AI readiness: What is it, and is your business ready?
Artificial intelligence (AI) readiness encompasses all the elements, processes and steps needed to prepare an organization to implement AI systems. AI readiness isn't simply deciding to purchase an AI system for use. It involves cultural, business process, governance and technology changes to adjust to an AI-driven future.
AI readiness is important because AI systems, especially generative AI tools, are widely used in enterprise settings across various industries. To remain competitive, business leaders must take AI readiness seriously and understand how AI products add value.
To effectively use AI, business leaders must understand how AI tools can help optimize operations and boost revenue. They need insight into what tools will help their organizations, how they work and what's available to meet their needs. They also must consider the training required to educate workers and prepare them to use AI tools.
How does AI readiness work?
Eagerness to adopt AI technologies isn't the same as readiness. AI readiness involves several steps, starting with conducting an AI readiness assessment, identifying the tools that best fit an organization's needs, selecting the right tools and training staff to use them. A big part of AI readiness requires shifting the company culture toward accepting the digital transformation that comes with AI.
This article is part of
What is GenAI? Generative AI explained
For instance, an organization using older technology infrastructures might find it challenging to implement new AI tools that have specific technical requirements. Also, its workforce might be reluctant or fearful of the complexities that come with AI platforms and the disruption they cause. Achieving readiness means performing various technology upgrades, training workforces to use AI tools or learn new skills and managing these tools to prevent possible AI risks.
Why is AI readiness important?
Business leaders increasingly recognize the value of AI systems assisting with menial and time-consuming tasks. According to a 2024 McKinsey report, 72% of the nearly 1,400 business executives and managers surveyed said their organizations used AI for at least one business function. AI readiness helps these users create strategies for implementing AI systems in the short term and maintaining them in the long run.
An eagerness to explore AI capabilities, when coupled with an AI strategy, means an organization is positioned to implement and reap the benefits of AI. AI tools let organizations automate repetitive tasks so workers can focus on more innovative and creative tasks that grow a business. AI can also give a company an edge over market competitors. For example, AI and machine learning (ML) algorithms can quickly analyze data on customer behavior and preferences to provide insights on how to better meet customer needs.
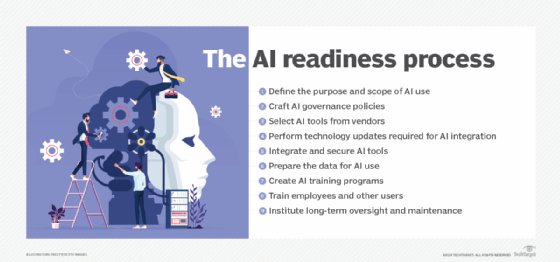
Foundations of AI readiness
Various aspects of an organization's IT infrastructure and overall approach to work must be considered when crafting an AI readiness strategy. They include the following:
- Purpose and scope. Before searching for AI tools, it's essential to understand which business processes require or benefit from AI and who in the workforce would use them.
- Technology infrastructures. Existing hardware and software must be examined to determine how AI tools would fit in and the ease of integration. For instance, an AI platform might require higher processing speeds, which means server and data center upgrades might be needed.
- Data collection methods and sources. Since AI tools are valuable for data analysis, the organization is responsible for generating and preparing reliable data for these tools to analyze.
- Workforce training. Employees undergo training to understand and navigate AI tools. Companies can create their own training programs or outsource that task to third parties.
- AI governance. Once an AI tool is implemented, AI governance frameworks or policies ensure that it's used as intended, prevent technical failures before they occur and ensure that AI use complies with regulations. This is also known as responsible AI.
Challenges facing companies wanting to achieve AI readiness
There are multiple challenges businesses face when assessing their AI readiness and selecting AI products, including the following:
- Complexities. AI technologies with advanced capabilities have steep learning curves for employees expected to use them.
- AI integration. AI technology providers typically list technical requirements that user organizations will need. If these requirements aren't met, new hardware parts or software might be required to seamlessly integrate with these products.
- Compliance. Laws and regulations that govern AI, particularly those enforcing data privacy, are evolving. Businesses must keep up with new rules and updates to existing regulations.
- Expertise. Business leaders might need to hire employees with skill sets for certain tasks, such as data scientists experienced in prepping data sets for AI and ML platforms.
- Costs. Smaller businesses might not be able to afford expensive AI tools.
- Employee reluctance. Employees might be hesitant to adopt new tools. It's essential to provide insight into how AI can help them do their jobs.
- Security. Threat actors target AI systems, particularly ones that use sensitive data. Various methods and controls are used to prevent cyberattacks.
Best practices to improve your organization's AI readiness
Before undertaking AI initiatives or implementing AI models and tools, organizations should take the following steps to prepare for the transition:
- Perform technology upgrades. Checking for outdated hardware and software should precede shopping for AI tools. Areas for optimization range from simple software updates to new hardware purchases.
- Assess data. Enough data should be collected to create data sets that AI tools can analyze. For example, databases with customer behavior and sales data can be combined to create a useful data set.
- Educate employees. Learning management systems and other resources can provide training programs for employees once AI projects or tools are fully implemented.
- Craft AI governance policies. Creating policies for employees to follow around AI and data prevents misuse of both. These policies also prove to stakeholders that AI use is legal and safe.
- Look for areas of process improvement. AI is adopted to improve specific processes, so examining workflows and processes individually will identify areas for improvement.
Future of AI's use in business
Various industries, including manufacturing, retail, e-commerce, finance and healthcare, already rely on AI and ML tools to handle repetitive tasks, gain insights from data and more easily meet customer needs.
In the future, AI will be used for a range of business functions and productivity innovations. For example, in healthcare, AI-powered chatbots already handle large volumes of patient interactions. They're expected to take on more tasks in the future, reducing wait times and preventing burnout among healthcare workers.
In adopting AI technology and tools, businesses will also have to navigate challenges, such as the following:
- Ongoing and new cyberattacks and other security issues.
- Safeguarding personal or sensitive data during AI use and retraining.
- Managing labor issues as AI role in operations displaces some workers.
- Complying with new AI governance laws that require responsible AI use.
Even as certain industries lag in AI adoption, others will continue using AI machinery and software for repetitive business processes. AI readiness is a principle that helps companies in all industries avoid AI implementation and maintenance issues before they occur.
An AI readiness assessment is a necessary first step in adopting artificial intelligence technology. Learn other elements required for an effective, long-term AI strategy.





