- Share this item with your network:
- Download
Storage
- Editor's letterPredictive storage analytics can watch your storage for you
- Cover storyInformation storage on the cloud is often the way to go nowadays
- InfographicSuccessful IT resiliency strategy based on high availability and DR
- FeatureStorage administrator skills and jobs in the age of convergence
- ColumnAutomated data management is a crucial part of IT's future
- ColumnPublic cloud workload success requires IT leadership
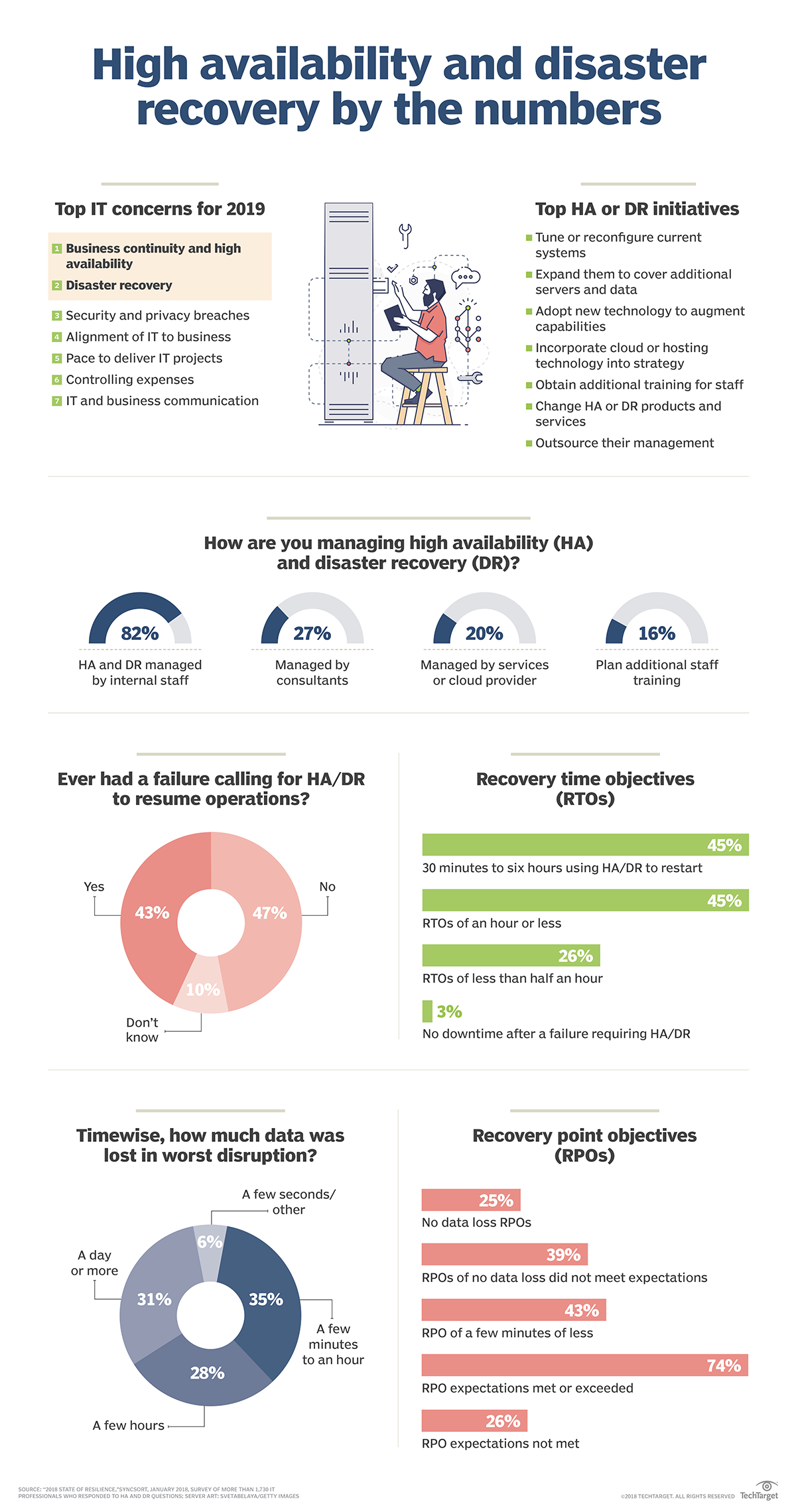
Successful IT resiliency strategy based on high availability and DR
Stringent yet realistic RTOs and RPOs are crucial to resiliency plans aiming to minimize interruptions to businesses operations should disaster or disruptions strike IT resources.Next to security, high availability along with disaster recovery are the most pressing IT initiatives for enterprises over the next 24 months, according to data integration and big data vendor Syncsort's "2018 State of Resilience" report. Businesses often measure HA relative to never failing or 100% operational or 99.999% availability. These criteria are difficult, if not impossible, to achieve. However, the goal for most companies is to get as close to these uptime targets as possible.
Disaster recovery planning and technologies help enterprises develop an IT resiliency strategy for increasing business continuity and maximizing HA. It achieves this by eliminating, or at least minimizing, the stress of an interruption to business operations by keeping data flowing and IT systems functioning in the face of a malfunction, whether it was caused by malfeasance, human error, natural disaster or some combination of the three.
Most enterprises use between one and three data protection technologies while more than 25% of them use four to six in the data protection component of their IT resiliency strategy. The larger the organization, the more data protection technologies used. So a tiny business with up to 10 employees uses about two data protection technologies for HA/DR and those with more than 1,000 employees need more than four. More than half of those surveyed deploy hardware-storage replication for data protection and archiving, with 45% tape backup and 40% software-logical replication. Thirty-five percent or so turn to snapshotting and clustering, and 20% to 30% use backup as a service, replication built into an application or hypervisor, disaster recovery as a service or a virtual tape library.
Forty-three percent of respondents experienced a failure that required them to implement their IT resiliency strategy through deployment of their HA/DR products, processes and services to resume operations. Roughly a third of them actually lost data: 35% up to an hour's worth, 28% for a few hours and 31% for at least a day. Reasons for data loss varied, but a lack of quality backup copies and operational issues led the way. Meanwhile, only about half of those affected by a disaster or total application or server failure actually met the recovery time objectives (RTOs) of their IT resiliency strategy, which were an hour or less for 45% and less than 30 minutes for 26% of those surveyed. Interestingly, while RTOs were off, nearly three quarters of enterprises met or exceeded recovery point objectives (RPOs) of their IT resiliency strategy.
Finally, 85% of those surveyed lacked confidence in their company's IT resiliency strategy and recovery plan. They felt it was incomplete and not tested thoroughly enough to fully meet RTO and RPO goals. However, 82% indicated their organizations had HA/DR initiatives planned for the coming year.