Energy Star
What is Energy Star?
Energy Star is a government-backed labeling program that helps people and organizations save money and reduce greenhouse gas emissions by identifying factories, office equipment, home appliances and electronics that have superior energy efficiency. In recent years, Energy Star ratings have been extended to new homes, as well as commercial and industrial facilities.
Energy Star origins
Energy Star originated in 1992 as a joint program of the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the U.S. Department of Energy. In 2007, the European Union adapted Energy Star, including related standards, for all its members. Australia and New Zealand have also adopted the program. Today, Energy Star is an international symbol for energy efficiency.

Any building or product that has received an Energy Star rating carries a blue logo that includes the word energy in scripted text, a star and an arc.
How Energy Star works
Energy Star is a voluntary labeling system, though most manufacturers find it commercially desirable to display the logo if their products qualify. The standards themselves, however, are set by governmental agencies. Energy Star labels are only awarded to homes independently verified to be at least 15% more efficient than the standard mandated by the relevant state or local energy codes.
Computers were among the first devices to get Energy Star ratings. In general, computer energy consumption can be reduced in two ways: by using components that require less power or by using power management software to modulate the energy consumption of these components.
Energy Star ratings are available for desktop computers, laptops, workstations and gaming consoles.
For any PC shipped through enterprise channels to receive an Energy Star rating, however, it must specifically do the following:
- Ship with an automatic sleep mode set to activate in 15 minutes.
- Automatically disable Wake on LAN enabled from sleep mode while on alternating current power.
- Maintain network connectivity while in sleep mode.
- Require between 65 and 95 watts of power, depending on its classification.
Energy Star provides online assessment tools that enable businesses and consumers to rate the efficiency of homes and industrial facilities. Energy Star ratings have become an important component of buying decisions for consumers and businesses. More efficient buildings, appliances and hardware can mean significant savings over time on heating or power costs.
Energy Star in data centers
A new specification for desktop computers emerged in 2007.
Version 4.0 mandated higher standards than the previous iteration, requiring 80% or greater power supply efficiency for the Energy Star label. This 80% efficiency standard is the subject of advocacy efforts by 80 PLUS, an electric utility-funded incentive program that encourages the integration of energy-efficient power supplies into desktop computers and servers.
According to the Energy Star website: "The 80 PLUS performance specification requires power supplies in computers and servers to be 80% or greater energy-efficient at 20%, 50% and 100% of rated load with a true power factor of 0.9 or greater. This makes an 80 PLUS-certified power supply substantially more efficient than typical power supplies." Six different 80 PLUS rating levels are available: Standard, Bronze, Silver, Gold, Platinum and Titanium.
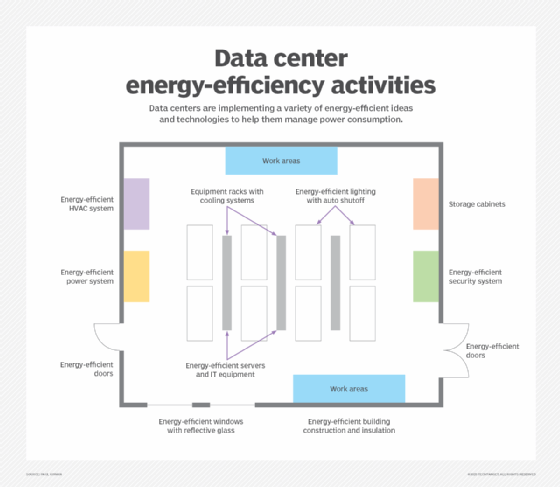
This figure depicts a data center showing the many different ways energy-efficient -- and Energy Star-certified -- devices and building elements can be deployed.
Pros and cons of Energy Star
The EPA estimated that, if every U.S. household and business replaced old computers with new Energy Star-qualified models, more than $1.8 billion in energy costs would be saved over the subsequent five years, avoiding greenhouse gas emissions equivalent to more than those produced by 2.7 million cars. Similarly, Energy Star-qualified fluorescent bulbs consume up to 75% less energy than standard incandescent bulbs, while providing the same amount of light and lasting up to 10 times longer.
Energy Star-rated appliances, such as washers, dryers, refrigerators, dishwashers and air conditioners, can reduce annual electricity costs as well.
Adoption of energy-efficient practices are an important component of the green computing movement, both in terms of lower operating costs and reduced pressure on the energy grid. This ultimately reduces, if not halts, the growth in greenhouse gases emitted by fossil fuel-based energy plants. These gases, according to recent reports from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, are the major component in the rapid warming of the Earth over the past century, a development widely considered to be potentially dangerous to both humans and ecosystems worldwide.
Businesses seeking guidance on green computing best practices can find it from sustainability consultants, who work to make energy conservation and efficiency an integral part of corporate culture.
The upfront cost for Energy Star products may be higher than similar nonrated units, but the energy savings anticipated over time from lower energy bills can offset the added cost. Another important benefit of Energy Star equipment is the potential tax credits available from using energy-efficient products in homes and businesses.
The future of Energy Star
Advances in technology such as artificial intelligence (AI) and the internet of things (IoT) present new opportunities to take the Energy Star rating system to new levels. Consider the benefits that could accrue from installation of IoT sensors in commercial buildings or data centers, capturing energy data from all kinds of systems and sending the data to a system with AI that can make decisions regarding how energy can be used and possibly even actively managing energy use. The technology can potentially identify devices that are experiencing problems or failing. Smart thermostats and lighting systems can also have an AI link to better manage energy usage and protect the environment more efficiently.
Check out eight green computing best practices, and see how to improve efficiency with server energy consumption tools.






