
rvlsoft - Fotolia
Overcome common cloud backup security issues in remote work
Your cloud backup and storage usage may be on the rise. Make sure you take the necessary security precautions detailed here to keep your data protected.
Cloud-hosted backup products -- including backup of data in the cloud and cloud-hosted backup software -- are seeing a surge in popularity as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. However, longstanding cloud backup security issues remain.
These issues are compounded because people are more frequently accessing data from less secure personal devices as they operate remotely.
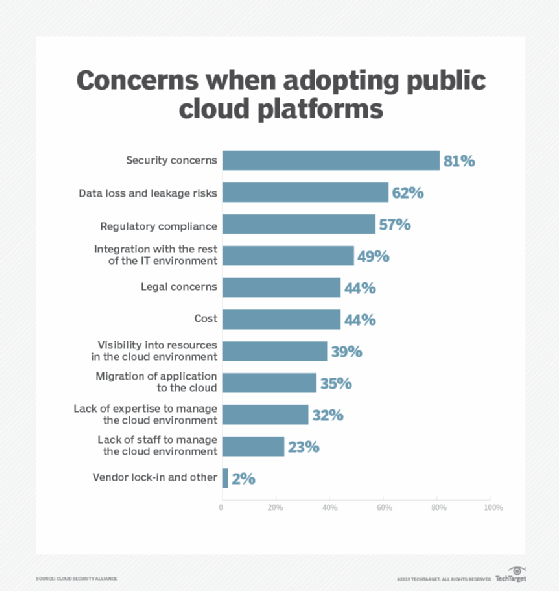
Inherent security of the cloud
The inherent security of cloud storage has been in question for as long as the cloud has been around. Some enterprises remain deterred from using the cloud for this reason. With this problem acknowledged, cloud storage and cloud backup providers have introduced capabilities to better prevent against cyberattacks.
Like with on-premises data, write once read many compliance and immutability are important features to look for in cloud backup security, in order to guard against ransomware and malicious or accidental deletion. Once written, immutable data cannot be changed or deleted for a predetermined length of time, which, in some cases, is forever. IT professionals should consider features like Amazon S3 Object Lock and Azure Blob immutable storage when considering their cloud backup service.
Many enterprise IT professionals are familiar with air-gapped tape systems, and a similar concept applies in the cloud. Isolate backup data in a separate account or location -- as opposed to just a different storage bucket -- so that it cannot be accessed with the same credentials.
To avoid bad actors from accessing the data to begin with, providers have baked in multifactor authentication features, role-based access control, multi-tenancy, encryption of data at rest and in flight, and encryption key management.
Control over data
Giving up direct control over data is a notable concern associated with cloud backup security, especially in today's compliance-heavy landscape. Furthermore, inconsistency between cloud providers opens security gaps and risks compliance issues.
Standards such as the Federal Information Processing Standards and regulations like the European Union's GDPR guide how cloud providers handle customers' data. IT professionals should look for appropriate certifications from their cloud providers and understand how their provider addresses applicable regulations.
General support and monitoring for suspicious activity
Ongoing testing of backups and planning for recovery are established best practices that carry through to cloud backup security. Typically, cloud backup products take this a step further, providing general support like upgrades and patching that help to shore up security vulnerabilities.
IT professionals should also consider cloud providers that monitor for and use analytics to identify suspicious activity, such as bandwidth spikes and anomalous user behavior like large volumes of files being duplicated. These are leading indicators that a ransomware or other security attack is underway, and picking up on them as soon as possible can help to reduce or avoid both downtime and data loss.
The cloud offers several potential advantages when it comes to meeting protection requirements, especially in today's era of remote connectivity and heavy cyberthreat activity. To determine an appropriate fit, organizations should closely evaluate backup products hosted in the cloud. They should particularly assess offerings from the standpoints of cloud backup security capabilities such as immutability, data governance, and analytics and monitoring.








