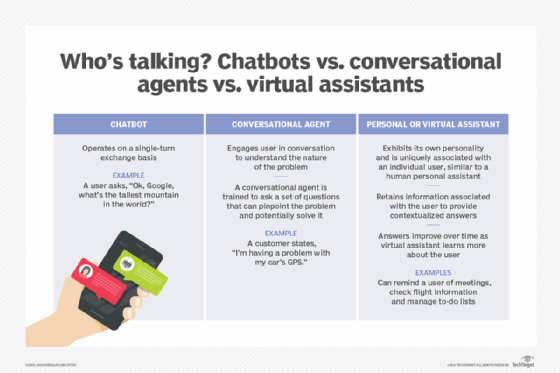
chatbot
What is a chatbot?
A chatbot is a software or computer program that simulates human conversation or chatter through text or voice interactions.
Users in both business-to-consumer (B2C) and business-to-business (B2B) environments increasingly use chatbot virtual assistants to handle simple tasks. Adding chatbot assistants reduces overhead costs, better utilizes support staff time and enables organizations to provide customer service around the clock.
Chatbots range from simplistic models that operate off of scripts to provide quick responses to specific questions, to artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) models that can converse with users and complete more complex tasks. Chatbots also simulate human conversation in either written or spoken form.
How do chatbots work?
How a chatbot works depends on the type of chatbot. Early chatbots followed predefined scripts. In a customer support setting, this included commonly asked questions with corresponding answers. The chatbot would look for a set of keywords a user would input and it would respond with the corresponding information. This type of chatbot couldn't interpret natural language or answer complex or unscripted questions.
More modern chatbots can use AI and ML to be much more flexible. These chatbots use natural language processing (NLP) and natural language understanding to interpret user inputs and respond similarly. They also use ML and large language models to learn and improve their service.
Chatbots have varying levels of complexity, being either stateless or stateful. Stateless chatbots approach each conversation as if interacting with a new user. In contrast, stateful chatbots can review past interactions and frame new responses in context.
Adding a chatbot to a service or sales department requires no or minimal coding. Many chatbot service providers use developers to build conversational user interfaces for third-party business applications.
A critical aspect of chatbot implementation is selecting the right NLP engine. If the user interacts with the bot through voice, for example, that chatbot requires a speech recognition engine.
The organization implementing the chatbot must also decide whether it wants structured or unstructured conversations. Chatbots built for structured conversations are highly scripted, which simplifies programming but restricts what users can ask. In B2B environments, chatbots are commonly scripted to respond to frequently asked questions or perform simple, repetitive tasks. For example, chatbots can enable sales reps to get phone numbers quickly.
Why are chatbots important?
Organizations looking to increase sales or service productivity might adopt chatbots for time savings and efficiency, as AI chatbots can converse with users and answer recurring questions. These services are also typically available 24/7.
As consumers move away from traditional forms of communication, many experts expect chat-based communication methods to rise. Organizations increasingly use chatbot-based virtual assistants to handle simple tasks, allowing human agents to focus on other responsibilities.
Chatbot use is increasing in business and consumer markets. As chatbots improve, consumers have less cause for dispute while interacting with them. Between advanced technology and a societal transition to more passive, text-based communication, chatbots help fill a niche that phone calls used to.
How have chatbots evolved?
Chatbots such as Eliza and PARRY were early attempts to create programs that could at least temporarily make a real person think they were conversing with another person. PARRY's effectiveness was benchmarked in the early 1970s using a version of the Turing Test; testers only correctly identified a human vs. a chatbot at a level consistent with making random guesses.
Chatbots have come a long way since then. The implementation of ML and other AI processes prompted a major step forward for chatbots in the early 2000s. ML and NLP processes found their way into several technologies in the 2010s, such as IBM Watson, Amazon Alexa and Apple Siri. Chatbots like Alexa and Siri, which focus on understanding natural language through voice, have become prominent AI assistants.
The next jump in chatbot technology occurred in 2016 with transformer neural networks -- also called transformer architectures. Chatbots like ChatGPT use this and neural network architectures. These chatbots require massive amounts of data to be properly trained. However, the transformer architecture is more efficient when compared to feedforward neural networks.
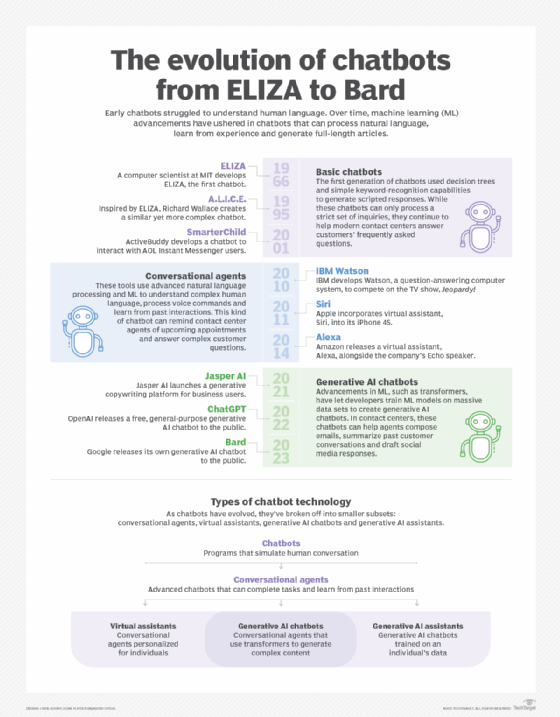
Types of chatbots
As chatbots are still a relatively new business technology, debate surrounds how many different types of chatbots exist and what the industry should call them.
Some common types of chatbots include the following:
- Scripted or quick reply chatbots. As the most basic chatbots, they act as a hierarchical decision tree. These bots interact with users through predefined questions that progress until the chatbot answers the user's question.
- Menu-driven chatbots. These bots require users to make selections from a predefined list, or menu, to provide the bot with a deeper understanding of what the customer needs.
- Keyword recognition-based chatbots. These chatbots are a bit more complex; they attempt to listen to what the user types and respond accordingly using keywords from customer responses. This bot combines customizable keywords and AI to respond appropriately. Unfortunately, these chatbots struggle with repetitive keyword use or redundant questions.
- Hybrid chatbots. These chatbots combine elements of menu-based and keyword recognition-based bots. Users can choose to have their questions answered directly or use the chatbot's menu to make selections if keyword recognition is ineffective.
- Contextual chatbots. These chatbots are more complex than others and require a data-centric focus. They use AI and ML to remember user conversations and interactions and use these memories to grow and improve over time. Instead of relying on keywords, these bots use what customers ask and how they ask it to provide answers and self-improve.
- Voice-enabled chatbots. These chatbots use spoken dialogue from users as input that prompts responses or creative tasks. Developers can create these chatbots using text-to-speech and voice recognition application programming interfaces. Examples include Amazon Alexa and Apple Siri.
AI and chatbots
The integration of ML and AI has increased the quality and function of chatbots. Rule-based chatbots, by comparison, can only give simplistic responses to specific questions. These systems are limited by their understanding of language and follow predefined scripts. AI-powered chatbots, however, can understand and respond to users in a much more natural sense because of their ability to process natural language.
Integrating chatbots with AI also enables chatbots to learn from their interactions with users. These chatbots learn from the data they collect to then provide increasingly accurate and personalized answers.
How do businesses use chatbots?
Chatbots have been used in instant messaging apps and online interactive games for many years and only recently segued into B2C and B2B sales and services.
Organizations can use chatbots in the following ways:
- Online shopping. Sales teams can use chatbots to answer noncomplex product questions or provide helpful information that consumers could search for later, including shipping price and availability.
- Customer service. Service departments can use chatbots to help service agents answer repetitive requests. For example, a service rep might give the chatbot an order number and ask when the order shipped. Generally, a chatbot transfers the call or text to a human service agent once a conversation becomes too complex.
- Virtual assistants. Chatbots can also act as virtual assistants. Amazon, Apple and Google all have forms of virtual assistants. Apps such as Apple's Siri or products like Amazon Alexa all play the part of a personal chatbot.
- Collect customer data and feedback. Chatbots can also actively or passively collect customer data and feedback. This is useful for better understanding and learning what to do to improve customer experience (CX).
- Omnichannel communication. Chatbots can interact with customers over multiple different -- omnichannel -- communication channels, creating a more unified customer experience.
How are chatbots changing businesses and CX?
The rapidly evolving digital world is altering and increasing customer expectations. Many consumers expect organizations to be available 24/7 and believe an organization's CX is as important as its product or service quality. Buyers are more informed about the variety of products and services available, making them less likely to remain loyal to a specific brand.
Chatbots serve as a response to these changing needs and rising expectations. They can replace live chat and other forms of contact, such as emails and phone calls.
Chatbots can enhance CX in the following ways:
- Reduce customer wait times and provide immediate answers.
- Offer customers 24/7 support.
- Remove the potential for unpleasant human-to-human interactions, as well as the moods and emotions of both the service or sales representative and the customer.
- Reduce wait times and streamline conversations to minimize the potential for customers' stress and annoyance.
- Improve the redirection of customer queries.
- Add customized elements to the chatbot to advance brand personality.
- Personalize CX with AI-enabled chatbots.
In addition, major technology companies, such as Apple, Google and Meta, have developed their messaging apps into chatbot platforms to handle services including orders, payments and bookings. When used with messaging apps, chatbots let users find answers, regardless of location or the devices they use. This interaction is also easier because customers don't have to fill out forms or waste time searching for answers within the content.
What are the benefits of using chatbots?
Chatbots provide many benefits for customers and companies. For example, improved CX and more satisfied customers due to chatbots increase the likelihood that an organization will profit from loyal customers.
Other benefits include the following:
- Increases productivity. Chatbots can converse simultaneously with thousands of buyers. This increases business productivity and eliminates wait times.
- Reduces costs. A chatbot is a faster and less expensive one-time investment than creating a dedicated, cross-platform app or hiring additional employees. In addition, chatbots can reduce costly problems caused by human error. User acquisition costs also decrease with a chatbot's ability to respond within seconds.
- Saves time. Chatbots can automate tasks performed frequently and at specific times. This gives employees time to focus on more important tasks and prevents customers from waiting to receive responses.
- Proactive customer interaction. In the past, organizations relied on passive customer interaction and waited for buyers to reach out first. With chatbots, organizations can interact proactively, as bots can initiate conversations and monitor how customers use their websites and landing pages. Organizations can then use the information gathered from monitoring to offer specific incentives to buyers, help users navigate the site and answer future questions.
- Monitors and analyzes consumer data. Chatbots collect feedback from each interaction to help businesses improve their services and products or optimize their websites. Bots can also record user data to track behaviors and purchasing patterns. This information can give organizations insight into how to better market their products and services, as well as common obstacles that customers face during the buying process.
- Improves customer engagement. Most companies already engage their customers through social media. Chatbots can make this engagement more interactive. Buyers rarely talk to the people within businesses, so chatbots open a communication channel where customers can engage without the stress of interacting with another person.
- Eases scalability to global markets. Chatbots can solve customer concerns and queries in multiple languages. Their 24/7 access enables customers to use them regardless of time or time zone.
- Expands the customer base. Chatbots can improve lead generation, qualification and nurturing. Chatbots can ask questions throughout the buyer's journey and provide information that could persuade the user and create a lead. Chatbots can then provide potential customer information to the sales team, who can engage with the leads. The bots can improve conversion rates and ensure the lead's journey flows in the right direction -- toward a purchase.
- Measures lead qualifications. Chatbots can help sales teams determine a lead's qualifications using identified key performance indicators, such as budget, timeline and resources. This can prevent companies from wasting time on unqualified leads and time-consuming customers.
What are the challenges of using chatbots?
While chatbots improve CX and benefit organizations, they also present the following challenges:
- New technology, new obstacles. AI-enabled chatbot technology is still new and faces obstacles that organizations might not know how to handle. While AI-enabled bots can learn from each interaction and improve their behaviors, this process can cost organizations a lot of money if the initial interactions cause customers to disengage and turn away. For example, an AI-enabled chatbot could hallucinate and provide users with incorrect information.
- Security. Users must trust the chatbot enough to share personal data. Therefore, organizations must ensure they design their chatbots to only request relevant data and securely transmit that data over the internet. Chatbots should have secure designs and be able to prevent hackers from accessing chat interfaces.
- Variations in usage. People type their messages differently, potentially leading to misunderstood intentions. Chatbots must handle both long and short sentences, as well as chat bubbles with lengthy content versus multiple short submissions.
- Lack of understanding. Chatbots can struggle to understand variations in the way people refer to things. For example, a user might misspell words or use acronyms or slang. Unfortunately, NLP is limited and can't fully resolve this challenge.
- Unpredictable human behavior, moods and emotions. Humans are random and emotions and moods often control user behavior, so users can quickly change their minds. After initially asking for a suggestion, they might want to give a command instead. Chatbots must adapt to this randomness and spontaneity.
- User satisfaction. Users always want the best experiences but are rarely satisfied. They always want the chatbot to be better than it currently is. This means organizations employing chatbots must consistently update and improve them to ensure users feel like they're talking to a reliable, smart source.
Future of chatbots
Chatbots won't be fully replacing humans in contact centers any time soon; however, the technology will continue to improve, evolve and grow in relevance.
Although public sentiment toward AI replacing human jobs is currently viewed negatively, many people still choose to interact with chatbots in scenarios like asking simple-to-answer questions on a product page. Likewise, many people interact with a chatbot before being transferred to a human. In these cases, it's common for the chatbot to collect data on user inquiries and then direct them to the right department.
Many experts expect chatbots to continue growing in popularity. In the future, AI and ML will continue to evolve, offer new capabilities to chatbots, and introduce new levels of text and voice-enabled user experiences that will transform CX. These improvements could also affect data collection and offer deeper customer insights that lead to predictive buying behaviors.
Voice services have also become common and necessary parts of the IT ecosystem. Many developers place an increased focus on developing voice-based chatbots that can act as conversational agents, understand numerous languages and respond in those same languages.
Chatbots are a technology that has grown and improved over time. Learn more about the evolution of chatbots and generative AI.







