Understanding the role of AI in cloud computing
AI is bringing previously unimagined capabilities in automation, optimization and predictive analytics to cloud management while posing new challenges for IT departments.
AI technologies are playing a growing role in cloud management. AI helps automate IT systems management, bolster security, understand complex cloud services, improve data management and streamline cloud cost optimization. It can also take on the convoluted task of provisioning new AI services across complex supply chains, most of which are delivered from the cloud. Managing the growing demand for AI while also taking advantage of its ability to manage complicated technology challenges is another reason IT departments need a coherent cloud management strategy.
All the major cloud and security platforms have been slowly infusing AI and machine learning algorithms into their tools in the race to support more autonomous enterprise IT systems. However, the recent hype spurred by generative AI (GenAI) has encouraged vendors to tout their specific AI capabilities.
Adnan Masood, chief AI architect at UST, a digital transformation consultancy, said the appeal of AI-powered cloud management is easy to understand because it could enable massive data centers hosting millions of applications, database instances, websites and other important digital services while being managed by just a handful of people. "Cloud management streamlines a wide range of common tasks, from provisioning and scaling to security and cost management, and from monitoring and data migration to configuration management and resource optimization," he said.
Traditionally, these CloudOps tasks required significant manual effort and expertise. Now, AI-driven automation, predictive analytics and intelligent decision-making are radically changing how enterprises manage cloud operations. "The common thread connecting these disparate applications is the shift from manual, reactive management to proactive, predictive and often autonomous operations to achieve self-managing, self-optimizing cloud environments," Masood said.
This article is part of
What is cloud management? Definition, benefits and guide
Enterprises also need to assess potential downsides in AI cloud management, such as complex data integration, real-time processing limitations and model accuracy in diverse cloud environments, he added. There are also business challenges, including high implementation costs, ROI uncertainty and balancing AI-driven automation with human oversight when automating processes.
How has AI transformed cloud computing?
AI enables a shift from reactive to proactive operations to enhance system reliability, resource utilization and cost efficiency. Key applications include predictive analytics for dynamic scaling, anomaly detection for identifying threats and bottlenecks, real-time resource optimization and AI-driven security tools that ensure data protection and compliance.
"The role of AI within cloud computing management enhances efficiency, scalability and flexibility for IT teams," said Agustín Huerta, senior vice president of digital innovation for North America at Globant, an IT consultancy. "With AI capabilities, cloud computing management enables a new phase of automation and optimization for organizations to keep up with dynamic changes in the workplace."
One of the most significant shifts in cloud management is the automation of redundant tasks, such as cloud provisioning, performance monitoring and cost automation. However, this is just scratching the surface of AI's capabilities.
Prasad Sankaran, executive vice president at IT services provider Cognizant, said AI could also help cloud providers and firms manage their security posture across compute, storage, and network infrastructure and applications to detect misconfigurations, malicious activities and vulnerabilities.
Nick Kramer, leader of applied solutions at consulting firm SSA & Company, said AI-powered natural language interfaces transform cloud management into a logical rather than a technical skills challenge. It can improve a business user's ability to manage complex cloud operations through conversational AI and drive faster and better problem-solving.
Ryan Mallory, COO at Flexential, a data center provider, said AI-enabled cloud computing tools and platforms can be categorized into several main types:
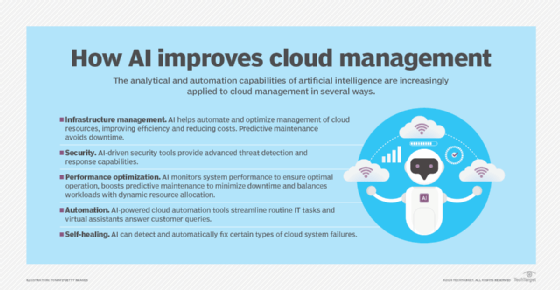
- Infrastructure management tools. These tools use AI to automate and optimize management of cloud resources, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
- Security platforms. AI-driven security platforms provide advanced threat detection and response capabilities, protecting data and infrastructure from cyberthreats.
- Performance optimization tools. These platforms use AI to monitor and enhance system performance, ensuring optimal operation and minimizing downtime.
- Automation platforms. AI-powered cloud automation tools streamline routine tasks, freeing up IT staff for more strategic work.
Self-healing systems
Kramer said his favorite example of the step change AI brings to cloud management combines fast reaction and prediction in actions that enable systems to optimize, heal and secure themselves with minimal human intervention. For example, AI can detect and automatically fix certain types of system failures, improving reliability and reducing downtime. AI data analysis can quickly determine the likely root cause when an anomaly is detected.
A process that might take human administrators hours or days can be completed by AI in seconds or minutes. Then, based on the identified issue, AI systems can initiate predefined remediation actions. These might include restarting services, reallocating resources or applying patches.
Beyond just fixing problems, AI in self-healing systems can also continuously optimize performance based on learned patterns and changing conditions by using machine learning to improve over time. "The AI learns from past incidents and outcomes, becoming more accurate in both problem detection and resolution," Kramer said.
Common applications of AI in cloud management
According to Bharath Thota, a partner in the digital and analytics practice at the Kearney consulting firm, AI is widely applied in managing cloud computing across several key areas, including workload optimization, predictive maintenance, security threat detection and automated scaling. He said interesting examples include the following:
- Workload optimization. Microsoft Azure's Machine Learning service and Google Cloud's AutoML enable dynamic resource allocation by analyzing data to ensure that computing resources are used efficiently.
- Predictive maintenance. This capability enables cloud providers to foresee and address potential system failures before they disrupt operations, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Security. Services such as AWS GuardDuty use AI to detect anomalies and unusual patterns that could indicate potential cyberthreats, enhancing the overall security posture.
- UI. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants, such as IBM Watsonx Assistant, are improving customer service by providing instant, context-aware responses to user queries, thereby enhancing the customer experience.
"As AI technology continues to advance, its role in cloud management will likely expand, introducing even more sophisticated tools for real-time analytics, advanced automation and proactive security measures," Thota said. This evolution will improve the efficiency and security of cloud environments and make them more responsive and adaptive to changing business needs.
The benefits of AI in cloud computing
Sankaran said AI is supercharging autonomous cloud management, making the vision of self-monitoring and self-healing systems viable. AI-enabled cloud management enables organizations to provision and operate vast, complex multi-cloud estates around the clock and at scale. These capabilities can increase uptime and mitigate risks to drive greater business potential and client satisfaction.
Chris Vogel, cybersecurity consultant at S-RM, a corporate intelligence and cybersecurity firm, also believes that AI extends beyond automation to far more advanced business analytical capabilities by enhancing data-driven insights from huge quantities of data to help inform business decision-making.
The challenges of using AI in cloud computing management
It is also important for IT teams to consider various challenges and downsides when using AI in cloud management. They include the following:
- Trust. Narayana Prasad Shankar, CTO and head of AI, data engineering and analytics at Zensar, a digital engineering services company, said the trust factor is not yet strong enough to make AI use mainstream or allow AI to be used on its own to manage the cloud.
- Cost. The costs of enabling many aspects of AI in cloud management are prohibitive, mainly due to the talent cost but also, to some extent, the running costs, according to Shankar.
- Complexity. Integrating AI systems into existing cloud infrastructure can be daunting, requiring specialized knowledge and extensive customization, which can be resource-intensive and time-consuming, Thota said.
- Continuous training. AI models that are based on deep learning require continuous training with large and diverse data sets to remain effective, which can strain computational power and escalate operational costs.
- Opacity. Lack of transparency in many AI algorithms can make it difficult for stakeholders to understand how decisions are made, which can erode trust, Thota said.
- Legacy applications. Sankaran said many applications are legacy, cloud-hosted systems that were never designed to take advantage of cloud capabilities. "This can make it challenging to fully implement AI capabilities without modernizing the application," he said.
AI's impact on IT cloud management
It is also important to consider how the burden of making AI available to users changes IT's cloud management responsibilities. IT departments will need to consider new categories of services related to AI.
"As with previous waves of new technology, shadow IT access to unauthorized and unsafe AI systems is a risk that needs to be managed," Sankaran said. Some of the new concerns include the following:
- Services. IT must provide enterprise-grade AI alternatives that are effective, private, quality-assured and governed.
- Data. Businesses need to ensure the availability, quality and security of their data sets, in addition to managing data pipelines, storage and governance across different cloud platforms and sources.
- Models. The lifecycle of AI models must also be thoroughly managed. From development and testing to deployment and monitoring, businesses must ensure AI models' compatibility, scalability and performance across cloud environments.
- Cost management. Teams must balance the benefits and costs of using AI across various platforms. It is also important to optimize allocation and utilization of cloud resources and services for AI workloads to avoid unnecessary or excessive spending.
- Skills. IT teams must stay current and develop the necessary skills and competencies to use AI on the cloud, which span processors, AI/ML middleware, model selections, ML operations and compliance management.
AI-enabled cloud computing tool vendors
There are many ways to break down the different categories of AI-enabled cloud computing tools. John Pettit, CTO at Promevo, a Google services provider, breaks the field into three categories that include artificial intelligence as a service (AIaaS) platforms, such as Vertex on Google; hybrid tools from third parties that integrate with many clouds and embed AI to improve efficiency; and specialized AI platforms that focus on managing and scaling AI workloads.
Organizations should be able to match capabilities with the right tool, depending on their goals and cloud footprint. Pettit recommends they start with an AIaaS option that minimizes vendor lock-in, which enables users to experiment with the open models while eliminating the need for direct management. For instance, Google Vertex doesn't require the use of their models.
Masood finds it more useful to characterize the main types of AI-enabled cloud management tools and platforms into six categories:
- Intelligent operations platforms like Dynatrace, New Relic and Datadog use AI to provide real-time monitoring, anomaly detection and predictive analytics across the entire cloud stack, delivering holistic insights that go beyond human capabilities.
- Autonomous resource optimizers such as Turbonomic and IBM Densify use AI to analyze workload patterns, making real-time, informed decisions to adjust resource allocation, balancing performance and cost automatically.
- AI-driven security platforms like Palo Alto Networks Prisma Cloud and CrowdStrike Falcon employ machine learning to detect zero-day vulnerabilities and anomalous behavior, shifting cloud security from a reactive to a proactive posture.
- Predictive analytics platforms such as VMware's Tanzu CloudHealth and Apptio Cloudability use AI tools to forecast cloud spending and pinpoint cost optimization opportunities, delivering actionable insights and concrete recommendations for cost reduction.
- Cloud AIOps platforms like IBM Cloud Pak for Watson AIOps and Moogsoft automate IT operations processes, from incident response to root cause analysis, and continuously learn from past incidents to enhance response strategies.
- Intelligent data management software such as Rubrik and Veeam uses AI to optimize data placement, predict failures and automate recovery, making data management more proactive and resource efficient.
Future AI trends in cloud management
These experts predict a promising future for AI in cloud management.
"We're only a year into this GenAI journey, but we're moving fast and the pace is accelerating. AI and cloud computing will continue to evolve symbiotically, each enhancing the capabilities of the other as they usher in a new era of hyperautomation," Sankaran said.
As AI capabilities evolve, cloud management will become more automated and autonomous. Sankaran believes AI cloud management will be as seminal as when cloud computing came onto the scene. Those who invest in AI for cloud management will unlock opportunities to operate at the speed of business as they eliminate technical debt, innovate and modernize, he said.
Thota expects AI to dominate cloud management, evolving toward fully autonomous cloud operations. The systems will be capable of adapting in real time to fluctuations in demand, emerging security threats and operational challenges, leading to a new era of cloud management that is more resilient, efficient and innovative.
"This shift will drive substantial efficiencies across industries, enabling organizations to focus more on strategic goals while AI handles the complexities of cloud management," Thota said.
Masood predicts a proliferation of specialized AI cloud platforms, with vendors selling more industry-specific offerings, enhanced platform interoperability and greater emphasis on ethical AI practices.
Kramer believes AI will encourage enterprises to increase their focus on making AI decision-making processes more transparent and interpretable, allowing for more targeted refinements of AI systems. "Let's face it, AI will be adopted when stakeholders can better understand and trust AI-driven cloud management decisions," he said.
George Lawton is a journalist based in London. Over the last 30 years, he has written more than 3,000 stories about computers, communications, knowledge management, business, health and other areas that interest him.






