10 strategies to improve contact center agent performance
Call monitoring, skills-based routing, positive reinforcement, training resources and coaching can help contact center agents improve their performance and customer interactions.
Customer relationships with a business don't end once a purchase is complete. They continue with service and support from the contact center.
Agents in a contact center are on the front lines. They're the face of the organization when a customer has a problem to be solved. And customers want their issues solved quickly, efficiently and with a smile. When agents don't perform at their best, customers can get a bad impression of the organization, which might translate into a loss of revenue if customers decide to take their business elsewhere. On the flip side, agents well versed in their job can turn irate customers into loyal ones, increasing customer retention and profit.
What factors contribute to declining agent performance?
There are many reasons agents don't perform at their best, which can also lead to burnout. Some of those reasons include the following:
- Outdated or obsolete contact center technology.
- Poor agent training and onboarding.
- Inefficient processes.
- Overworked agents due to inadequate staffing.
- Lack of communication from leadership.
- No advancement opportunities.
- Toxic work environment.
- Low employee morale.
10 strategies to help contact center agents perform at their best
Keeping contact center agents productive -- especially as more and more of them work from home -- is difficult, but not impossible. Businesses can improve contact center agent performance in several ways. The goal is to assist agents in meeting their performance goals while enhancing overall customer satisfaction.
1. Diagnose underlying performance issues
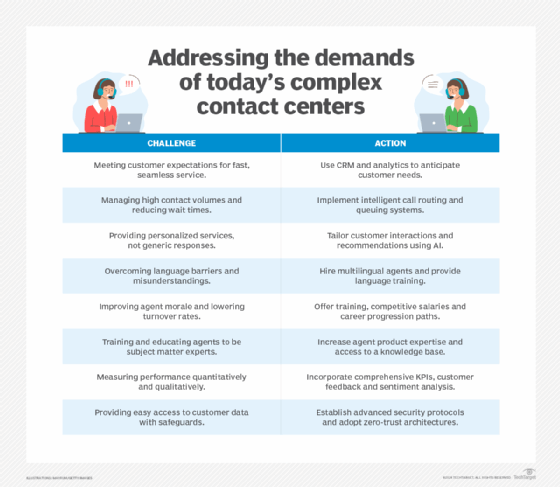
Contact center managers should analyze the data gathered from an agent's evaluation in quality assurance forms to determine where performance opportunities exist and identify any trends. These forms will show whether an agent consistently receives low or failing scores in certain metrics or from data collected in a call monitoring program.
Managers should also determine if there are multiple agent performance issues, such as problems with communication skills, adhering to processes, accessing customer data and processing transactions.
Another way to gain insights is by conducting side-by-side sessions with agents working in the office to see firsthand where and when challenges arise or if work habits contribute to their performance issues. Based on the results of the trend analysis and observations from side-by-side sessions, contact center managers can identify the underlying causes of performance problems.
2. Record and monitor calls
Contact center software often includes a call monitoring feature, enabling contact center managers to review recorded calls or listen to them in real time. Monitoring calls lets managers identify customer pain points and where agents need additional training.
Contact center managers might also consider adding AI call analysis software to their stack. Managers can use AI to comb through customer contact data -- recorded calls, emails, chat logs and customer feedback -- to uncover patterns and trends, improve contact center operations and better serve the customer.
3. Review key performance indicators
If management finds multiple agents are failing according to the same performance metrics, it might be time to take a closer look.
Average handling time is one KPI that businesses might need to address. If AHT is too short, agents might be rushing through customer interactions to meet their goals. Customers will also often end up with unresolved issues and be forced to reach out again. If AHT is too long, there could be longer wait times for customers. But that's not necessarily a bad thing. Long AHT might be due to new or upgraded business products or services that customers need assistance with, technical difficulties that require more time or a focus on first contact resolution. Any issues with an AHT KPI are best addressed when contact centers set acceptable ranges instead of hard targets.
4. Create an action plan
An action plan can address the underlying issues and where an agent needs improvement. Contact center managers should identify all available resources to support the agent's skill development, including the following:
- Provide additional agent training or goal-oriented uptraining sessions.
- Make reference materials or job aids available.
- Offer additional system or communication skills training.
- Regularly assign time for the agent to sit with an overperforming colleague to learn the proper way to handle customer interactions.

5. Communicate with agents
Depending on the structure of an organization, the quality assurance or the contact center manager should discuss performance issues with the agent. Be sure the agent understands the quality of evaluation metrics and how calls are scored.
The assessment must be constructive and include recognition of the agent's strengths and performance opportunities. Review the action plan with the agent and emphasize that the program's intent is to provide help and support. It's also important for contact center managers to communicate any policy changes immediately so that agents know what's expected of them and they don't fall behind from the get-go.
6. Provide consistent feedback and reward improvements
The most effective agent performance improvement programs provide continuous and encouraging feedback to motivate agents. When an agent struggles to perform, it's important for managers to recognize and praise incremental improvement.
Managers should conduct routine evaluations of the agent's contacts and provide timely feedback. Provide additional targeted coaching sessions to address the agent's specific needs to reinforce what they're doing right. These actions will improve overall contact center performance and create a better customer experience.
But employee recognition shouldn't just be limited to job improvement. Recognition can include employment anniversaries, birthdays or a simple thank-you to employees during a company celebration. It can improve employee engagement, individual well-being and company culture.
7. Implement a knowledge base
Implementing a customer service knowledge base benefits customers and agents. An external, or public-facing, knowledge base enables customers to find answers to basic questions without the need for human assistance, which can increase customer satisfaction. In return, it eliminates unnecessary customer contacts and frees up agents for more important customer issues.
An internal knowledge base accessed by agents enables them to quickly find answers to questions and accurately resolve customer problems. Internal knowledge bases can also store training materials on contact center software and processes for agents who need a quick brushup.

8. Empower agents
Contact center agents need to feel valued and part of the team. Managers can take several steps to empower agents, including the following:
- Involve agents in decision-making and ask for their feedback. They are on the front lines and often know where to make changes.
- Provide agents with the proper tools. Be sure they have access and can log in to all the necessary software to do their job. Also consider upgrading to the latest technologies. If agents are forced to use obsolete tech, their job could be more difficult and compound the frustration for agents and customers.
- Enable agents to make decisions. Provide agents with a certain amount of funds, for example, to credit a customer's account, eliminating supervisor involvement and expediting the process, or let agents deviate from their scripts when it's necessary to resolve a customer problem.
9. Provide customer self-service channels
Customer self-service channels can take some pressure off frontline agents as customers attempt to resolve their issue without human intervention. CSS is also available 24/7 so that customers can contact a company at a convenient time. Types of CSS channels include the following:
- FAQ pages are connected to a knowledge base on the company website. They should include information like operating hours, return policies, shipping information, contact information and how to make a payment.
- Interactive voice response systems eliminate the need for a switchboard operator. When customers call in, the IVR presents a menu of options that attempts to answer FAQs.
- Online chatbots on a company's website can be connected to a knowledge base or use AI and machine learning. AI chatbots use natural language processing and natural language understanding to interpret customer queries and respond. They can also use machine learning and large language models to provide better service.
- Video tutorials can be helpful to customers who are troubleshooting a product or service by providing simple instructions on how to do basic tasks.
CSS tools won't always address a customer's needs, so it's important to provide an easy way out of the self-service loop for customers who need to speak with a human agent.
10. Use skills-based routing
Poor distribution of inbound calls, emails, chat messages and texts can irritate customers and reduce agent productivity. Skills-based routing, or skills-based distribution, directs a customer call to an agent with the most relevant skills, expertise and language fluency. Customers who speak Portuguese, for example, can be matched up with an agent fluent in that language, or a customer with a billing problem can be routed to an agent who specializes in billing.
This strategy can increase the opportunity for first contact resolution, reduce AHT and improve the customer's experience. Agents also feel more confident in their abilities when customers are matched with their skill sets.
Donna Fluss contributed to this article.
Sarah Amsler is a senior managing editor for the Learning Content team at TechTarget.







