content services platform
What is a content services platform?
A content services platform is cloud-based SaaS software that enables users to create, share, collaborate on and store text, audio and video content. Content services platform (CSP), not to be confused with cloud service provider, is a relatively new term that is gaining acceptance as a successor to enterprise content management (ECM) software.
Several prominent vendors -- notably Box, Hyland and Nuxeo -- use the term, or variants such as content services to describe their software.
Also, tech analyst firm Gartner formally declared in 2017 that it would henceforth use CSP instead of ECM to identify vendors and their services in what Gartner described as a fast-growing market.
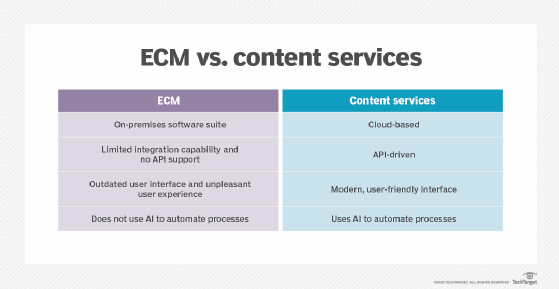
Content services vs. ECM
One way of explaining the evolution to content services platforms from ECM systems is that the newer concept of delivering content services reflects a shift from self-contained systems and repositories to open services, according to Gartner.
A content services platform expands the range of what an ECM has traditionally done from handling documents to managing more diverse forms of data.
In contrast to ECM systems and their main function of storing content in the enterprise, content services platforms are designed for active use of content data by individuals, workgroups and teams across the extended enterprise. In addition to internal employees, partners, contractors and others can interact with the enterprise through a CSP.
Security capabilities of a content services platform can easily extend to external third parties.
Content services platform capabilities
CSPs also are defined by their emphasis on services and microservices and can be installed either as a product suite or as separate applications with common APIs and repositories.
Also, CSPs serve a variety of parties, including users, systems and applications.
Common capabilities include the following:
- the ability to store data a single time by linking multiple repositories with common APIs so different servers are not storing the same content -- the CSP serves as repository of record, the so-called single source of truth;
- automatic document version control so documents and other data are always displayed in the most recent version with access to previous versions;
- enabling users and processes to use, co-edit, share and manipulate documents, images, audio recordings and other content;
- the ability to manage and store the metadata of digitized content;
- enterprise file sync and share;
- systematic administration of content services; and
- application packages that can include features such as content search, including AI or machine learning technologies to augment search; speech to text; automatic object recognition of images; content analytics; and security services.
Content services platform vendors
Many of the vendors with products in the CSP category have simply expanded their ECM products and spun them into service-oriented architecture platforms with integrated content-related services and microservices, content repositories and tools.
Content services platform vendors include OpenText, Microsoft, IBM, M-Files, Oracle, Alfresco, Laserfiche, Newgen Software, Micro Focus, iManage, Fabasoft and Objective.
Editor's note: This article was written by Shaun Sutner in 2018. TechTarget editors revised it in 2022 to improve the reader experience.





