What is quality of experience (QoE or QoX)?
Quality of experience (QoE or QoX) is a measure of the overall level of a customer's satisfaction and experience with a product or service and the vendor that's providing that product or service. QoE is related to quality of service (QoS), although the two concepts are not the same.
The International Telecommunication Union defines QoE as "the overall acceptability of an application or service, as perceived subjectively by the end-user." QoE is a measure used to help understand the individual experiences of actual users when they interact with an application or service. Thus, QoE takes the user's viewpoint while assessing the quality of a product or service. Most importantly, it aims to answer the question, "Did this product or service deliver a sufficient or good experience to end users, and to what extent?"
QoE metrics can generally be applied to any consumer- or customer-related business or service. They are often used to measure customer satisfaction in the information technology (IT) and consumer electronics sectors.
A real-world analogy of QoE can be made with the example of the quality of medical care provided to a patient. The experience can be evaluated in many ways; however, the most meaningful results of the care being provided are how long the patient lives and how well they feel. The former result is numerically quantifiable (years, months, days), but the latter result is not quantifiable. Even so, both factors are important and help to determine the patient's overall QoE. Regardless of how these factors are defined (broadly or narrowly), they -- and thus the QoE -- can profoundly affect the patient's life and ultimately impact the long-term success of the medical organization. That's why it is in the best interest of any enterprise to act early to maximize the QoE of its users or customers.
Factors affecting QoE
When delivering a product or service, many factors can affect customer experiences and the resulting QoE, including the following:
- Cost.
- Reliability.
- Efficiency.
- Scalability.
- Speed.
- Accuracy.
- Privacy.
- Security.
- User-friendliness and usability.
- Features.
- User confidence.

For IT- or telecommunications-related products or services, factors such as available bandwidth, jitter, latency, delay and packet loss rate can also affect customer satisfaction and QoE. Examples of such services include cloud computing, telecommunications, video streaming services, Wi-Fi, digital services, multimedia and networking.
Environmental variables, such as the user's working environment and hardware, can also influence QoE. For example, the method used (e.g., landline, cordless or mobile phone) to access or use the product can be a factor. The type of network used and its associated network performance may also affect QoE, as experiences can vary significantly if a free public network that's prone to delays and buffering is being used rather than a high-speed enterprise LAN.
The importance of the application to the user can also affect the QoE. For example, expectations and QoE results may be different if the user is using an application for personal use rather than using a business application to get work done.
Among the goals of QoE are optimization of the overall experience from service providers, addressing user expectations, effective use of analytics tools and experience metrics, and achieving customer retention and reduction of churn.
How QoE is measured
Organizations have many ways to measure and evaluate QoE. The most common and subjective method is to poll or sample a large number of customers. For example, providers may ask users to rate the product or service quality on a fixed scoring scale, such as from 5 to 1, where 5 means the best quality and 1 indicates the worst quality. The numbers 2 to 4 may indicate poor, fair and good quality. Based on the responses from all polled users, the vendor calculates the mean opinion score (MOS).
Following is an example of how MOS can be calculated.
| Rating values | Number of responses | Value x number of responses |
| Excellent = 5 | 15 | 75 |
| Very Good = 4 | 8 | 32 |
| Acceptable = 3 | 12 | 36 |
| Fair = 2 | 7 | 14 |
| Poor = 1 | 9 | 9 |
| Totals | 46 | 166 |
Dividing the total number of calculated values (166) by the number of responses (46) results in an MOS of 3.6.
MOS can be calculated in any situation where human opinions are useful and where there is a need to understand human subjective experiences. For example, the metric is commonly measured to assess the quality of VoIP calls and video sessions in call centers. Measuring MOS enables providers to identify quality issues that may be affecting user experiences and implement appropriate measures to eliminate the issues and improve experiences.
AI and machine learning-driven QoE
Tools that use AI and machine learning (ML) may be able to automatically identify QoE issues and make suggestions on how to address those issues. Such tools may provide enhanced visualizations of the product or service so vendors can see where quality issues typically occur.
AI/ML technology may also pinpoint or predict performance issues before they affect users or customers. Such early warnings may help providers to proactively improve user experiences from the outset.
QoE vs. QoS
QoS is a useful measure of the performance of a product or service, such as an IT network. It enables vendors or providers to understand performance gaps and then implement measures to address those gaps to help meet customer requirements. For example, an IT team may implement traffic shaping to improve the network's latency, reduce congestion and increase usable bandwidth for certain types of packets.
Generally speaking, QoS embodies the notion that hardware and software characteristics can be measured, improved and, in some cases, even guaranteed. In contrast, QoE measures how a user experiences a service. By taking the user's perspective instead of relying on the vendor's performance measurements, QoE expresses user satisfaction. Moreover, it does so both objectively and subjectively, so QoE is not always numerically quantifiable. Even so, it is one of the most significant factors in evaluating user experiences in the real world and using this understanding to improve the quality and performance of a product or service, often in conjunction with QoS.
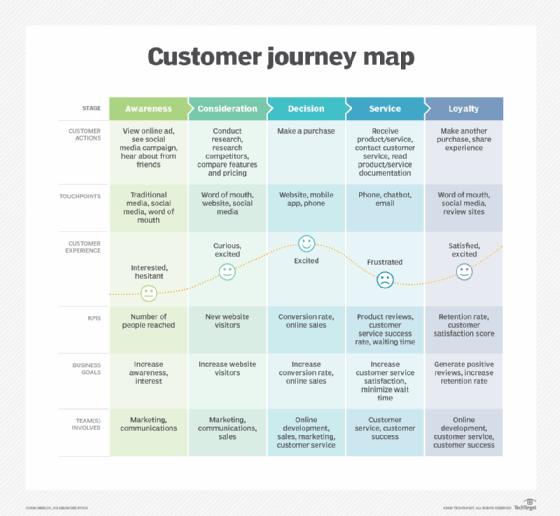
In many situations, particularly in IT-related scenarios, vendors need to measure both QoS and QoE to improve their offerings and meet customer expectations. QoE provides a high-level view of performance and quality from the customer's or user's perspective, while QoS provides more detailed and specific insights into individual performance parameters. Together, QoS and QoE provide a full picture of quality that vendors can use to assess the gap between where they are versus where they want to be to satisfy their users.
Challenges in QoE
When determining QoE, communication from customers about their experience is essential. Data gathering on user experience includes listening to what the customer is saying and providing responses to that feedback, followed by additional questions to capture more data. Good customer experience data can be an indicator of customer satisfaction and loyalty. However, challenges to that goal must also be addressed, such as the following.
1. Insufficient or inadequate responses from customers. A considerable amount of data should be collected when performing QoE measurements and analyses. If this is not possible, QoE initiatives may be unsuccessful.
2. Lack of a QoE strategy or tools. Many channels may be present in a customer experience strategy. If they are not effectively used there may be insufficient data for a QoE initiative. The use of sophisticated customer relationship management (CRM) systems may be important, but they must be able to read all customer experience channels. This is an area where AI can be effective, by linking to all channels and collecting and analyzing the data.
3. Is qualitative data enough? Data from customer experience feedback is typically qualitative, e.g., good, better, best. But is that enough to effectively determine QoE? It may be necessary to use AI to examine text analytics and other data to determine customer feelings and sentiments.
4. Lack of employee awareness of QoE data. Employees in an organization who analyze QoE data must have access to that data. Without access to QoE data to close a feedback loop to internal employees, those employees and departments that can respond and contribute may be unable to do so.
5. Presence of corporate silos and cultural issues. Corporate silos and cultural influences must be mitigated to enhance communications among all players in QoE activities. It may be necessary to consolidate all enterprise customer data into a single, centralized repository such as a customer data platform (CDP).
6. Lack of appropriate tools and technology. As noted before, availability of AI and ML systems can greatly enhance the analysis of QoE data. Advanced analytics can improve the transition of customer data into relevant data outputs.
QoE advantages and limitations
Knowledge of user experience and preferences helps organizations deliver the best products and services to their customers. QoE initiatives provide the intelligence needed to develop new products, update and enhance existing products and eliminate poorly performing products.
Information gleaned from customer communications is essential as are the systems for capturing this data. It is also essential to remove traditional barriers, such as silos, to encourage both internal and external communications. Senior management support and access to funding are also required to avoid compromising the ability to analyze and use QoE data.
AI and the future of QoE
As noted earlier, the use of AI and ML technologies is essential for capturing QoE data, analyzing the data and using insights to provide recommendations. When looking at systems for use in QoE activities, be sure that AI/ML capabilities are available.
The future of QoE is strong because it provides insights into what customers need, what they like and dislike, and what can be done to improve existing products and services and develop new ones.
Learn about benefits of customer experience management and see the best customer experience management software available today.





