Illustrated history of the converged data center
Data center convergence emerged as an alternative to the traditional data center and it continues to evolve. Learn more about CI, HCI and composable infrastructure in this infographic.
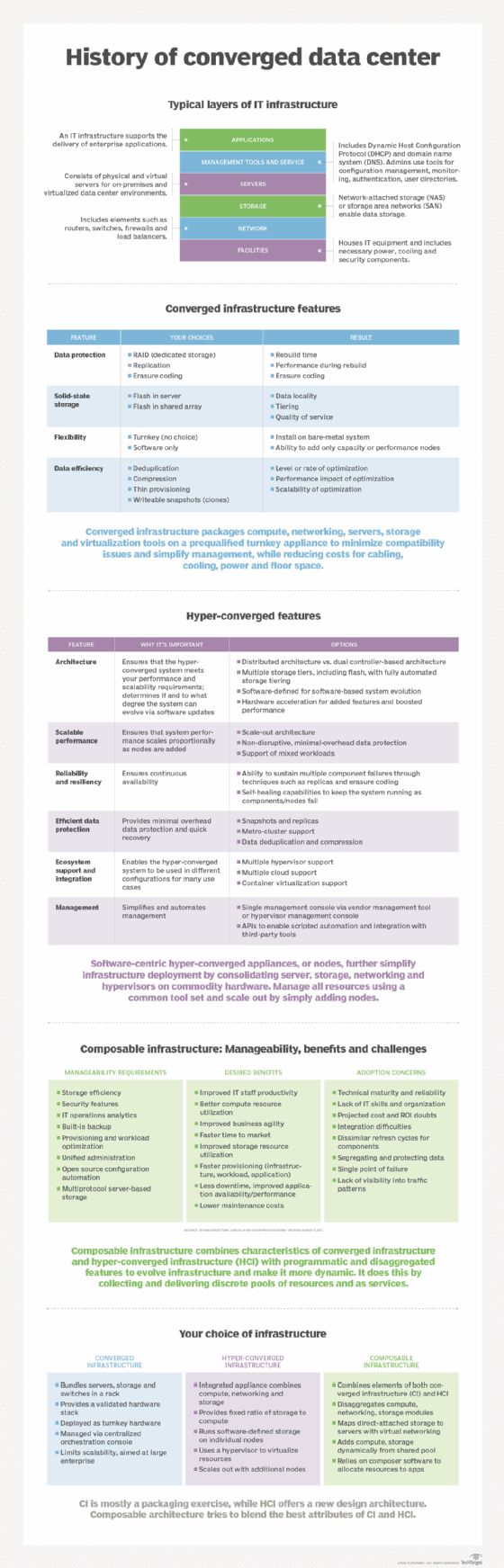
Today's heterogeneous traditional IT infrastructure requires tremendous cost, complexity and effort when it comes to integrating, optimizing and managing servers, storage, network and other data center components, often from diverse vendors. This led to the development of the converged data center with the appearance of modern converged infrastructure over a decade ago.
Individual vendors started packaging components into homogenous prequalified turnkey appliances to reduce compatibility problems and ease management. Convergence evolved into hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI), which further simplified things by consolidating compute, storage and network resources and hypervisors into software-defined and easily managed, highly scalable nodes. New kid on the block, composable infrastructure, takes the converged data center in a different direction.
Unlike converged infrastructure (CI) and HCI, composable disaggregates rather than integrates resources across infrastructures. It then collects them into discreet compute, storage and network pools, for example, which users can dynamically draw upon to address the specific requirements applications, workloads and uses.
There's overlap between the various infrastructure options available today, and each has its strengths and weaknesses. Which you choose, or which combination you go with, depends on a number of factors (spending, staff, space, etc.) particular to your organization.