
putilov_denis - stock.adobe.com
How to use generative AI for marketing
Organizations can use generative AI to write marketing content and analyze customer data quicker than a human. However, the tools require basic prompt engineering skills.
Generative AI doesn't replace human creativity in marketing, but it can enhance it.
Shortly after OpenAI launched ChatGPT in November 2022, professionals in many industries took an interest in GenAI. These tools run on foundational models, such as large language models (LLMs), which developers train on massive data sets. Marketers can use the technology to automate creative tasks, such as generating copy, video and surveys. However, GenAI's most transformational marketing use cases relate to analytics, said Liz Miller, vice president and principal analyst at Constellation Research.
This article explores the evolution of GenAI in marketing, key use cases and risks to avoid.
The evolution of GenAI in marketing
GenAI has been a strategic priority for marketing leaders ever since its widespread emergence in late 2022. The technology's ability to generate creative content, personalize customer experiences and automate routine tasks has all the ingredients to transform marketing. However, in the initial months after GenAI's emergence, many chief marketing officers didn't know where to start.
Marketing leaders saw two main pathways: Use a generic, public model -- like ChatGPT -- and edit the output heavily, or build and train their own models, Miller said. Yet, this binary view of adoption became more nuanced over time as marketing leaders realized models vary widely in how they're built, what data they're trained on and what they're best suited to do. For example, some GenAI tools excel at summarization, whereas others are better at reasoning, creativity or industry-specific tasks.
 Liz Miller
Liz Miller
"Not all artists use a single color, and not all artists use a single paint brush, and that's really where we are with these AI models. It's like opening a giant toolbox and seeing all the tools in there," Miller said.
Marketing teams are experiencing some excitement as they experiment with GenAI use cases. But many teams are just starting to learn which tools and training data work best for certain tasks. To be successful, they're learning to use the best-suited model for the job and not necessarily the newest or most expensive tool.
Most brands have started with use cases that improve employee workflows, such as streamlining content creation, Miller said. Yet, over time, she anticipates that brands will embrace more advanced, data-driven use cases that offer deep insights and hyperpersonalized CX.
Creative-focused use cases
GenAI's ability to quickly create textual and visual content makes it suitable to streamline creative-focused tasks. Marketing teams new to AI typically start with simple versions of these use cases.
1. Marketing copy generation
Marketers write a lot of content, including ad copy, product descriptions, emails and blogs, which can take considerable time and effort. However, GenAI tools, like ChatGPT and Microsoft Copilot, enable marketers to expedite the writing process for both short- and long-form content. For example, copywriters can prompt a GenAI tool to create 50 social media posts for their organization, and the tool does it almost instantaneously.
A content marketer, on the other hand, might use GenAI to write full-length blog articles. Marketers can prompt the tool to write the article from scratch, or they might craft an outline and have the tool flesh it out.
GenAI tools can write more quickly than humans, but marketing leaders may have concerns about the quality of the content -- and rightly so. AI content can feel overly formulaic or lack the right tone if marketers don't use highly specific prompts.
A skilled prompt engineer knows which information to include in the prompt to get quality results. For example, an advertisement for life insurance needs a more serious tone than one for a pizza delivery app. GenAI users must refine their prompts when tools generate content that misses the mark in terms of tone, style or level of detail.
Free tools, like certain tiers of ChatGPT and Gemini, serve a general audience. But some paid tools, like Jasper, cater specifically to marketers. These tools offer prompt templates to help users input the right information for different types of marketing copy. Additionally, organizations can fine-tune models on their brand guidelines to help match the right style and tone.
2. Video generation and virtual product placement
In addition to marketing copy, GenAI tools can help marketers create video content for various use cases, including advertisements, social media posts and product demos. AI video tools can vary in their capabilities. But, typically, users enter a prompt, and the tool generates a video as the output.
Types of GenAI video tools include the following:
- Text to video. Tools like Runway and Sora transform text prompts into video content.
- Image to video. Applications like LTX Studio and Synthesia can animate static images to make product and brand images more engaging without filming new footage.
- Virtual avatars. AI-powered tools, like HeyGen and DeepBrain AI, offer digital presenters that can deliver marketing messages in multiple languages. Users can customize the presenter's voice and appearance.
- Virtual product placement. AI tools like Rembrand and Mirriad use AI to insert branded products and logos into existing digital content, such as video podcasts or television shows.
These tools enable marketing teams to create high-quality video campaigns without having to invest in production staff, Miller said. This lowers the barrier to entry for smaller marketing teams and can cut costs for larger ones.
3. Transformation of content into different formats
Brands often launch campaigns in their primary markets and tweak them for secondary markets months later. For example, a global sportswear brand might launch a major campaign in the U.S. with English-language content and then spend weeks or months adapting it to resonate with European, Asian and Latin markets. This approach lacks efficiency and creates an inconsistent brand presence across the world.
GenAI tools can help teams quickly tweak the language, color scheme and music in their campaigns to match audiences in different regions. This reduces marketers' manual workload and helps them create a coherent brand presence.
"We're able to localize, customize -- we're able to translate so that all these brand experiences … can now all be ready to launch at the same time," Miller said.
4. Marketing survey creation
Organizations conduct market research, often in the form of surveys, to understand customers' wants and needs. Marketing teams can use GenAI to quickly create a variety of marketing surveys, such as segmentation, purchase process and customer loyalty surveys. This automation can save marketers' time and increase overall productivity.
As with most AI-generated content, marketers may need to fine-tune their prompts or edit the tool's output. However, GenAI can quickly offer marketers a foundational survey draft, which they can augment and edit as they see fit.
Analytics and data-driven use cases
More advanced use cases of AI center around data, analytics and operations. These cases can be more complex to implement but potentially offer the most value for organizations.
1. Connection of disparate data sources
Marketers have access to valuable data sources, such as campaign metrics, customer sentiment data and third-party research, but they've long struggled to integrate them all. However, GenAI's ability to understand vast amounts of structured and unstructured data is making this possible.
"[Analytics] is where we're going to see the most heavy lifting when it comes to GenAI because that's where … the data lies," Miller said.
Traditional marketing analytics was often limited to how campaigns performed, but GenAI can draw on more data and answer more complex questions. For instance, organizations that integrate their data with a GenAI analytics tool can answer why a campaign performed the way it did -- not just how, Miller said.
2. Content tagging and metadata enrichment
Effective analytics relies on good-quality data, which depends heavily on content tagging and rich metadata. Historically, marketers struggled with this labor-intensive manual process, but GenAI can automate metadata enrichment.
For example, GenAI can automatically analyze and tag the following content types:
- Video content analysis. AI can identify scenes, people, actions, emotions and key moments within videos.
- Document processing. The technology can extract topics and themes from PDFs and Microsoft Word documents.
- Image recognition. It can identify objects, people, settings and visual elements in images.
- Content classification. AI can categorize content by type, purpose, tone and target audience.
This automation lets marketing teams tag content far more quickly and thoroughly than they could manually. GenAI tools can then use that rich metadata to improve enterprise search, enhance personalization and generate deeper insights.
3. Marketing segmentation and personalization
Marketing teams can enhance market segmentation efforts if they integrate a GenAI model with a data lake or customer data platform that contains a large amount of customer and prospect information. Customer segments -- groupings based on common characteristics -- help organizations understand their customers and offer personalized experiences.
To create accurate segments, marketing teams must analyze a lot of data, which can take considerable time. However, GenAI can automate this process, as it can analyze large amounts of data more quickly than a team of humans.
GenAI's underlying LLMs can also let marketers use natural language to uncover new customer segments. For instance, a retail store marketer that integrated store data with a GenAI tool could ask the tool, "Which customers are most likely to show interest in our upcoming Father's Day offer?" The tool could analyze all relevant customer data to generate a group of customers that the team may not have identified previously.
Marketers can then use GenAI to craft personalized outreach for specific segments. For example, a marketer for an online surf shop could prompt a GenAI tool to write personalized email offers for specific segments.
4. SEO brainstorming and searcher intent analysis
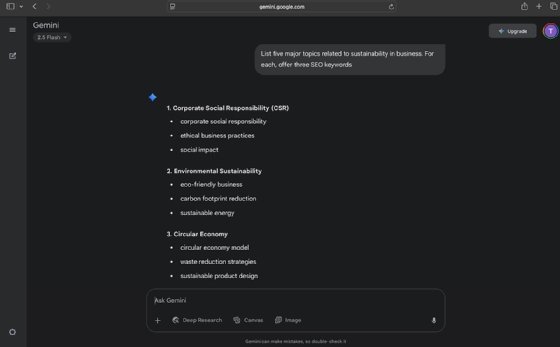
While traditional search engine optimization (SEO) platforms, like Ahrefs and Moz, offer search volume data, content marketers can use public GenAI tools for initial brainstorming and topic ideation. For example, content marketers who manage a blog for a sustainability reporting software vendor might prompt Gemini to list topics related to sustainability in business, along with associated keywords. They can then take the keywords and feed them into a traditional keyword research tool for further analysis.
GenAI can also help marketers understand searcher intent -- the purpose behind a user's search query. For instance, some SEO platforms, like Semrush, offer AI-generated intent analysis reports that surface insights into what users expect to find when they enter specific search terms. The AI examines top-ranking content to offer actionable recommendations about content format, structure and focus. This integration of AI-powered intent analysis with traditional search metrics lets marketers create highly targeted content, while maintaining competitive visibility in search results.
Risks of using generative AI in marketing
If marketing teams fail to edit AI-generated content or ensure data privacy, a GenAI tool can do more harm than good.
Common shortfalls of the technology include the following:
- Low content quality. If marketers lack basic prompt engineering skills or use AI-created copy without making their own edits, the copy can feel unoriginal and superficial. A blog that lacks originality and depth may struggle to rank on search engines against competitors that use human writers.
- Content that doesn't match brand tone. Free GenAI tools don't inherently understand how to write content in line with a brand's particular style or tone. Marketers need to carefully phrase -- and often refine -- their prompts. They also may need to manually edit the results to match the brand's tone.
- Knowledge limitations. GenAI models receive frequent updates, but their base training has a knowledge cutoff date, which means they cannot offer insights into recent events. Most major platforms offer internet search capabilities that enable them to access current news and information. But the quality of this real-time information can vary, and marketers should still verify time-sensitive information.
- Data privacy issues. Not all GenAI tools have guardrails in place to store sensitive data in compliance with privacy regulations, like GDPR and CCPA. To prevent a data breach, organizations should consult with risk management teams before they put customer information into a GenAI tool.
- Bias potential. Many LLMs that power GenAI tools were trained on a wide array of internet content. Therefore, political or racial biases found on the internet can make their way into responses, which can damage a brand's reputation.
GenAI has the potential to automate various tasks and boost productivity, although the tools require marketers to alter their creative processes. To reap the benefits of GenAI, organizations can offer basic prompt engineering training and guidelines to help marketers use the tools effectively in their daily workflows.
Editor's note: This article was updated to reflect changes in generative AI technology.
Tim Murphy is site editor for Informa TechTarget's SearchCustomerExperience and SearchContentManagement sites.








