
What is a customer journey map?
A customer journey map is a visual depiction of the stages customers go through when interacting with a company -- from buying products online to accessing customer service on the phone to airing grievances on social media.
To create effective visual maps that reflect customers' journeys through these channels, journey maps must be rooted in data-driven research and visually represent the different phases customers experience based on a variety of dimensions, including customer sentiment, business goals and touchpoints.
To be comprehensive, companies often need to create several customer journey maps based on a 360-degree view of how customers engage with the company. For example, one journey map might begin with a customer commenting on X (formerly Twitter) about a company, product or brand; then using the phone to call customer support; and finally, posting a comment on the company's website. Another scenario might begin with online browsing, proceed to a phone inquiry and so on.
How does customer journey mapping work?
Customer journey mapping works by using data and research to help businesses visualize the customer journey. Customer journey mapping often includes the steps and motivations behind customer interactions, and can be used to improve conversion rates, optimize onboarding or enhance customer retention.
Organizations usually begin mapping by gathering customer data and analytics. These data points are then used to create customer personas that represent different segments of a company's audience. The map is then expanded to include touchpoints, or the places where customers interact with an organization. These can include in-store visits, website interactions and post-purchase communication.
Once the map is created, it can be analyzed to discover areas for improvement in the customer journey and places where the customer-centric experience can be enhanced. Metrics such as conversion rates can also be used to help understand where the map is most successful and where it needs improvement.
Benefits of customer journey mapping
In today's market, customer expectations are evolving across all businesses, independent of their size, and customers require a seamless omnichannel approach to customer service, marketing and sales.
A customer journey map enables companies to view their products from a different perspective so they can analyze different user scenarios and identify loopholes. It helps them understand customer needs and the routes and channels they take to reach a product. It's a valuable tool that can also be used to forecast future customers' paths.
The main benefits of building a customer journey map include the following:
Extracts insightful information. Creating a customer journey map can provide insight for all levels in an organization -- from a sales rep who needs to figure out the best ways to interact with potential customers to managers looking for insight on which outlets customers use most. A customer journey map, for instance, can show that a certain department lacks the resources or tools needed to follow up with clients after a sale.
Predicts consumer behavior. A customer journey map helps companies assess the current state as well as the future state of the customer's journey. As clients move through the different stages of the sales funnel, journey maps can forecast their behavior and predict the likelihood that a certain prospect converts. Companies can decide how to effectively facilitate and expedite the sales process for potential consumers by having a thorough understanding of the target demographic.
Detects gaps and loopholes. A customer journey map can effectively identify loopholes in processes and break down silos between departments. It can also highlight and identify gaps in the customer experience (CX), including the following:
- Gaps between devices, when a user moves from one device to another.
- Gaps between departments, where the user might get frustrated.
- Gaps between channels, where the experience of going from social media to the website could be better.
Shows customer progress through the sales funnel. One of the main benefits of a customer journey map is that it provides clear information on how customers move through the sales funnel. Maximizing the efficiency of that path means more sales at a quicker pace.
Helps businesses understand the customer's experience. Understanding what the customer is experiencing in real time is vital for sales and marketing, as it enables the organization to walk in the customer's shoes. Businesses can improve customer experience by mapping out the client's path, which includes both the pain points as well as positive customer interactions with the product.
Increases customer loyalty. Once a customer's roadblocks are addressed, it leads to higher customer satisfaction, which in turn leads to customer loyalty.
Boosts revenue. Improving the customer experience can lead to improved sales, since customers are more likely to buy products or services from companies that deliver a positive customer experience.
Provides benchmarks and comparisons. Businesses can track their development over time and evaluate their performance against industry benchmarks and rivals by mapping out the customer journey.
Drawbacks of customer journey mapping
Creating a customer journey mapping process isn't always easy or simple. Some common challenges include the following:
Failure to involve necessary departments. When creating a customer journey map, organizations must involve a variety of roles and departments, especially customer-facing ones. Companies should involve the stakeholders and receive input from their employees during the creation of a customer journey map. They should also distribute the maps and educate customer experience, marketing and sales teams about how to use them to market to target audiences and, ultimately, improve CX.
Lack of customer data. Customer journey maps are difficult to create without relying on data to determine the customers' behaviors, preferred touchpoints and customer satisfaction levels during each stage in the journey. Companies can gather customer data through incorporating voice-of-the-customer programs, deploying surveys and monitoring social media channels.
Treating the customer journey map as a static entity. Customers, markets and products change, and companies should consistently update customer journey maps to reflect those changes. Without frequent updates, customer journey maps can become inaccurate or outdated.
Potential for accumulating useless data. Thanks to modern technology, it's easy to collect and store data. However, just because a piece of data can be collected doesn't automatically imply that it's significant to the customer journey. The collection and analysis of useless data can make it harder to draw meaningful inferences and make decisions.
Components of a customer journey map
According to Salesforce, 88% of customers value the experience as much as a company's products or services. Therefore, a customer journey map should prioritize the customer experience and interactions with the product over everything else.
A customer journey map is made up of several components, including the following:
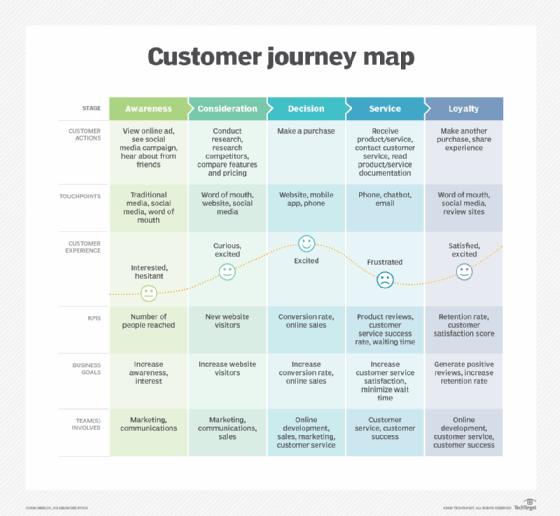
- Customer stages. One of the first steps of creating a customer journey map is to identify stages in the customer journey. There are at least four stages in a customer journey: inquiry, comparison, purchase and installation. These stages can have different names; inquiry, for example, is sometimes called awareness. Often, there's a fifth stage called loyalty or advocacy.
- Buyer personas. A buyer persona is a composite representation of a market segment. It is an important tool for creating journey maps because CX teams can more accurately predict those customers' behaviors and feelings using personas.
- Customer touchpoints. A customer journey map should always include touchpoints that a customer is likely to use at each stage of the journey. For example, during the installation or service stage, a customer might use phone calls or chatbots to communicate with a brand.
- Emotions. One of the main goals of creating a customer journey map is to predict the customers' emotions and feelings. This way, a brand can pinpoint potential customer pain points and customer successes.
- Opportunities. Once the customer journey is sketched, opportunities, or the desired outcomes, should be identified. Mapped opportunities are insights that show how the user experience could be improved. To find out where clients are running into obstacles that prevent them from making purchases or coming back as repeat customers, for instance, would be an excellent question that companies can ask themselves at this point.
Creating a customer journey map
Each stage of the customer journey is vital for the sales and marketing departments. The customer journey begins when a customer asks about a product or service. At that point, they become prospects. The comparison stage is where customers use readily available information about different products in any given market to compare, for example, features, pricing and customer service ratings. The purchase stage is when the prospect becomes a customer, which then triggers the service department to begin the final phase: installation.
There are several steps to map customer journeys effectively.
- Focus on customer perspective. The journey map needs to focus on how a customer experiences interactions, not how the company perceives those experiences.
- Account for customer segments. Acknowledge that different customer segments experience products, brands and services differently.
- Create research maps. Tools such as customer analytics should be used to develop maps to best reflect constituencies and their likely behavior.
- Ensure that maps reflect all touchpoints. Maps must show all potential communication points -- including email, text, websites and social media platforms -- through which customers want to connect with companies. Maps must also reflect different sequences in which customers take different paths.

Explore the different stages of the customer journey map, including customer actions, touchpoints, business goals, teams involved and KPIs.
To create a customer journey map, organizations should perform the following six steps:
- Set clear objectives. Before diving into the process of creating a customer journey map, organizations should first consider the purpose of the map and how it aligns with their broader organizational goals. Every map should be driven by a specific business objective, such as improving customer experience or increasing sales. To achieve this, some questions businesses might consider asking include how and why customers choose to purchase from them, or how they can enhance the overall customer experience.
- Create a customer persona. A customer persona is a prototype of real customers that helps businesses understand the customer's expectations and needs. To develop customer personas, businesses should identify and understand their target audience, taking into account their goals, motivations and pain points. By mapping out these characteristics, companies can create personas that accurately reflect the needs and preferences of their customers.
- Define customer touchpoints. A customer journey map should identify where exactly a customer interacts with the brand within each phase of the journey -- whether it's online or offline. It's important to know that some touchpoints carry more weight than others. For example, a bad check-in experience at a hotel can spoil a customer's entire stay. Therefore, to avoid setbacks and to uphold customer satisfaction, it's important that the customer journey map has a record of all touchpoints and transactions that take place between the brand and the customer. To gather data for creating touchpoints, various customer feedback channels, such as customer surveys, interviews and analytics tools can be used.
- Create a visual representation. The customer's journey should be visualized by drawing a timeline, flowchart or pictograph. All of the journey's phases as well as the previously mentioned touchpoints should be included in the visual representation.
- Add the customer's emotions and actions. The map should indicate the feelings and behaviors that customers are likely to have at each stage of the customer journey. This can include emotions, such as excitement, irritation, satisfaction or bewilderment, as well as behaviors, including searching, weighing alternatives, making a purchase or asking for help.
- Brainstorm improvements. Based on the opportunities and pain points identified in the map, businesses should brainstorm potential improvement processes. For example, a business can try to figure out how to provide a pleasant experience for customers at every stage of the touchpoint. To ensure that obstacles are kept to a minimum throughout the customer's lifetime, the organization should analyze the customer journey map with the customer service teams.
When designing a customer journey map, there's no set protocol, but there are guidelines and a plethora of customer journey map templates that businesses can use. The customer journey map should be visually appealing, comprehensive and understandable. Typical customer journey maps include infographics, diagrams, pictographs and timelines. Multimedia, including videos and storyboards -- can also be used for customer journey maps.
The information included on the map should have both statistical and anecdotal insight and should be customer-facing.
Customer journey mapping tools and software
With customer journey maps being such an important visual for sales departments, there's a plethora of tools, customer journey map templates and software to help ease the process.
There are two types of tools that can be used to create a customer journey map. The first is software that helps identify the different customer touchpoints and compiles that information for the department. Then, if there's a graphics team or graphic designer in-house, creating a customer journey map is left to them.
There are also ready-to-use tools that can help with customer journey mapping visualization. Some examples include Adobe XD, Canvanizer, Lucidchart, Salesforce Journey Builder, Sketch and Smaply.
These tools vary in terms of features, pricing and user experience. Therefore, it's essential for businesses to evaluate their specific requirements and choose the product that best fits their needs.
Types of customer journey maps
Customer journey maps can be used for different purposes. There are several different kinds of customer journey maps that reflect these different purposes. These include the following:
- Current state maps, which illustrate existing customer experience and reflect how users interact with a brand, from initial awareness to post-purchase.
- Future state maps, which envision ideal experience maps that represent planned improvements or customer experience goals for the future.
- Day in the life maps, which provide insight into the customer's daily activities and how a brand fits into them.
- Service blueprints, which detail the customer-facing journey and back-end processes that support the journey.
- Onboarding maps, which focus on the onboarding journey and visualize the process a new customer undergoes.
Stages of a customer journey
The customer journey is often divided into separate key stages. These stages include:
- Awareness. Awareness is the initial stage of the customer journey, in which a customer first becomes aware of a brand or product.
- Consideration. This is the information gathering stage of a customer's journey, including reading reviews and comparing options.
- Conversion. In the conversion stage, customers complete a purchase of a brand's product or service.
- Onboarding. This is the stage after a purchase, in which a brand helps familiarize customers with the product or service through customized messaging or literature relevant to the product or service. This can help extend engagement and improve retention.
- Post-purchase engagement. Similar to onboarding, the organization continues to strengthen brand and customer loyalty through emails, support services and personalized offers.
- Advocacy. In the final stage, satisfied customers may become advocates, providing positive reviews or referring others to a brand.
To ensure the accuracy and effectiveness of customer journey maps, CX teams should adhere to specific best practices. Discover the top customer journey mapping strategies.







