How to conduct a data privacy audit, step by step
The vital importance of a data privacy audit can't be underestimated in today's climate of proliferating customer data, more stringent regulations and sophisticated cyber threats.
Businesses are entrusted with an ever-expanding trove of personal information in today's digital ecosystem, emphasizing the importance of navigating the intricate landscape of data privacy and the critical role of a data privacy audit.
What is a data privacy audit?
A data privacy audit is a comprehensive review process undertaken by an organization to assess its handling of personal information. It requires scrutinizing the data collected, the means of processing the data and the security measures in place to protect it. The audit's scope typically encompasses policies, procedures and practices to ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations, such as the GDPR and CCPA.
Why is a data privacy audit important?
For enterprises, data privacy audits are not a mere formality. They're the linchpin of maintaining the integrity of the company's operations and reputation. Audits serve as an internal check to safeguard customer data, preempt data breaches and ensure adherence to data protection standards. Moreover, they provide a framework for a data protection officer to guide data management and security measures effectively.
How to conduct a data privacy audit
Embarking on a data privacy audit can seem daunting, but a structured approach can simplify the process. The following steps address IT and broader business perspectives as well as recent developments reshaping audit protocols.
1. Prepare for the audit
Before diving into an audit, appoint a cross-functional team led by a chief data protection officer or someone in a similar position to steer the process. Secure management's support and establish clear objectives for the audit, keeping in mind the legal and regulatory requirements pertinent to the company's industry and locales of operation. Assume such reports are likely to go to the company board, so plan appropriately.
2. Map company data flows
Create an inventory of all data processing activities. Understand where data originates, how it flows through the organization, where it's stored and how it's disposed of. A data protection impact assessment is typically included to identify the risks associated with data processing.
3. Evaluate compliance procedures
Assess current data protection practices against relevant privacy laws like GDPR and any sector-specific regulations. Review consent mechanisms, data subject rights fulfillment processes and data breach response plans. Data loss prevention tools can identify critical data leaks.
4. Analyze gaps
Identify discrepancies between current practices and legal/regulatory requirements. Pay particular attention to security measures, data accuracy and storage limitations. Some regulations have changed what types of data companies need to retain, so examine the data retention policy as well as the length of retention rates.
5. Assess risks
Conduct a risk assessment to gauge the potential impact of identified gaps on personal information security. Prioritize risks based on their severity and likelihood of occurrence by plotting a graph showing the likelihood of occurrence on one axis and the impact on the business on the other axis.
6. Plan for remediations
Develop a plan to address identified risks and compliance gaps, including timelines, responsible parties and required resources. Based on the information obtained from the risk assessment, create quadrants on the graph to prioritize the risks and actions to be taken. Each quadrant constitutes a different approach to how risk should be mitigated. If the likelihood of occurrence is low and the impact on the business is minimal, for example, then these actions are considered the lowest priority and little needs to be done. If likelihood is high but impact low, then perhaps education and awareness should be focused on personal responsibility. If likelihood is low but impact high, then the best approach might be to invest in insurance that covers these types of exceptional circumstances. Greatest overall priority should be placed on factors where the likelihood of occurrence and impact on the business are high. Unfortunately, an increasing number of situations are moving into this area, especially with the advent of generative AI, machine learning and automation, which can assist the business as well as the criminals.
7. Execute the remediation plan
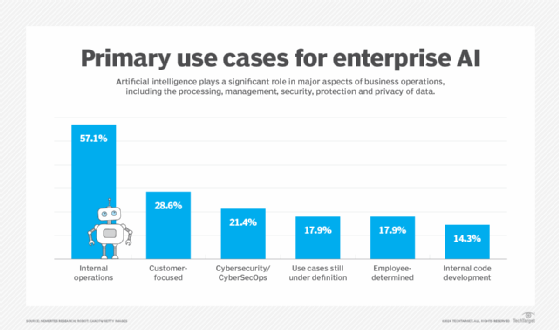
Update policies, enhance security measures and train staff as needed. Artificial intelligence is becoming an increasingly major part of enterprise security measures. Cybersecurity ranks among the top applications of AI in enterprises.
8. Document and follow-up
Document all findings, the actions taken and any ongoing concerns. Set a schedule for regular audits to ensure continuous compliance and improvement. Conduct audits at least annually, but considering the exponential increase in the frequency and types of cyber threats, audits should be conducted as often as quarterly.
Beyond the Basics
Incorporating these steps into regular business practices not only ensures compliance with the GDPR, CCPA and other regulations, but also builds trust with customers, who are increasingly concerned about their personal information. In addition to the step-by-step approach, businesses should maintain an ongoing dialogue about data privacy and encourage a culture of transparency and accountability. Statistics indicate that proactive data management and security measures significantly reduce the risk and impact of data breaches.
As business environments become more complex with the adoption of IaaS/PaaS platforms and cloud services, the role of data privacy audits becomes even more paramount. When looking at third-party services, consider how service providers comply with regulations and assist businesses in their compliance efforts.
Factors influencing data privacy audits
The data privacy landscape is evolving rapidly due to a whole host of factors, including AI, generative AI, more stringent regulatory enforcement and fines, the proliferation of new or updated regional, state and local laws, and more prevalent and sophisticated data security threats.
Artificial Intelligence and generative AI. AI technologies are raising new ethical and privacy concerns, requiring enhanced scrutiny of algorithms and data processing practices. As critical as these technologies are to improving data security, the very same tools make it easier for cybercriminals to increase the scope and impact of their attacks.
Regulatory enforcement. There's a global trend toward stronger enforcement and heftier fines for data protection violations. Newer regulations are changing data retention policies in terms of what needs to be retained and for how long. Companies should conduct regular reviews of these policies.
Emerging legislation. Businesses must adapt to new and updated laws, including the proliferation of state and local regulations. This trend is especially daunting for international companies due to significant differences among these laws, depending on type of business and geographical location.
Data security threats. The sophistication of cyber threats mandates more robust security measures and continuous monitoring. Numerous security products and services can provide security monitoring and generate reports that comply with various industry audits. Products and services that adhere to ongoing privacy regulations can help ensure a business is complying with the latest regulatory guidance.
Jerald Murphy is senior vice president of research and consulting at Nemertes Research. He has more than three decades of technology experience, including neural networking research, integrated circuit design, computer programming, global data center designing and CEO of a managed services company.








