headless commerce (headless e-commerce)
What is headless commerce?
Headless commerce, also called headless e-commerce, is a platform architecture that decouples the front end of an e-commerce website with the back end. The front end, or the "head," is typically a content management system (CMS) or customer experience management (CEM) platform that stores, manages and distributes content. The back end is the e-commerce platform that provides the purchasing logic, data and capabilities. This headless approach combines the customization of a CMS with the security of a software as a service (SaaS) e-commerce platform.
Headless commerce may be a good solution for businesses that focus heavily on content marketing or branding, use unconventional design templates or rely on B2B operations. E-commerce platform vendors that support a headless approach include the following:
- BigCommerce
- WooCommerce
- SAPCX Commerce Cloud
CMS products that can be integrated with a headless approach include the following:
- WordPress
- Adobe Experience Manager
- Drupal
- BloomReach Content
Headless commerce has risen in popularity as a way to combat the growth of the internet of things (IoT). Since the content of an e-commerce platform is not connected to the back end, businesses can deliver a consistent, functional experience to devices like computers, smartphones, smartwatches, kiosk screens and AI assistant skills.
How headless commerce works
The headless commerce architecture works by passing requests between the presentation and application layers of a platform. This is done through web services of API calls that connect the front end with back end functionality.
For example, a user may click an "Add to Cart" button that is registered on the presentation layer, or the front end. An API call will then be sent to the application layer, or back end, of the platform that registers the product as active for future action, such as purchase.
Benefits of headless commerce
In many scenarios, a headless commerce approach can provide the following benefits:
- Increases flexibility with updating or developing new front end functionality.
- Makes it easier and quicker to perform optimization test cases.
- Helps to create a consistent and personal user experience.
- Allows businesses to become omnichannel, or compatible with any devices and platforms.
- Lowers risk of error in back-end code.
- Enables a faster release of new content or design changes.
However, a few drawbacks that should be considered include the potentially high cost of ownership and the requirement of maintaining two systems.
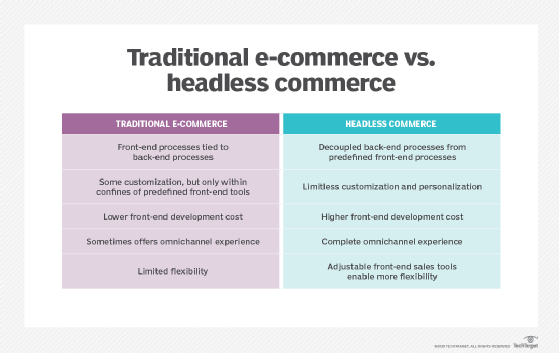
Headless e-commerce vs. traditional e-commerce
Headless e-commerce is an evolution of traditional e-commerce. Traditional e-commerce relies on a front end and back end that function together. Due to this, developers experience the following constraints with traditional e-commerce:
- Changes or updates that require more time as all edits need to be made within the databases, code and user interfaces.
- Business is limited in terms of customization as traditional platforms come with predefined functionality.
- Because the front end and back end are coupled, there is a higher risk associated with making a change that could disrupt logic or operations.
Editor's note: This article was written by Sarah Lewis in 2019. TechTarget editors revised it in 2023 to improve the reader experience.







