
.shock - Fotolia
What is the role of HCI in a disaster recovery architecture?
Is hyper-convergence a good fit for disaster recovery? More organizations appear to believe so and are increasingly using hyper-converged infrastructure in backup and DR.
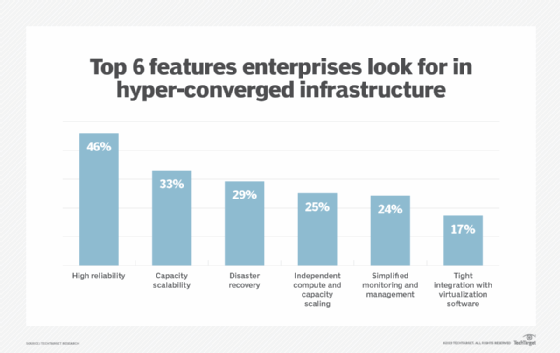
Backup and disaster recovery are two areas where hyper-convergence is playing a bigger role, and disaster recovery is a particularly interesting area of use. In a disaster recovery architecture, where speed and simplicity can be game-changing, hyper-convergence can make a big difference in recovery time.
What makes hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) well-suited to perform disaster recovery functions is that the systems come equipped with storage, compute and network resources. These systems are also usually equipped with a hypervisor.
This means that production systems can be replicated to the HCI setup on an ongoing basis, thereby creating replicas of production virtual machines. If the production infrastructure were to suffer a failure, the replica virtual machine could be brought online and hosted on the hyper-converged system.
There are several vendors who offer products that make this type of instant recovery possible in a disaster recovery architecture. Although the hyper-converged system could conceivably host the failover workload indefinitely, the systems are usually designed to perform a more conventional restoration in the background, thereby enabling the workload to transition back to its original location.
Although third-party backup vendors typically receive most of the attention with regard to using HCI as a disaster recovery tool, there are also native features in the Windows Server operating system that enable Windows Server to function as a hyper-converged cluster and that organizations can use in a disaster recovery architecture.
Most notably, Storage Spaces Direct enables Windows Servers to cluster together, with the cluster nodes using local storage rather than shared storage. This feature enables Windows Server to function as a hyper-converged system, but admins can enable disaster recovery through another Windows Server feature called Storage Replica. Windows replicates the contents of one Storage Spaces Direct cluster to a second cluster. This secondary cluster can exist on premises, in a remote data center or in the Azure cloud. If the primary cluster fails, the secondary cluster can be set to primary, and operations can resume.
In a disaster recovery architecture, flexibility, speed and reliability are of the utmost importance. The added support and streamlined nature of a hyper-converged system can offer a leg up during a failure.






