
What is artificial general intelligence (AGI)?
Artificial general intelligence (AGI) is the representation of generalized human cognitive abilities in software so that, faced with an unfamiliar task, the AGI system could find a solution. The intention of an AGI system is to perform any task that a human being is capable of.
Definitions of AGI vary because experts from different fields define human intelligence from different perspectives. Computer scientists often define human intelligence in terms of being able to achieve goals. Psychologists, on the other hand, often define general intelligence in terms of adaptability or survival.
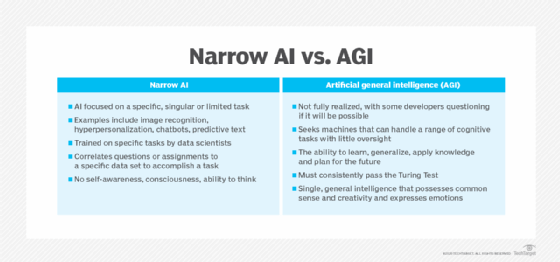
AGI is considered to be strong artificial intelligence (AI). Strong AI contrasts with weak or narrow AI, which is the application of artificial intelligence to specific tasks or problems. IBM's Watson supercomputer, expert systems and self-driving cars are examples of narrow AI.
What can artificial general intelligence do?
AGI in computer science is an intelligent system with comprehensive or complete knowledge and cognitive computing capabilities. As of publication, no true AGI systems exist; they remain the stuff of science fiction. The theoretical performance of these systems would be indistinguishable from that of a human. However, the broad intellectual capacities of AGI would exceed human capacities because of its ability to access and process huge data sets at incredible speeds.
This article is part of
What is enterprise AI? A complete guide for businesses
True AGI should be capable of executing human-level tasks and abilities that no existing computer can achieve. Today, AI can perform many tasks but not at the level of success that would categorize them as human or general intelligence.
An AGI system should have the following abilities and understanding:
- Abstract thinking.
- Background knowledge.
- Common sense.
- Cause and effect.
- Transfer learning.
Practical examples of AGI capabilities include the following five:
- Creativity. An AGI system would theoretically be able to read and comprehend human-generated code and improve it.
- Sensory perception. AGI would excel at color recognition, which is a subjective kind of perception. It would also be able to perceive depth and three dimensions in static images.
- Fine motor skills. An example of this includes grabbing a set of keys from a pocket, which involves a level of imaginative perception.
- Natural language understanding (NLU). The meaning of human language is highly context-dependent. AGI systems would possess a level of intuition that would enable NLU.
- Navigation. The existing Global Positioning System (GPS) can pinpoint a geographic location. Once fully developed, AGI would be able to project movement through physical spaces better than existing systems.
AI researchers also anticipate that AGI systems will possess higher-level capabilities, such as being able to do the following:
- Handle various types of learning and learning algorithms.
- Create fixed structures for all tasks.
- Understand symbol systems.
- Use different kinds of knowledge.
- Understand belief systems.
- Engage in metacognition and make use of metacognitive knowledge.
AGI vs. AI: What's the difference?
Existing artificial intelligence capabilities are referred to as narrow AI when compared with artificial general intelligence. AGI is theoretical, whereas narrow AI is in practical use today.
AGI should theoretically be able to perform any task that a human can and exhibit a range of intelligence in different areas without human intervention. Its performance should be as good as or better than humans at solving problems in most areas.
In contrast, weak AI excels at completing specific tasks or types of problems. Many existing AI systems use a combination of machine learning (ML), deep learning (a subset of machine learning), reinforcement learning and natural language processing (NLP) for self-improving and to solve specific types of problems. However, these technologies do not approach the cumulative ability of the human brain.
Examples of AI in use today include the following:
- Customer service chatbots.
- Voice assistants like Apple's Siri and Amazon's Alexa.
- Recommendation engines such as those Google, Netflix and Spotify use to promote content to users.
- AI-powered business analytics and business intelligence (BI) tools that conduct data analysis, gauge customer sentiment and present data visualizations for end users.
- Image and facial recognition applications as well as the deep learning models they use.
Examples of artificial general intelligence
True AGI systems are not on the market yet. However, examples exist of narrow artificial intelligence systems that approximate or even exceed human abilities in certain areas. Artificial intelligence research is focused on these systems and what might be possible with AGI in the future.
Here are some examples of those systems:
- IBM's Watson. Watson and other supercomputers are capable of calculations that the average computer can't handle. They combine their immense computing power with AI to carry out previously impossible science and engineering tasks, such as modeling the Big Bang theory of the birth of the universe or the human brain.
- Expert systems. These AI-based systems mimic human judgement. They can recommend medicine based on patient data and predict molecular structure, for example.
- Self-driving cars. These AI-guided vehicles recognize other vehicles, people and objects on the road and adhere to driving rules and regulations.
- ROSS Intelligence. ROSS is a legal expert system that is also called the AI attorney. It can mine data from about 1 billion text documents, analyze the information and provide precise responses to complicated questions in less than three seconds.
- AlphaGo. This is another example of narrow intelligence that excels at a specific type of problem solving. AlphaGo is a computer program that can play the board game Go. Go is a complex game that is difficult for humans to master. In 2016, AlphaGo beat the world champion Lee Sedol in a five-game match.
- Language model Generative Pre-trained Transformer. GPT-3 and GPT-4 are release versions of a program from OpenAI that can automatically generate human language. The technology is consistently able to emulate general human intelligence. In some cases, the text is indistinguishable from human output; however, the AI output is often flawed.
- Music AIs. Dadabots is an AI algorithm that, given a body of existing music, can generate a stream of its own approximation of that music.
If AGI were applied to some of the preceding examples, it could improve their functionality. For example, self-driving cars require a human to be present to handle decision-making in ambiguous situations. The same is true for music-making algorithms, language models and legal systems. These areas include tasks that AI can automate but also ones that require a higher level of abstraction and human intelligence.
What is the future of AGI?
Many experts conducting AI research are skeptical that AGI will ever be possible. Some question whether it is even desirable.
English theoretical physicist, cosmologist and author Stephen Hawking warned of the dangers of AGI in a 2014 interview with the British Broadcasting Corp. "The development of full artificial intelligence could spell the end of the human race," he said. "It would take off on its own and redesign itself at an ever-increasing rate. Humans, who are limited by slow biological evolution, couldn't compete and would be superseded."
Some AI experts expect the continued development of AGI. In an interview at the 2017 South by Southwest Conference, inventor and futurist Ray Kurzweil predicted computers will achieve human levels of intelligence by 2029. Kurzweil has also predicted that AI will improve at an exponential rate, leading to breakthroughs that enable it to operate at levels beyond human comprehension and control. This point of artificial superintelligence is referred to as the singularity. Artificial general intelligence is one of the types of AI that will contribute to the eventual development of artificial superintelligence.
In 2022, this vision came much closer to reality, fueled by developments in generative AI that took the world by storm. With the debut of ChatGPT in November 2022 and advent of other user-friendly generative AI interfaces, users worldwide have witnessed firsthand AI software that could understand human text prompts and answer questions on a seemingly limitless range of topics, albeit not always accurately. These generative AI models have demonstrated they can produce a vast array of content types, from poetry and product descriptions to code and synthetic data. Image generation systems like Dall-E are also upending the visual landscape, generating images that mimic famous artists' work or photographs, in addition to medical images, 3D models of objects, and videos.
For all their impressive capabilities, however, their flaws and dangers are well-known among users at this point, meaning they still fall short of fully autonomous AGI. Whether it is because of the propensity of such tools to generate inaccuracies and misinformation or their inability to access up-to-date information, human oversight is still needed to mitigate potential harm to society.
Other perspectives include the Church-Turing thesis, developed by Alan Turing and Alonzo Church in 1936, that supports the eventual development of AGI. It states that, given an infinite amount of time and memory, any problem can be solved using an algorithm. Which cognitive science algorithm that will be is up for debate. Some say neural networks show the most promise, while others believe in a combination of neural networks and rule-based systems.
Another potential initiative comes from neuroscience: neuromorphic computing, which uses artificial neurons and synapses to replicate the biological framework and functioning of the human brain.






