web content management system (WCMS)
What is a web content management system (WCMS)?
A web content management system (WCMS) is a type of content management system (CMS) that provides an organization with a way to manage digital information on a website through creating and maintaining content without prior knowledge of web programming or markup languages.
Managing web content effectively can have useful applications in the enterprise, producing insights for decision-making and delivering results, as well as value.
How does a WCMS work?
A WCMS helps users maintain, control, change and reassemble content on a webpage. Users store content within a database and can assemble the content using a flexible language such as Extensible Markup Language (XML) or .Net. Users can access the WCMS through a web browser, then edit the content and maintain control of the layout from that browser-based interface.
A WCMS has the following two parts:
- Content management application (CMA). This user interface lets users -- such as marketers and content creators -- design, create, modify and remove content from the website without requiring help from the IT department.
- Content delivery application (CDA). This provides back-end services that take the content that users create in the CMA and turn it into a website that visitors can access.
An organization can run a WCMS in its own data center or in the cloud.
Why use a WCMS?
A WCMS helps businesses create, manage and publish content on websites, which are essential marketing channels. Typically, digital marketing tactics such as email, social media, print and other advertisements direct the customer to the company website, so it's important for the business to have and maintain a web presence. A WCMS is the technology that powers websites that focus on content creation and sharing -- such as blogs and portfolios. However, organizations can also use a WCMS for other purposes, including online stores or online forums.
This article is part of
What is enterprise content management? Guide to ECM
A WCMS provides businesses with tools that enable brand consistency across mobile and web channels by separating content and presentation. These systems let businesses have editorial control, automate marketing efforts and publish content quickly and easily while maintaining version control.
Capabilities and features
A WCMS typically enables users to do the following:
- Design, create and maintain personalized content for a website.
- Review and approve content prior to publication.
- Use an automated publishing process.
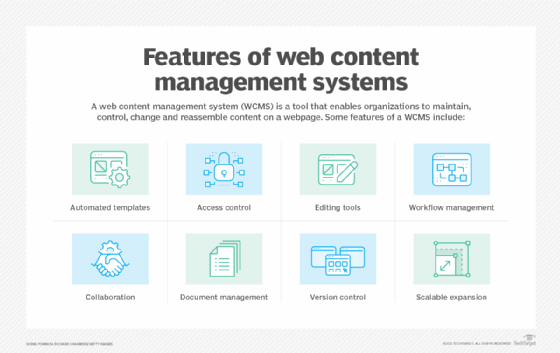
A WCMS generally includes the following features:
- Automated, standard templates. Users can easily add new or existing content, rather than having to design their own templates.
- Access control. Administrators can control who has access to a page on a website.
- Scalable expansion. Organizations can expand an implementation across multiple domains.
- Web-based editing tools. Users can create and customize content, such as adding titles and headers to improve content structure or designing webpages with drag-and-drop tools.
- Personalization tools. Users can create a customized digital experience. Marketers and content developers can present targeted content pages to users based on their customer profiles and past behaviors.
- Plugins. Plugins or modules extend a site's functionality.
- Software updates. These keep the WCMS up to current web standards.
- Workflow management. This lets authorized users review and approve content before publishing.
- Collaboration tools. Multiple users can modify content and include features for gathering user feedback.
- Document management. Businesses can manage the document lifecycle, including creation, revisions, publication, archive and removal.
- Multilingual. Organizations can display content in various languages.
- Versioning. Editors can retrieve previous versions of content.
Advantages of using a WCMS
A WCMS offers organizations the following benefits:
- Low cost. A WCMS is typically inexpensive, often being free or offering subscriptions that outweigh overall costs.
- Ease of use. Most WCMS options are user-friendly and let people who don't have a technical coding background create or maintain content.
- Ease of customization. A WCMS creates a universal layout that lets beginner users create and customize front ends easily.
- Workflow management. Administrators can control and personalize workflow management in a WCMS. Some WCMS options let administrators set up their own workflow management rules and provide them with a series of steps to set up each task.
- Search engine optimization (SEO). A WCMS gives businesses the editing tools required to improve search engine ranking. Users can easily create content with the correct keywords, provide meta information -- such as description, keywords and alternative text for images -- and link content within the text.
Disadvantages of using a WCMS
On the other hand, a WCMS isn't the best fit for all organizations. The disadvantages of a WCMS include the following:
- High cost for larger implementations. A WCMS can be expensive for larger companies because it can require extensive training and certifications. WCMS maintenance can also be expensive because the software often requires upgrades and licensing updates.
- Latency issues. Larger systems can become slower over time if the business doesn't keep the hardware up to date or if the cache files grow too large.
- Security risks. If an administrator doesn't regularly patch the WCMS for security threats, it remains vulnerable to hackers. To minimize security risks, administrators must monitor and maintain the many moving parts of a WCMS -- such as the web server software, MySQL and any plugins or add-ons.
Types of WCMSes
- Offline processing. This type of WCMS processes content before publishing it to the live server. Offline processing systems let users work on content when they aren't connected to the internet. Using this system, content that a user uploads to a CMS doesn't go live until the content author approves it.
- Online processing. Online processing systems employ templates on demand and whenever the user adds content to a webpage for publication. Whenever a user is logged into their CMS via a web browser and accesses a webpage, HTML is generated. Unlike an offline processing system that preprocesses content and applies templates beforehand, an online processing system processes templates only when the user requests it. Online processing systems include Joomla and Drupal.
- Hybrid processing. Hybrid processing systems use a combination of offline and online processing. These systems can produce executable code, such as Java Server Pages, Active Server Pages or PHP (PHP Hypertext Preprocessor) instead of HTML, meaning that the system doesn't need to be installed on every web server.
Traditional CMS vs. WCMS
There are many similarities between a traditional CMS and a WCMS, so the two terms are often used interchangeably, but there are differences between the two systems. A traditional CMS is software that businesses use to create, edit, manage and publish content -- typically structured content -- such as documents or records, as well as video and audio files. A WCMS, on the other hand, is a type of CMS that focuses primarily on managing webpage content, which includes graphics, video, audio and images.
Web content management systems and vendors
Numerous vendors provide web content management software, simplifying the process of creating and uploading unique content. Examples of WCMSes include the following:
Adobe Experience Manager
Adobe Experience Manager, which is part of Adobe Experience Cloud, is designed to help enterprise organizations build websites, mobile apps and forms. Product highlights include the following:
- Offers digital asset management, analytics and targeting features.
- Integrates with other Adobe products as well as with Salesforce and Microsoft Dynamics.
Drupal
Drupal is an open source CMS platform that's customizable and can handle large amounts of data. It offers many options for flexible custom content types. Product highlights include the following:
- Users can add modules to sites, similar to plugins on WordPress.
- Offers a built-in user management system, where users can create new roles and specify permissions.
- Integrates with marketing automation tools to send abandoned cart emails or assign visitors to a particular list.
Hubspot CMS Hub
Hubspot CMS Hub is a platform focused on digital experience, with versatile tools for personalization; different users might see different pages, etc. It's user-friendly to marketers and content editors and offers a library of themes and a range of content structures, as well as optimization for different devices. Product highlights include the following:
- Highly scalable.
- Easy to use -- even for complex pages.
- Ideal for competitive small businesses.
- Excellent SEO toolset.
WordPress
WordPress.org is a web software platform that lets users create and manage websites, blogs and apps with a variety of themes. WordPress.org is a free open source CMS, while WordPress.com is a blog hosting platform. Users can build any kind of website, such as an online store or membership site. Product highlights include the following:
- Offers both paid and unpaid themes and plugins, which let users add more content to their sites, including contact forms and photo galleries.
- Well-designed for SEO and lets users create categories and tags for posts.
- Users can download content in XML format, making it easier to move to a new system, if necessary.
Learn about the different types of AI-based content generators that can provide text, images, speech, video, music and code.







