
Henrik Dolle - Fotolia
Data catalog comparison to help you choose your best fit
Data catalog options vary across vendors, but, as with most decisions in the data realm, it takes self-knowledge to make the right choice and understand each option's capabilities.
Data catalogs have become an essential part of an organization's data management strategy, but settling on a vendor can be a difficult decision. One must understand the different options in the market and what to prioritize before committing to a decision.
Data catalogs are metadata management tools that help organizations find and manage large amounts of data. The idea behind data catalogs is to centralize metadata in one location and provide a full view of your organization's data across databases. It also contains information about each specific data point's location.
Before approaching vendors, an organization needs an understanding of the market and what their needs and wants are. Use this data catalog comparison to help you choose what will work best with your organization's data.
Why data catalogs are essential
Data catalog tools come from the need for organizations to handle three factors, according to Joe Maguire, senior research director at Gartner.
The first driving force for data catalog adoption is that metadata management has gotten more difficult. Data architectures are more complex and data volumes have grown too large for manual approaches to collecting and describing metadata.
"Even technologies that purport to simplify architectures -- like data lakes, which offer a single architectural component for storage of all kinds of data -- can complicate metadata management," Maguire said.
While the amount of data grew, some organizations didn't scale up their metadata management.
"It was through the neglect of metadata in data lakes that forced people to coin the term 'data swamp' to describe a data lake whose data is unknown, poorly organized or misunderstood," Maguire said.
The second factor is that as organizations pursue self-service analytics and data science, the need for data governance increases. This has also led to a higher demand for data catalogs. Metadata is the oil of data governance and data catalogs allow for easier access to metadata.
The third factor is that the market has proved itself. Vendor offerings have become more diverse and are genuinely helpful to organizations that need data governance and metadata management. Features for automatic metadata discovery, data lineage and support for data stewardship activities make data catalogs attractive to enterprises.
Data catalog categories
The most important distinction when discussing data catalogs is understanding the differences between enterprise data catalogs and embedded data catalogs, according to Maguire.
"Enterprise data catalogs exist to consolidate metadata from various metadata silos," Maguire said. "Embedded data catalogs are sets of metadata management features that are provided within other products."
An enterprise data catalog option can be a DBMS, data warehouse or BI platform. Embedded data catalogs constitute the metadata silos that enterprise data catalogs work to consolidate.
Here's a data catalog comparison list of some of the most common options.
Standalone data catalogs. Generalist, independent and business-oriented, these data catalogs are for broader use in data management, analytics and data governance. This option is for an organization that has to catalog data for multiple use cases. Vendors that offer standalone data catalogs include Alation, Collibra, Informatica and Data.World.
Metadata management tools providing catalog capabilities. Modern data catalogs are aimed at data stewards and data analysts who can automate metadata management tasks. Gartner warned in a recent report on augmented data catalogs that, some vendors have rebranded their metadata management tools as data catalogs. Do your research to be sure you're investing in the proper tools.
Data lake enablement tools with data catalog capabilities. As organizations continue to build data lakes, they need to be searchable and the data reusable. This has led to an uptick in vendors including a data catalog aspect in their offering. Zaloni and Cloudera Navigator both fall into this category. Organizations daunted by the adoption of data lakes should look to these.
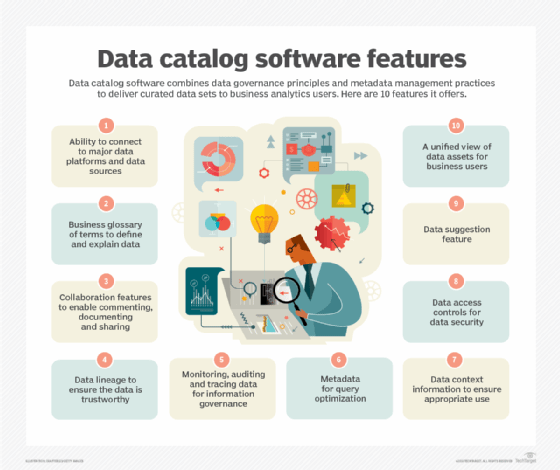
Once your organization has an understanding of whether or not an enterprise or embedded data catalog makes the most sense, you can move forward with finding features. A good data catalog should offer a number of features.
What should a good data catalog offer?
As an organization, it is up to your own team to decide which offering is the most relevant to your data. Data catalogs across vendors share certain common traits that must first be assessed on their quality.
A data catalog is only as useful as its ability to be searched. Without flexible search and filter options, users won't be able to find the data sets they need for data engineering and analytical purposes. A data catalog must also harvest metadata from a wide array of connected data assets. It must also offer automation and data intelligence to handle the manual tasks associated with data catalogs. AI and machine learning have the capability to augment data through recommendations.
A data catalog should have the ability to connect to various components of your data architecture within an organization. Maguire said an enterprise data catalog can be thought of as a data warehouse for metadata. A data catalog consolidates metadata from metadata siloes similar to how data warehouses consolidate data from data silos.
A data catalog lives and dies on its ability to provide connectors that can harvest metadata from various components such as a DBMS, BI tools and data warehouses. Data catalogs support various forms of metadata in these four types:
- Technical metadata describes data models, storage schemas, file layouts and APIs.
- Operational metadata describes data lineage, performance and log file output by various operations on data.
- Business metadata falls into two categories. One is metadata describing the business, such as the contents of the business data glossary. The other describes how business role players -- e.g., data stewards, data custodians, self-service analysts -- interact with data assets, as in which data steward is responsible for a particular data asset.
- Social metadata constitutes knowledge such as certifications or endorsements of certain data assets or other user-generated annotations on items in the data catalog.
Common vendors
There are numerous options in the market for both enterprise and embedded data catalogs, and these options often have similar features and overlapping capabilities. Here is a short data catalog comparison of top options.
Alation Data Catalog. Alation is a standalone data catalog tool that uses AI to capture the context of data within your organization. It is regarded as an easy-to-use option for all employees.
Qlik Catalog. Qlik's data catalog also has automated data preparation and metadata tools to assist in the transformation of raw data. It also has a data marketplace that permits users to search for and publish data sets.
Cloudera Data Catalog. Cloudera's data catalog allows users to discover, document and monitor their data. At the same time this offering allows users to audit access and protect sensitive information from those who shouldn't see it.
Collibra Catalog. This option is another standalone data catalog that has been built with business end-users in mind. It is a searchable repository, which makes locating and understanding data easier. It also allows administrators to document roles and responsibilities.
IBM Watson Knowledge Catalog. This is an open and intelligent data catalog for artificial intelligence model governance as well as data. This option offers users real-time data virtualization support, dynamic data masking and automated metadata generation.
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure. Oracle's offering has a search and explore option that allows users to find data from a variety of different sources through multifaceted search and filters and harvest technical metadata about data assets.








