The LLM uses this information to generate content, which is then presented to the user within the UI context. For example, the UI context could be an application such as Word or Teams where the user is interacting with Copilot and viewing the content it produces.
Microsoft 365 Copilot recent updates
Since its initial release in November 2023, Microsoft 365 Copilot has undergone several updates, including the following:
- Support for new languages, both for the UI and content.
- Integration with Microsoft Planner.
- Integration with Microsoft OneDrive.
- Introduction of Copilot Extensions, enabling integration with third-party systems using APIs.
The addition of Copilot Studio also brought new features to Copilot 365, letting users extend Copilot 365's personalized generative AI capabilities by developing extensions and integrations. It also supports the creation of custom functions and commands, as well as specialized virtual assistants and generative AI chatbots tailored to specific subjects, similar to OpenAI's custom GPTs.
Marius Sandbu is a cloud evangelist for Sopra Steria in Norway who mainly focuses on end-user computing and cloud-native technology.








