data center capacity planning
What is data center capacity planning, simply explained?
Data center capacity planning is the establishment of a strategy that ensures an IT organization's computing resources, power load, footprint and cooling capacity will be able to meet the workload demands of its users and customers.
Why is capacity planning important?
Data centers are limited in terms of footprint, power consumption and cooling capacity. While redundant backup power and fault-tolerant server clusters can potentially increase uptime, they can also reduce the total available power capacity.
Planning too much capacity for the given workloads wastes capital expenditures and might draw power to idle, unused servers. Over-provisioning computer room air conditioners also results in below optimal efficiency operation.
Under-planning capacity is also a big problem, because it can debilitate business operations. Without adequate power and cooling for the data center's workload, outages are more common. Without enough computing, network and storage capacity, applications encounter bottlenecks and potentially stop working or take too long to ramp up new applications.
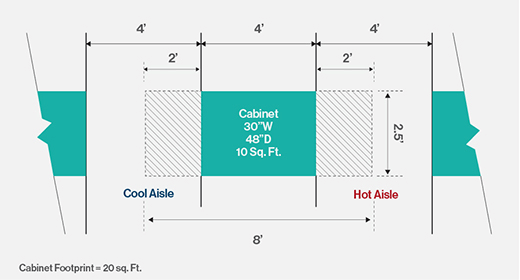
How does capacity planning work?
IT organizations should start capacity planning with agreed-upon service performance metrics, such as storing data for X amount of days, and running applications with a response time of X. To be effective, the capacity planning process requires sophisticated load calculations both at normal and peak performance times. To determine optimal capacity, IT organizations can benchmark operations with either simulated or real load testing, trend analysis or modeling using tools designed for this purpose.
Capacity planning software tools can help the administrator calculate the resources and power draw that a data center must support, given current and projected future operations. Such tools range from simple spreadsheets to 3D renderings of the data center with automated asset discovery and documentation. Some sophisticated capacity management tools will even suggest outsourcing options when major power, space and cooling upgrades to the physical site are cost or time prohibitive.
Virtualization, which allows data center managers to consolidate servers by stacking multiple workloads onto one physical server and powering off others, should also be considered in data center capacity planning. With virtualization and cloud computing, companies can plan for more flexible capacity that scales up and down without one-to-one investments in power or IT systems. For example, the retail organization can scale up on hosted cloud servers in Q4, keeping its data center build appropriate to normal demand. To handle a temporary spike in transactions during a large sale, the retailer can increase server utilization via virtualization. This requires applications to be designed for agility across platforms and management tools that can oversee multiple infrastructures.
Who is responsible for data center capacity planning?
It is usually the data center manager or IT director's responsibility to chart a capacity plan and determine what strategy will accomodate business needs best. IT service management frameworks like ITIL provide the planner with detailed recommendations for capacity management.






