
What is artificial intelligence (AI) governance?
Artificial intelligence governance is the legal framework for ensuring AI and machine learning technologies are researched and developed with the goal of helping humanity adopt and use these systems in ethical and responsible ways. AI governance aims to close the gap that exists between accountability and ethics in technological advancement.
AI use is rapidly increasing across nearly all industries, including healthcare, transportation, retail, financial services, education and public safety. As a result, governance has taken on a significant role and is getting increased attention.
The main focus of AI governance is on AI -- in terms of how it relates to justice, data quality and autonomy. Overall, AI governance determines how much of daily life algorithms can shape and who monitors how AI functions. Some key areas governance addresses include the following:
- AI safety and misuse.
- Sectors appropriate for AI automation.
- Legal and institutional structures around AI use and technology.
- Control and access to personal data.
- Moral and ethical questions related to AI.
- AI bias.
Why is AI governance needed?
AI governance is necessary when machine learning algorithms are used to make decisions -- especially when those decisions can negatively affect humans. For example, AI governance determines how to best handle scenarios where AI-based decisions could be unjust or violate human rights. Machine learning biases, particularly in terms of racial profiling, can incorrectly identify basic information about users. This can result in unfairly denying individuals access to healthcare and loans, or misleading law enforcement in identifying criminal suspects.
This article is part of
What is enterprise AI? A complete guide for businesses
The rapid adoption of AI tools, systems and technologies in various industries has also raised concerns about AI ethics, transparency and compliance with other regulations -- such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Without proper governance, AI systems could pose risks such as biased decision-making, privacy violations and misuse of data. AI governance seeks to facilitate the constructive use of AI technologies while protecting user rights and preventing harm.
AI governance pillars
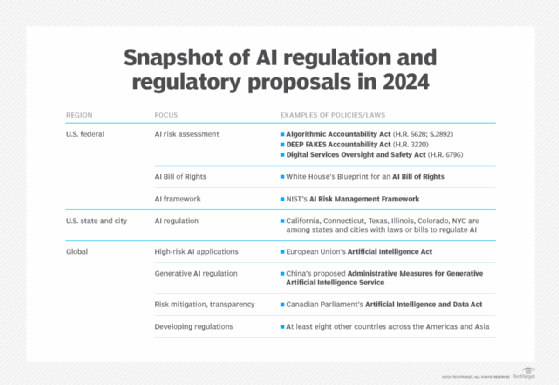
The White House's Office of Science and Technology has made a Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights that outlines a collection of five guiding principles and practices for the design, deployment and usage of AI systems. The goal of this blueprint is to help protect the rights of the American public regarding the use of AI. These principles include the following:
- Safe and effective systems. This principle states that AI systems should be thoroughly tested and monitored to ensure they are safe and function as intended -- and should not be designed in a way that can endanger individuals.
- Algorithmic discrimination protections. This principle states that AI systems should not exhibit any unfair discrimination based on race, color, ethnicity, sex, religion, age, nationality or other classifications protected by law.
- Data privacy. This principle states that individuals should have control over their data and should be protected against abusive data practices using built-in protections.
- Notice and explanation. This principle states that individuals should know when an AI or automated system is being used and should be informed on how it works.
- Human alternatives, consideration and fallback. This principle states that individuals should be able to opt out of using an AI or automated system in favor of a human alternative where appropriate.
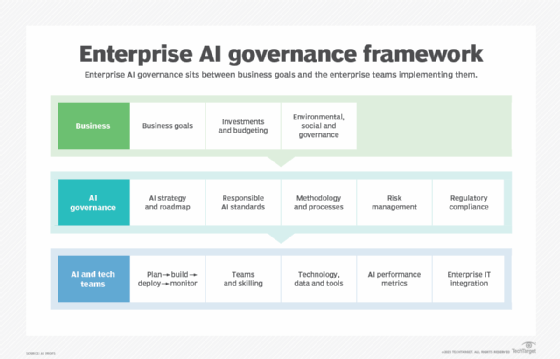
Some other components of a strong AI governance framework include the following:
- Innovation. Facilitating efforts in business and science to harness and optimize AI's benefits.
- Trustworthy AI. Ensuring AI is transparent and doesn't violate civil liberties, the rule of law or data privacy.
- Educating and training. Encouraging the use of AI to expand opportunities and access to new jobs, industries, innovation and education.
- Infrastructure. Focusing on expanding ethical access to data, models, computational infrastructure and other infrastructure elements.
- International cooperation. Promoting international collaboration and partnerships built on evidence-based approaches, analytical research and multistakeholder engagements.
- Decision-making and explainability. Explainability, or the ability to understand the reasons behind AI outcomes, is important for building trust and accountability.
- Regulatory compliance. Organizations must adhere to data privacy requirements, accuracy standards and storage restrictions to safeguard sensitive information. AI regulation helps protect user data and ensure responsible AI use.
- Risk management. AI governance ensures the responsible use of AI and effective risk management strategies, such as selecting appropriate training data sets, implementing cybersecurity measures, and addressing potential biases or errors in AI models.
- Stakeholder involvement. Engaging stakeholders, such as CEOs, data privacy officers and users, is vital for governing AI effectively. Stakeholders contribute to decision-making, provide oversight, and ensure AI technologies are developed and used responsibly over the course of their lifecycle.
How organizations should approach AI governance
There are many actions an organization can take to implement effective and sustainable AI governance practices. They include the following:
- AI culture. Everyone in an organization should feel that they have a role to play in AI governance. This process happens over time and requires training programs for employees so that a continuous learning culture can be formed around AI governance.
- Communication. In particular, employers should always communicate the risks of poorly governed AI systems with employees.
- AI governance committee. Forming an oversight and governance committee with members who have expertise in this area can ensure compliance with AI policies throughout an organization.
- Continual improvement. Collecting feedback from employees and customers using AI tools and systems enables an organization to continually improve its AI applications and products. Continually monitoring AI use and identifying and correcting problems are also important.
- Risk assessment. Third-party organizations that specialize in AI risk assessments and audits can provide an alternative perspective on how to improve AI use and governance and minimize the risks involved.
- Governance metrics. Using metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs) can validate whether an organization is adhering to AI governance policies. AI can degrade over time, so monitoring and managing these policies over time is also important. AI KPIs can be quantitative or qualitative, and should include those that measure provenance, veracity and quality of data, as well as data security, financial value and algorithm bias.
- Environmental impact. The process of training and continually running AI over time can have a massive impact on the environment. An organization should take note of and make every effort to mitigate its impact on the environment.
What is AI model governance?
AI model governance is a subset of AI governance that specifically entails how organizations should develop and use AI and machine learning models safely and responsibly. Organizations that develop and use these models must have the following considerations in mind:
- Model ownership. AI development typically involves teams of people working on a model. Tracking the work each team member completes is key to ensuring model success, improving collaboration and avoiding issues such as unnecessary duplications.
- Rules and regulations. Implementing a set of rules ensures aspects of model development -- such as data quality, feature engineering and documentation -- are free of errors and compliant with laws and regulations that mitigate AI-related risks.
- Data quality. Standards must be in place to ensure the quality and security of training data sets used to train AI models. Data must be accurate and unbiased so that the model learning from that data functions properly and produces the desired outputs.
- Continuous monitoring. Once a model passes into the postproduction phase, it must be continuously monitored to be sure it is working as intended. Model governance ensures there are steps in place to continuously train and monitor a model as needed.
The future of AI governance
The future of AI governance depends on collaboration among governments, organizations and stakeholders. Its success hinges on developing comprehensive AI policies and regulations that protect the public while fostering innovation. Complying with data governance rules and privacy regulations, as well as prioritizing safety, trustworthiness and transparency, are also important to the future of AI governance.
Various companies are focused on the future of AI governance. For instance, in 2022, Microsoft released version 2 of its "Responsible AI Standard," a guide for organizations managing AI risks and incorporating ethical AI governance into their strategies. Other companies that have committed to implementing governance standards and guardrails include Amazon, Anthropic, Google, IBM and Inflection.
U.S. government organizations working in this area include the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy's National Artificial Intelligence Initiative Office, which launched in 2021. The National Artificial Intelligence Advisory Committee was created in 2022 as part of the National AI Initiative to advise the president on AI-related issues. Also, in collaboration with both the public and private sector, the National Institute of Standards and Technology has developed a framework that recommends certain risk management approaches to those working with AI.
Some AI experts still insist that a gap exists in the legal framework of AI accountability and integrity, however. In March 2023, technology leaders and AI experts such as Elon Musk and Steve Wozniak signed an open letter urging a temporary halt to AI research and the codifying of legal regulations. In May, the CEO of OpenAI, Sam Altman, testified before Congress urging AI regulation. Elon
Musk and OpenAI have more recently, in 2024, found themselves in controversy for Musk's Grok generative AI's location, environmental impact and its operation on fewer ethical boundaries, while OpenAI has reportedly been putting profit over safety.
Other such companies have also been pushing the boundaries regarding AI governance. Adobe, for example, updated its terms of service in 2024 to allow the company access to user-generated content to train its machine learning software. After a large amount of backlash, Adobe backtracked and updated its terms of service agreement, pledging not to train its AI on user content.
As AI adoption continues to increase and the technology improves, companies are likely to continue to push ethical boundaries related to AI in their product offerings, and proper implementation of AI governance will become more and more relevant. This means the AI field will likely see more public calls for regulatory oversight. The White House's Blueprint for an AI Bill of Rights is a step in this direction, but it lacks concrete details on how each principle should be implemented and doesn't require organizations to follow it.
AI governance is the responsible regulation of artificial intelligence in the private and public sectors. Learn what businesses need to know about AI regulation.







