
Getty Images/iStockphoto
10 e-commerce marketing strategies for your business
Marketers have myriad tools in their belts -- from SEO to influencers to technology and tools. These strategies can improve anyone's e-commerce marketing plan.
Without a clear e-commerce marketing strategy, organizations could face significant challenges as consumer behaviors change.
E-commerce sales boomed in 2020 and beyond due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Since then, online shopping has continued to grow, as have competitors and changing demands from customers. If organizations invest time and resources into e-commerce marketing strategies, they can help establish, increase and retain their customer bases.
E-commerce marketing strategies involve promotional tactics to drive traffic to an online store. A well-thought-out marketing plan, coupled with an engaging website, can convert visitors into paying customers, help businesses retain them and increase their overall Customer lifetime value (CLV). If marketing teams stay up to date on the latest trends, they can help the organization reach and retain new customers.
These 10 e-commerce marketing strategies can help set an organization apart from its competition, strengthen the brand, attract new customers and increase sales over time.
1. Search engine optimization
Launching a website is a win for any e-commerce company, but websites aren't enough for consumers to easily find the brand. To improve visibility, marketing teams must optimize websites for search engines. Positive search engine optimization (SEO) requires marketing teams to continually update websites with rich and relevant content that provides useful information for customers.
An SEO strategy can help organizations ensure their content shows up on search engine results pages (SERPs) for relevant queries and deliver positive CX when customers find the information they need. Marketing teams should use SEO keywords and phrases organically within content to alert search engines to the site's relevance for those queries.
Marketing teams should also use easy-to-read URLs and descriptive page names that contain a primary keyword. These URLs and names can also include familiar words or phrases that customers likely use as they search. This strategy requires keyword research to identify opportunities for new content.

2. Content marketing
To support SEO and build brand authority, marketing teams should embrace content marketing in their e-commerce marketing strategies.
For example, a blog can help build a successful marketing strategy and enable brands to produce relevant content about their products. Blogs let marketing teams target important keywords that might not fit naturally on product or category pages. This content can speak directly to consumer needs, offer helpful solutions, build trust and strengthen relationships. Overall, blogs can lead to increased brand visibility and higher conversion rates from new and existing customers.
Content marketing helps answer customers' questions, educate them, deliver the company narrative and lead people to make a purchase. Additionally, different content types, like video, downloadable guides and user-generated content, can strengthen a brand's reputation. This content can also feed the blog and bring more eyes to the organization and its offerings.
3. Social media marketing
In addition to strong SEO that helps content show up on SERPs, brands should meet consumers where they are: on social media. These channels can help engage an active audience.
Billions of people use social media each month, and social media can help brands create authentic connections with their followers. On social media platforms, marketing teams can also respond to comments, publish relevant content and provide more information about their company's products.
Marketing teams should select the right platforms to manage and distribute this content. For example, people on Twitter want to see different content than people on Instagram. Marketing teams should know which platforms the customer base is most likely to use and align the channel they use with them.
4. Email marketing
Email marketing can also let prospects and customers know about new products or information. If marketing teams provide timely and relevant information through this channel, they can inform new and existing customers of sales, new product releases and new blog content.
Personalized email communications have lasting benefits in customer retention and repeat purchases. If marketing teams show they understand a buyer's purchase or browsing history through personalized communications, they can establish a strong and loyal customer base.
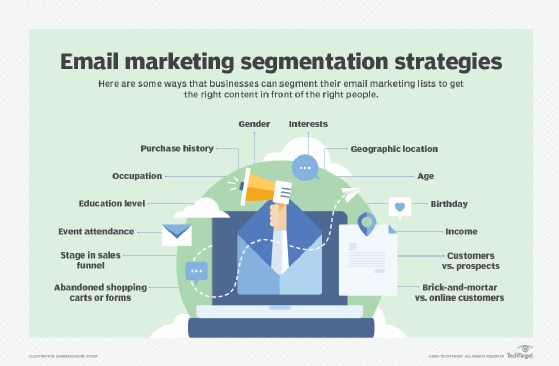
5. Customer loyalty programs
Customer loyalty programs can help increase revenue and retain customers over time. Loyal customers are highly valuable because they have already made purchases. If marketing teams incentivize loyalty and repeat purchases, they can increase CLV and create strong brand advocates.
Marketing teams have various types of loyalty programs to choose among, but programs that are consistent and add value to the consumer often succeed the most. Loyalty programs also have strong personalization opportunities, as they can collect more information about consumers and insights into the best times to trigger communications to these individuals.
Additionally, loyalty programs can provide special offers, discounts and birthday wishes to strengthen the relationship between business and consumer.
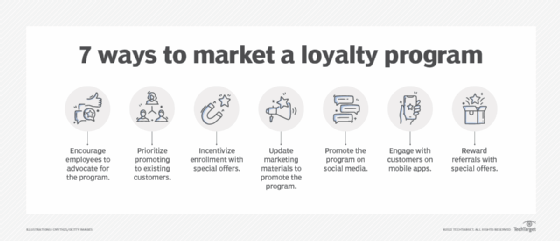
6. Optimized product pages and checkout experiences
An e-commerce website includes category and product pages. However, optimizing the product pages can help with conversion rate optimization. These pages should make it easy for visitors to see the product, learn about its specifications or features and make a purchase.
Product marketers can evaluate which pages to optimize for conversion based on analytics data to see where sales come from or where sales are lost. These teams should also optimize the checkout experience for ease of use and reduce the number of steps it takes for someone to complete their purchase.
7. Pay-per-click advertising
Some e-commerce marketing strategies have a lower cost associated with implementation, but sometimes, brands need to pay to get their products and services in front of consumers. Pay-per-click (PPC) strategies can ensure that product pages are at the top of SERPs in the form of ads.
Good PPC campaigns contain an ad, offer and landing page. This approach can support SEO efforts and let businesses use marketing budgets to get offers in front of consumers. Marketing teams can deploy search and display campaigns within search engines or within their support ad networks. Within ad networks, these campaigns can follow users to other sites they visit and increase visibility to products and offers. Additionally, marketing teams can use paid advertising strategies on social media platforms.
8. Retargeting
Building off a PPC strategy, a retargeting strategy is another paid approach to get people to revisit a website they already visited and expressed interest in. While PPC can bring new eyes to a website, retargeting tracks people who already visited a page but left without making a purchase.
Brands can build different audience lists based on website pages viewed. If someone comes to an e-commerce site and views various product pages, representing an interest in those items, brands can deploy relevant ads on other websites within the brand's ad networks. These ads can drive users to the specific product pages they visited before and reinforce that they should buy the product.
9. Influencer marketing
Influencer marketing is a growing strategy among brands that want to tap into a specific audience through someone the community trusts already. Influencers exist in all different types of markets and industries. From tech review blogs and YouTube channels to lifestyle products and TikTok channels, brands that use influencers can reach their followers.
In particular, this approach can benefit organizations releasing new products. Companies can send influencers free products in exchange for reviews, promotions, a third-party perspective on the product and an increased reach for the brand. While organizations can engage with influencers in many ways, they often include product or sponsorship costs depending on the influencer's terms.
Marketing teams should consider influencer marketing as a strong channel for an e-commerce marketing strategy, as it involves positive relationships with influencers and ensures they can provide a positive review or promotion for the products.
10. SMS marketing
SMS texting is a resurging and growing channel for e-commerce marketing strategies. While the mix of strategies includes creating relevant content, sending emails and promoting through paid channels, social media or influencers, marketing teams can't ignore that consumers are on their phones most often.
Brands that want to take advantage of an SMS marketing strategy can collect phone number details from consumers and send frequent and timely offers to both prospects and customers.
Online shopping retailers are currently some of the most successful businesses that uses SMS marketing. This approach offers cross-sell and upsell opportunities and abandoned cart recovery, and it can also provide exclusive offers or promotions to drive increased sales.





