
Elnur - stock.adobe.com
The top 5 video conferencing use cases
Recruiting, training and collaboration are among the top video conferencing use cases for businesses, and they will remain so as the video market continues to expand.
2020 was a memorable year, and one aspect of it that remains in people's personal and professional lives is how commonplace it is to speak with people face to face, no matter where they are.
Remote work and telemedicine have become the norm. Individuals, educators and government agencies began regularly video conferencing -- technology that businesses used for many years. Not only has video conferencing's user base expanded, but how consumers use video technology continues to grow.
In the past, objections to remote work largely involved its lack of nonverbal cues, including facial expressions, tone and whether someone is paying attention. However, video enables people to communicate with colleagues while working remotely. As a result, it has become a key part of how people work together.
Why use video conferencing platforms?
The different purposes of video conferencing technology are the following:
- interpersonal communication
- collaboration
- presentations and education
Interpersonal communication
When people use video conferencing to connect personally, the technology requirements differ from those for a formal meeting or presentation. Therefore, ease of use is critical.
Zoom's video conferencing platform offers ease of use, which helped lead to the platform's widespread adoption amid the COVID-19 pandemic. Zoom is also not tied to any OS or device, so people can use the platform anywhere and on any device.
Video conferences are central to interpersonal communications. Some examples include the following:
- Faculty members can keep in touch with classes while at conferences.
- An HR Department interviews a job candidate.
- A patient and doctor have a telemedicine appointment.
Collaboration
Collaboration is more collegial and may require an IT team to assist remote workers or distributed teams who virtually meet to complete tasks or reach conclusions. Collaborative interactions may contain business-related documents or other artifacts, including spreadsheets and reports. Teams should also gain all parties' consent to ensure they can record the session, if necessary, as the artifacts may have sensitive or private information. Collaborative video conferences also include calendar integrations and enhanced security for information shared during the session.
Products like Microsoft Teams build collaboration bundles that combine artifacts and communication channels, including instant messages, voice technologies, co-author capabilities and video conferences.
Some examples of collaboration include the following:
- college faculty planning upcoming curricula;
- planning and executing HR open enrollment; and
- doctors reviewing diagnostic tests and collaborating on diagnoses.
Presentations and education
This category includes interactive, live presentations, such as seminars or company meetings, and recorded videos. For live presentations, organizations face additional considerations, such as integration for customer relationship management (CRM), marketing systems to track and schedule attendee registration and support for many users and features, like raising hands, breakout rooms, video recording and other audience management capabilities.
Cisco Webex has traditionally led this area, as it was one of the first web-based meeting and presentation tools for businesses. It continues to lead in the CRM and business equipment integration space. However, Zoom has entered this space and is also becoming a leader, as it also handles breakout rooms well.
Typically, when a video conference aims to present to or educate a group, the host stores a meeting recording. Useful recordings depend on how the organization stores and delivers them to end users. Video hosting platforms are a top choice to watch videos seamlessly across devices, optimize video quality, handle playback across browsers and devices, video player customization, closed captioning, video security, etc. Several tools, including YouTube, provide this service at varying costs -- from a free service to million-dollar investments.
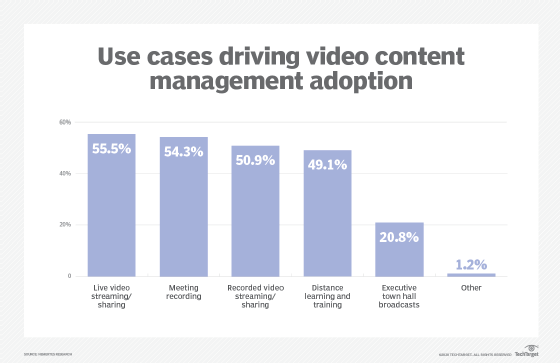
5 video conferencing use cases
Video technology operates across vertical industries, such as law, education and healthcare, and across horizontal business functions like sales, HR and product development. The top video conferencing use cases are the following:
- recruiting
- training
- project management
- collaboration with customers
- sales presentations and negotiations
Recruiting
HR teams may face challenges as they try to hire the right people for the organization. Video conferencing enables recruiters to broaden the applicant pool, as it invites people to work for the organization remotely from locations other than the main office. It also enables recruiting teams to screen applicants more efficiently with a range of interview resources.
Training
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, video conferencing technology enabled training centers to continue operations. A video conferencing platform can deliver all aspects of training sessions, including registration, digital whiteboard features, breakout sessions, prerecorded content, individual interaction with instructors and test-taking. Centers and other organizations that already used this technology had a head start over organizations that learned about video technology due to the pandemic.
Project management
Regardless of the project management approach an organization uses -- such as Scrum -- collaborative meetings can occur regularly to manage deliverables. For example, organizations can have geographically dispersed teams collaborate to review use cases, update project plans, manage risks, and complete code and quality reviews. This capability can save time and money.
Schedules no longer depend on travel, and team leaders don't have to assign projects to people or teams based on their locations over their skills. Video conferencing technologies mean organizations can use the best people or teams for projects regardless of location.
Video conferencing also enables better communication with business stakeholders and end users to ensure project deliverables meet project requirements.
Collaboration with customers
Customer or client meetings build rapport and can affect satisfaction and success. The people involved in meetings can also directly affect the level of engagement and customer stickiness. Video conferencing meets these needs, reduces the cost of maintaining customer relationships and ensures customers engage at the right time, with the right people, without complex scheduling and travel.
Sales presentations and negotiations
A presentation-style webinar is arguably the most common video conferencing use case. Sales teams use video platforms for presentations, contract negotiations and other agreements, although the latter two are less common. When due diligence is involved, having the affected parties interact, review materials and work on contracts can contribute to better outcomes in an efficient, cost-effective manner.
The ability to see people face-to-face enhances communication. It has also become a way of life for people professionally and personally amid the COVID-19 pandemic. As a result, organizations can expect to see continued growth and innovation in video conferencing for years to come.








