
Use ISO 22332 to improve business continuity plans
Standards offer guidance on business continuity and disaster recovery plans. ISO 22332 is no exception, providing great detail on how to prepare and execute a BC plan.
Organizations develop business continuity and disaster recovery plans in a variety of ways and formats. While existing standards provide guidance on plan frameworks and basic content, little has been done to explain what activities should be in each element of a BCDR plan.
In May 2021, ISO released ISO 22332:2021 Security and resilience -- Business continuity management systems -- Guidelines for developing business continuity plans and procedures to address this issue. The new standard is part of the ISO 223XX series of BC standards.
Structure of the ISO 22332 standard
The ISO 22332:2021 standard takes earlier standards, such as ISO 22301:2019 Security and resilience -- Business continuity management systems -- Requirements and ISO 22313:2020 Security and resilience -- Business continuity management systems -- Guidance on the use of ISO 22301, and expands on the details that go into BC plans.
ISO 22332 recommends organizations develop BC plans at three levels:
- A strategic plan provides a high-level view of the steps an organization must take during a disruptive event.
- A tactical plan covers the overall management and execution of the BC plan's response activities.
- An operational plan is based on department levels and is designed around specific business unit requirements, as found in a manufacturing facility or laboratory, along with various administrative departments.
The ISO 22332 standard also addresses components of a BC plan: procedures, or actions to be performed; guidance on documentation and document control; plan maintenance; awareness and training; and plan monitoring and review activities.
For example, Section 7 of the standard, "Content of business continuity plan and procedures," provides a basic outline of a BC plan, starting with purpose, objectives and assumptions. It then provides details on key activities addressed in a typical BC plan, including the following:
- activating and assembling a BC team;
- defining team roles;
- identifying tasks to be performed during the event;
- linking with other plans, such as technology DR plans;
- communicating with various players;
- standing down the plan;
- establishing contact information; and
- distributing the plan.
Other standards cover essential activities to prepare ISO BC plans, such as business impact analyses and risk analyses. A relatively new standard, ISO 22331:2018 Security and resilience -- Business continuity management systems -- Guidelines for business continuity strategy, explains which business strategies organizations must address when developing a BC plan.
Apply the ISO 22332 standard
The purpose of ISO 22332 is to identify activities that should be included in a plan, often in a logical sequence of occurrence. While organizations can enter these BC activities into a plan, the plan's author must develop the specific step-by-step procedures involved.
The standard provides a familiar structure for BC plans and, sometimes, groups certain activities -- such as managing the media -- into other activity buckets. It then becomes the plan author's job to decide if activities embedded in the standard need to be broken into separately defined actions.
Two special cases ISO 22332 addresses
The ISO 22332 standard includes guidance on two familiar disaster scenarios: pandemics and cyber attacks. Due to the ongoing impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and the rise in cyber and ransomware attacks, Section 8 of the standard provides steps for managing these two situations.
How the new standard relates to resilience
The framework in the following figure depicts how the ISO 22332 standard is positioned toward achieving organizational and operational resilience.
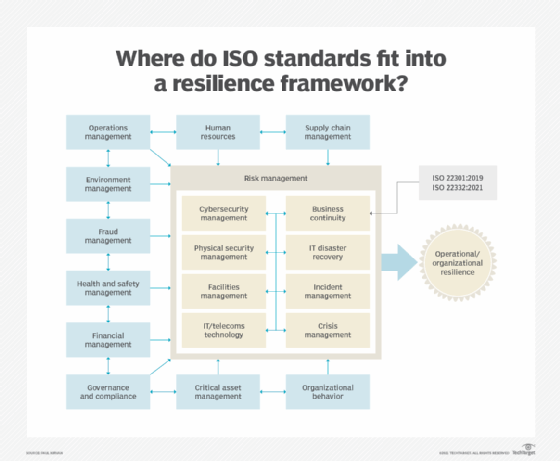
The standard identifies the activities an organization should perform to achieve the BC goals of response, recovery, resumption and restoration. Resilient organizations perform these activities to effectively adapt to and deal with disruptive events that could threaten business processes, people, technology and facilities.
How to achieve compliance with ISO 22332
The ISO 22301 standard is often used as a benchmark when auditing BC plans, as it identifies the many control activities that go into a BC plan. ISO 22332 provides additional information on a plan's internal content and structure and can be a supplementary control document when preparing a BC plan audit.
Organizations can also use ISO 22332 to assess an existing BC plan for content thoroughness. When using the two standards as part of an audit, use ISO 22301 for the basic audit structure and ISO 22332 for the details within each audit category.





